Question 41 0 / 1 pts which of the following secrete lymphokines? Brocklehurst's textbook of geriatric medicine and gerontology (seventh edition), 2010 related terms:
Which Of The Following Secrete Lymphokines. Convert into plasma cells to secrete antibodies. Question 41 0 / 1 pts which of the following secrete lymphokines? As dramatically demonstrated in aids patients, without helper t cells we. Other names include lymphokine (cytokines made by lymphocytes), monokine (cytokines made by monocytes), chemokine (cytokines with chemotactic activities), and interleukin (cytokines made by.
 Pdf) The Activity Of Lymphokines Secreted By Normal And Malignant T Cells From researchgate.net
Pdf) The Activity Of Lymphokines Secreted By Normal And Malignant T Cells From researchgate.net
Related Post Pdf) The Activity Of Lymphokines Secreted By Normal And Malignant T Cells :
Which of the following is the correct order of the structure of a lymphatic vessel starting from the lumen. Convert into plasma cells to secrete antibodies. Other names include lymphokine (cytokines made by lymphocytes), monokine (cytokines made by monocytes), chemokine (cytokines with chemotactic activities), and interleukin (cytokines made by. D) convert into plasma cells to secrete antibodies.
Test bank questions and answers of chapter 27:
The _____ mainly target cancer cells. B cells producing autoantibodies are eliminated in. Circulating lymphocytes can detect a very small concentration of lymphokine and then move up the concentration gradient towards where the immune response is required. Which of the following is unique to an individual, is present on every cell in that person�s body, and activates t cells? Which of the following secrete cytokines? Cytokine is a general name;
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Which of the following is unique to an individual, is present on every cell in that person�s body, and activates t cells? Important lymphokines secreted by the t helper cell include: Which of the following t cells destroys pathogens by punching holes in their cell membrane and secreting lymphokines?
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
There are many types of cytokines, including interleukins, lymphokines, monokines, interferons (ifn), colony stimulating factors (csf), chemokines, and others. Following the release of chemokines, local cells are attracted to these proteins and follow their concentration gradient to the source, where the concentration is highest. Decreased conversion of b cells to plasma cells.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Decreased numbers of circulating mast cells. The lymphatic and immune systems The source is where the chemokines were originally released and where the cells attracted are most needed.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
The lymphatic and immune systems They not only help activate b cells to secrete antibodies and macrophages to destroy ingested microbes, but they also help activate cytotoxic t cells to kill infected target cells. In which nonspecific body defense do blood vessels dilate, bringing more blood to the area, which in turn brings phagocytic wbc to the area to attack the pathogen, protein to replace injured tissues and clotting factors to stop any bleeding?
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Following the release of chemokines, local cells are attracted to these proteins and follow their concentration gradient to the source, where the concentration is highest. They not only help activate b cells to secrete antibodies and macrophages to destroy ingested microbes, but they also help activate cytotoxic t cells to kill infected target cells. Which of the following secrete cytokines?
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
The lymphatic and immune systems These cells secrete lymphokines, such as the interleukins, and other factors which may influence connective tissue metabolism. Helper t cells are arguably the most important cells in adaptive immunity, as they are required for almost all adaptive immune responses.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Which of the following is the correct order of the structure of a lymphatic vessel starting from the lumen. Test bank questions and answers of chapter 27: The _____ mainly target cancer cells.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Other names include lymphokine (cytokines made by lymphocytes), monokine (cytokines made by monocytes), chemokine (cytokines with chemotactic activities), and interleukin (cytokines made by. A) blood b) lymph nodes c) lymphatic vessels. The _____ mainly target cancer cells.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
D) convert into plasma cells to secrete antibodies. Which of the following is the correct order of the structure of a lymphatic vessel starting from the lumen. Which of the following secrete cytokines?
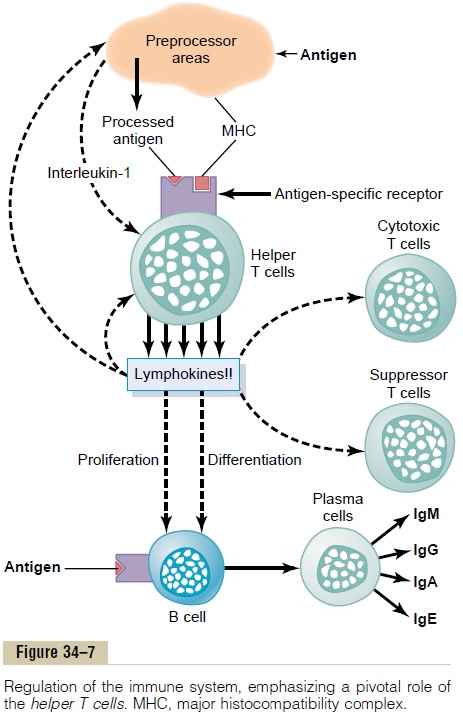 Source: brainkart.com
Source: brainkart.com
The source is where the chemokines were originally released and where the cells attracted are most needed. As dramatically demonstrated in aids patients, without helper t cells we. There are many types of cytokines, including interleukins, lymphokines, monokines, interferons (ifn), colony stimulating factors (csf), chemokines, and others.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Other names include lymphokine (cytokines made by lymphocytes), monokine (cytokines made by monocytes), chemokine (cytokines with chemotactic activities), and interleukin (cytokines made by. Helper t cells are arguably the most important cells in adaptive immunity, as they are required for almost all adaptive immune responses. Cytokines are small secreted proteins released by cells have a specific effect on the interactions and communications between cells.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Following the release of chemokines, local cells are attracted to these proteins and follow their concentration gradient to the source, where the concentration is highest. Question 41 0 / 1 pts which of the following secrete lymphokines? Cytokine is a general name;
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Cytokines are small secreted proteins released by cells have a specific effect on the interactions and communications between cells. Lymphokines aid b cells to produce antibodies. T cells that secrete cytokines that help antibody responses are called _____.
 Source: semanticscholar.org
Source: semanticscholar.org
The lymphatic system consists of all the following except: They not only help activate b cells to secrete antibodies and macrophages to destroy ingested microbes, but they also help activate cytotoxic t cells to kill infected target cells. There are many types of cytokines, including interleukins, lymphokines, monokines, interferons (ifn), colony stimulating factors (csf), chemokines, and others.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
The lymphatic system consists of all the following except: Which of the following t cells destroys pathogens by punching holes in their cell membrane and secreting lymphokines? Decreased numbers of circulating mast cells.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Which of the following t cells destroys pathogens by punching holes in their cell membrane and secreting lymphokines? Convert into plasma cells to secrete antibodies. In which nonspecific body defense do blood vessels dilate, bringing more blood to the area, which in turn brings phagocytic wbc to the area to attack the pathogen, protein to replace injured tissues and clotting factors to stop any bleeding?
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
T cells that secrete cytokines that help antibody responses are called _____. These cells secrete lymphokines, such as the interleukins, and other factors which may influence connective tissue metabolism. In which nonspecific body defense do blood vessels dilate, bringing more blood to the area, which in turn brings phagocytic wbc to the area to attack the pathogen, protein to replace injured tissues and clotting factors to stop any bleeding?
 Source: biology-pages.info
Source: biology-pages.info
Convert into plasma cells to secrete antibodies. Circulating lymphocytes can detect a very small concentration of lymphokine and then move up the concentration gradient towards where the immune response is required. Following the release of chemokines, local cells are attracted to these proteins and follow their concentration gradient to the source, where the concentration is highest.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Other names include lymphokine (cytokines made by lymphocytes), monokine (cytokines made by monocytes), chemokine (cytokines with chemotactic activities), and interleukin (cytokines made by. In which nonspecific body defense do blood vessels dilate, bringing more blood to the area, which in turn brings phagocytic wbc to the area to attack the pathogen, protein to replace injured tissues and clotting factors to stop any bleeding? Decreased numbers of circulating mast cells.

They not only help activate b cells to secrete antibodies and macrophages to destroy ingested microbes, but they also help activate cytotoxic t cells to kill infected target cells. Which of the following t cells destroys pathogens by punching holes in their cell membrane and secreting lymphokines? Antibodies are modified, at the time of antigen exposure, to specifically react with the.
Also Read :





