When an acid dissolves in water it donates the h+ to h2o molecules and form h3o+. Hence it can act as both acid and base.
Which Of The Following Is A Bronsted Lowry Acid. Out of all the four complex ions, the only one that can donate a proton is the hexa aquairon (iii)ion [fe(h2 o)6 ]3+. Which of the following is the correct net ionic equation for the reaction between nitrous acid and hydrogen sulfide ion? But these species are much too reactive to. Hno 2 b) h 2 so 3;
 Brønsted-Lowry Acids And Bases | Chemistry For Majors From courses.lumenlearning.com
Brønsted-Lowry Acids And Bases | Chemistry For Majors From courses.lumenlearning.com
Related Post Brønsted-Lowry Acids And Bases | Chemistry For Majors :
Of course, this equilibrium lies to the left, as it does for weakly acidic hydrogen fluoride. When an acid dissolves in water it donates the h + molecules to h2o and forms h3o +. Charge can accept the hydrogen ion. (2) both acidic and nonacidic hydrogen atoms may be present in an acid molecule.
Weaker acid) a) hno 3;
Hclo 2 e) h 2 so 4; Login is required in order to view results and track your progress. Therefore, h 2 s (hydrogen sulphide) acts as a bronsted acid but not a bronsted base. H 2 seo 3 c) hclo 4; Which one of the following is a bronsted lowry acid : It will not make many compounds.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
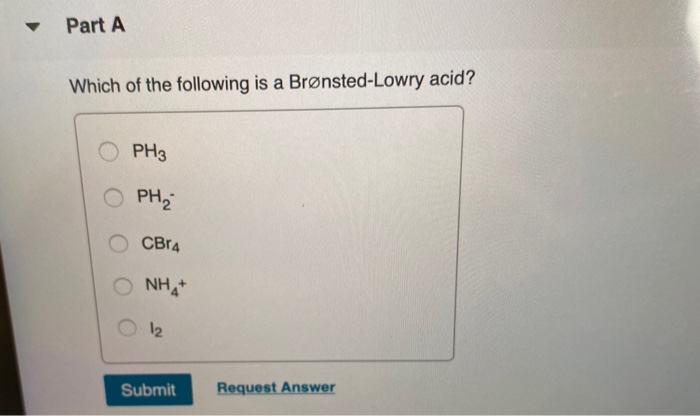
The arrhenius definition says that anything that donates a pair of electrons is an acid. B) basic which of the following salts, when dissolved in water, produces the solution with the highest ph? Any species that will donate h+ (protons) in solution, and makes ph lower (i.e hcl) bronsted lowry base:
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
A bronsted lowry acid is defined simply as a proton donor. Usually bronsted acids have an h bonded to a halogen or an oxygen. According to the theory, acid and base react with each other and by an exchange of proton acid, forms its conjugate base and the base forms its.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
So it is a bronston lowry base. Weaker acid) a) hno 3; I�m concerned that the complexity of this molecule is what the authors air referring to where it is less.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Hydrobromic acid, hbr, is a strong acid, meaning it practically entirely dissociates in water. When an acid dissolves in water it donates the h + molecules to h2o and forms h3o +. Acids release a proton, or h+, in water.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Charge can accept the hydrogen ion. The arrhenius definition says that anything that donates a pair of electrons is an acid. (2) both acidic and nonacidic hydrogen atoms may be present in an acid molecule.
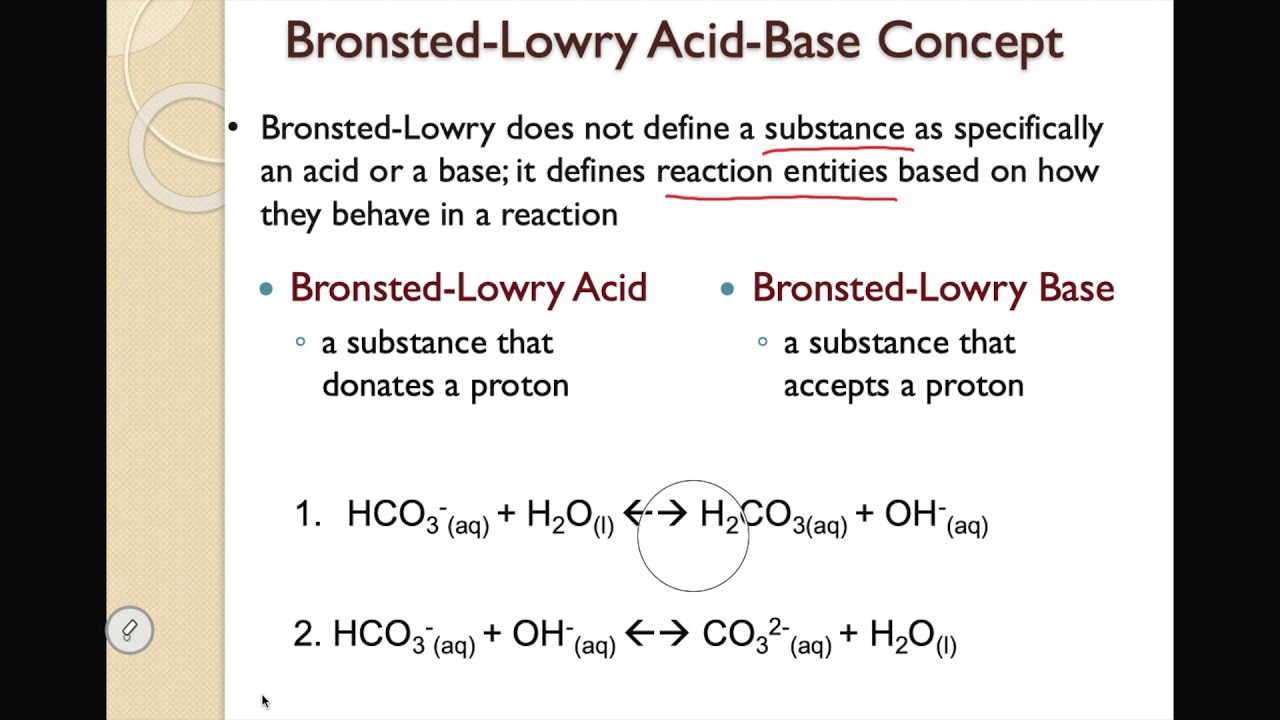 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
So it is a bronston lowry base. Hno 2 b) h 2 so 3; Aslso, the proton, may combine h + of.

So it is a bronston lowry base. H2o is amphoteric so it can act as both a bronsted acid or base at neutral conditions. Its conjugate acid is the ammonium ion.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
H c o 3 − is the conjugate base of carbonic acid and the conjugate acid of the carbonate ion. Hclo 2 e) h 2 so 4; Please continue with your google account.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Which of the following is the correct net ionic equation for the reaction between nitrous acid and hydrogen sulfide ion? Please continue with your google account. When an acid dissolves in water it donates the h + molecules to h2o and forms h3o +.

Which of the following is the correct net ionic equation for the reaction between nitrous acid and hydrogen sulfide ion? H2o is amphoteric so it can act as both a bronsted acid or base at neutral conditions. Usually bronsted acids have an h bonded to a halogen or an oxygen.

B) basic which of the following salts, when dissolved in water, produces the solution with the highest ph? On the other hand, cl2, can donate no protons to the solvent, and is not classified as an acid. Charge can accept the hydrogen ion.
 Source: numerade.com
Source: numerade.com
According to the theory, acid and base react with each other and by an exchange of proton acid, forms its conjugate base and the base forms its. I�m concerned that the complexity of this molecule is what the authors air referring to where it is less. Which one of the following is a bronsted lowry acid :
 Source: numerade.com
Source: numerade.com
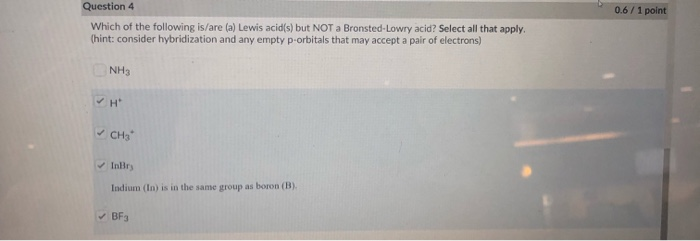
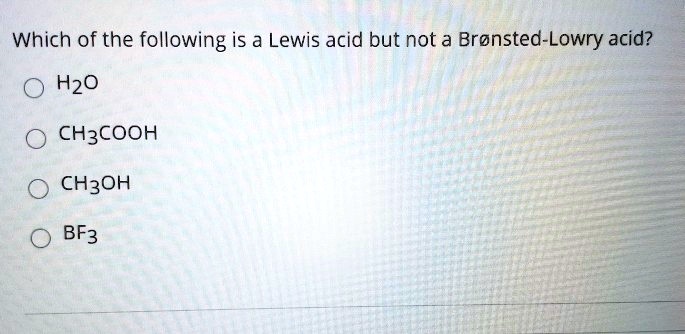
Please continue with your google account. For the lewis theory, acid is the substance that can gain a pair of electrons, and the base is the substances that can donate the pair of electrons. The second option is h 2 o (water).
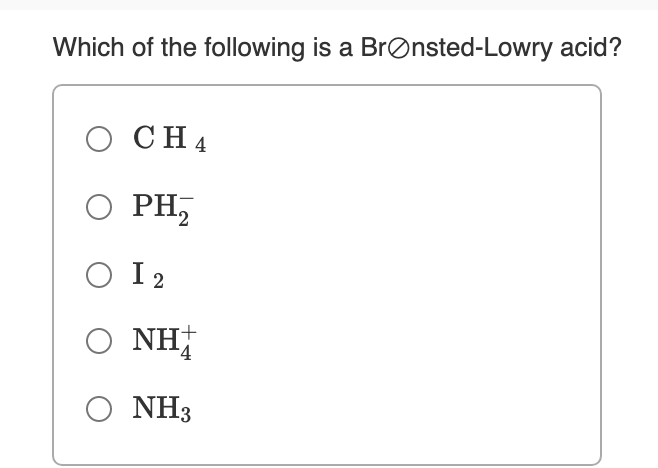 Source: bartleby.com
Source: bartleby.com
It is a bronston lowry base water can accept a hydrogen ion that has two lone pairs here. Usually bronsted acids have an h bonded to a halogen or an oxygen. Which one of the following pairs of acids is incorrectly listed?
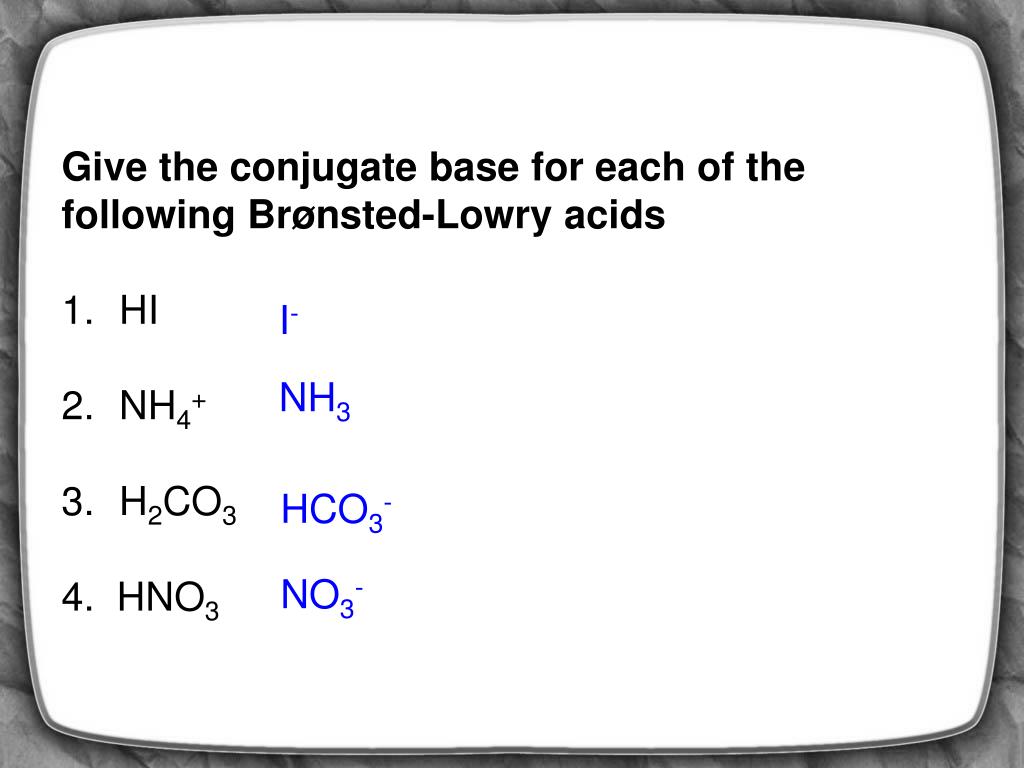 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
A bronsted lowry acid is defined simply as a proton donor. Please continue with your google account. Aslso, the proton, may combine h + of.
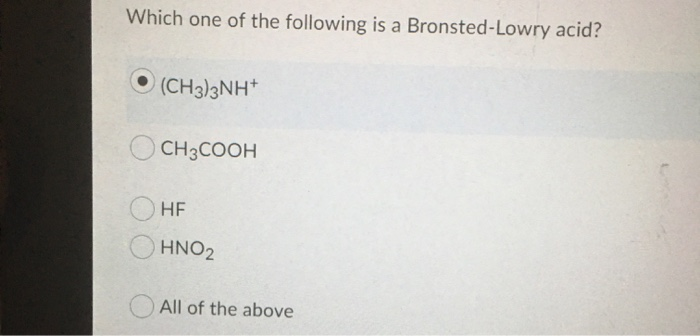 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
According to the theory, acid and base react with each other and by an exchange of proton acid, forms its conjugate base and the base forms its. Weaker acid) a) hno 3; Charge can accept the hydrogen ion.

Of course, this equilibrium lies to the left, as it does for weakly acidic hydrogen fluoride. (2) both acidic and nonacidic hydrogen atoms may be present in an acid molecule. Any species that will donate h+ (protons) in solution, and makes ph lower (i.e hcl) bronsted lowry base:
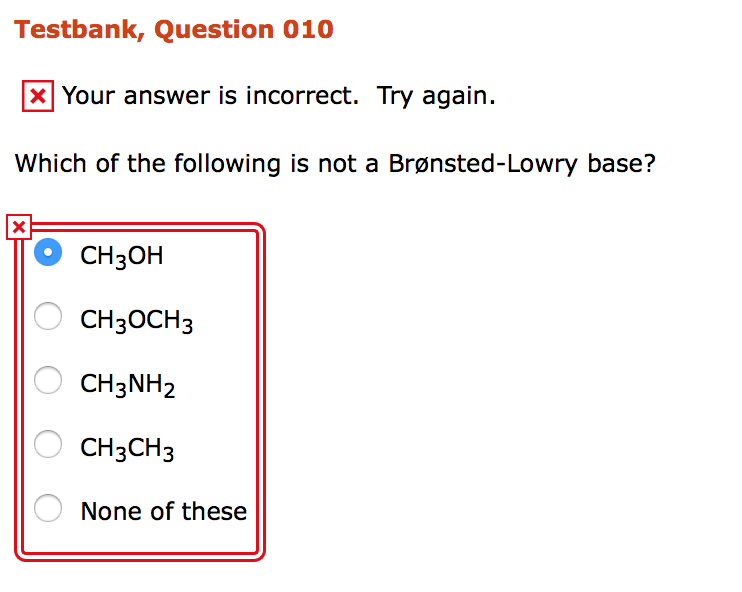 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Aslso, the proton, may combine h + of. The chloride ion is its conjugate base. H 2 seo 3 c) hclo 4;
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
First, let us define the b.l. Hence it can act as both acid and base. Since the question does not specify conditions, we should assume this to be at a neutral condition (ph = 7) which would make nh3 a base.
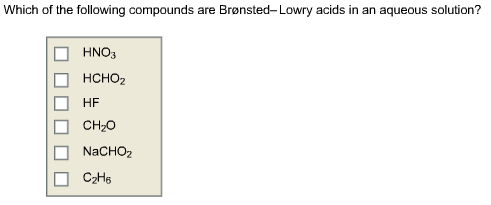 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Which one of the following pairs of acids is incorrectly listed? Out of all the four complex ions, the only one that can donate a proton is the hexa aquairon (iii)ion [fe(h2 o)6 ]3+. The second option is h 2 o (water).
Also Read :





