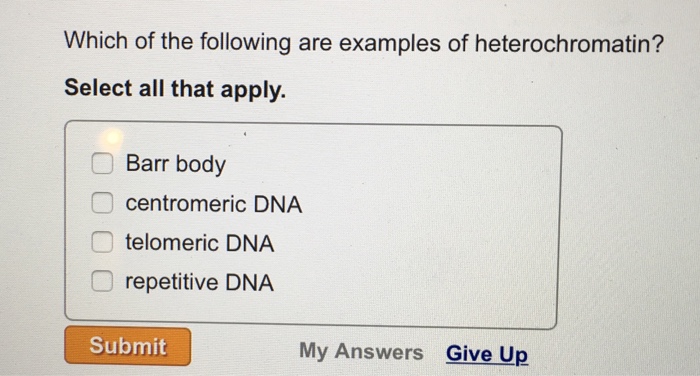
Which sequence is not an example of repetitive dna? Centromeric dna telomeric dna barr body repetitive dna nucleosome x chromosome y chromosome attention:
Which Of The Following Are Examples Of Heterochromatin. Chromatin is a macro molecule which consist of dna (deoxyribonucleic acid), rna (ribonucleic acid) and protein and this chromatin is results in the formation of the chromosomes. 736 students attemted this question. Which of the following is an example of heterochromatin? Hence, it is not a permanent feature of the cell’s nucleus but it can be seen in the nucleus some of the.
 Unravelling Heterochromatin: Competition Between Positive And Negative Factors Regulates Accessibility: Trends In Genetics From cell.com
Unravelling Heterochromatin: Competition Between Positive And Negative Factors Regulates Accessibility: Trends In Genetics From cell.com
Related Post Unravelling Heterochromatin: Competition Between Positive And Negative Factors Regulates Accessibility: Trends In Genetics :
Facultative heterochromatin facultative heterochromatin contains the inactive genes in the genome; Heterochromatin protein 1 (hp1) causes changes in heterochromatin structure when hp1 dimers. This region often contains genetic. A) heterochromatin of eukaryotic nucleus stains densely with simpler dyes than euchromatin.
A) heterochromatin of eukaryotic nucleus stains densely with simpler dyes than euchromatin.
Heterochromatin contains relatively few genes. Which of the following are examples of heterochromatin in a mammalian chromosome? Heterochromatin protein 1 (hp1) causes changes in heterochromatin structure when hp1 dimers. A) telomeric dna b) barr body c) repetitive dna d) centromeric dna It is found in the nucleus of eukaryotes as well as prokaryotes. The organization of heterochromatin is so highly compact in the way that these are inaccessible to the protein which is engaged in gene.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
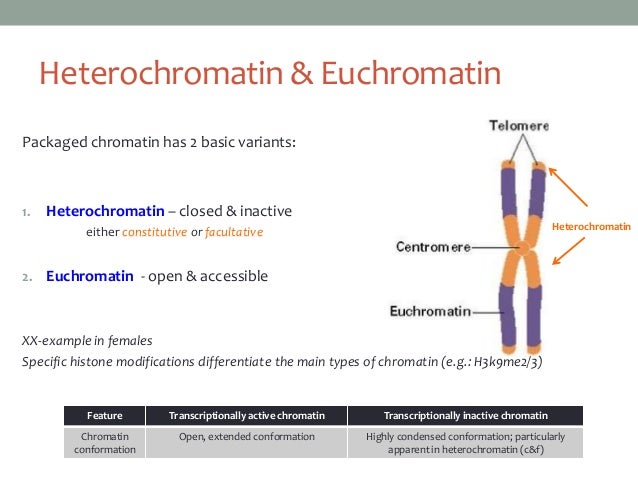
Group of answer choices the histones genes for cell membrane components expressed in many cells the telomere region the arms of the chromosome between the centromere and the telomere genes for the protein components of muscle that are only expressed in muscle cells Heterochromatin has tightly packed dna. Heterochromatin remains relatively condensed throughout the cell cycle and condenses early in cell division.
 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
This region often contains genetic. Which of the following is an example of heterochromatin? Which of the following are examples of heterochromatin in a mammalian chromosome?
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
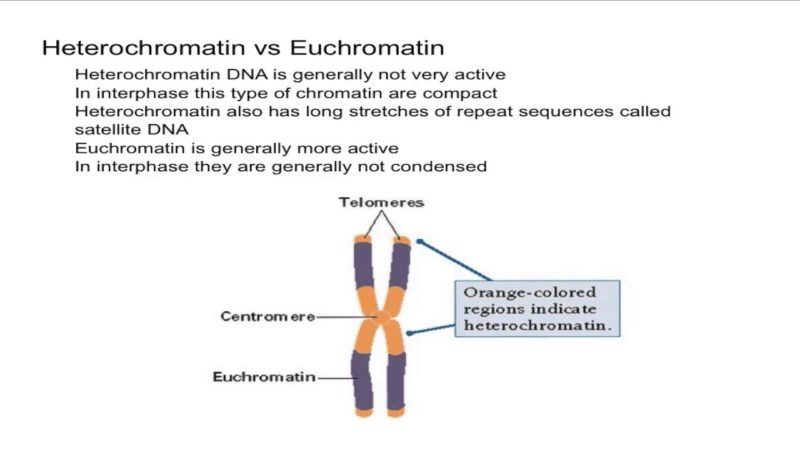
Heterochromatin is observed both on the outer edge of the nucleus or buried withinside the indoors of a chromosomal domain. This region often contains genetic. It is present in the nucleus of the eukaryotic cells.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
All the chromosomes in the genome except the heterochromatin are examples of euchromatin. Heterochromatin replicates early in s phase. Which of the following are examples of heterochromatin in a mammalian chromosome?
A) the addition of methyl groups to cytosine bases of dna b) the binding of transcription factors to a promoter c) the removal of introns and alternative splicing of exons d) gene amplification contributing to cancer e) the folding of dna to form. This region often contains genetic. Chromatin is a macro molecule which consist of dna (deoxyribonucleic acid), rna (ribonucleic acid) and protein and this chromatin is results in the formation of the chromosomes.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
Which sequence is not an example of repetitive dna? It is present in the nucleus of the eukaryotic cells. It is found in the nucleus of eukaryotes as well as prokaryotes.
 Source: atlasgeneticsoncology.org
Source: atlasgeneticsoncology.org
Centromeric dna telomeric dna barr body repetitive dna nucleosome x chromosome y chromosome attention: Facultative heterochromatin facultative heterochromatin contains the inactive genes in the genome; Repetitive dna barr body centromeric dna telomeric dna
 Source: atlasgeneticsoncology.org
Source: atlasgeneticsoncology.org
Which of the following is an example of heterochromatin? The process of dna to protein development is a complicated one! Chromatin is a macro molecule which consist of dna (deoxyribonucleic acid), rna (ribonucleic acid) and protein and this chromatin is results in the formation of the chromosomes.
 Source: jbc.org
Source: jbc.org
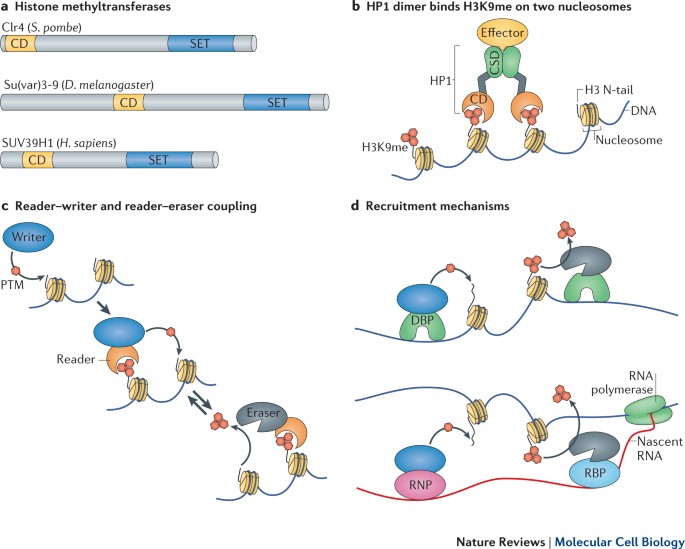
Heterochromatin protein 1 (hp1) causes changes in heterochromatin structure when hp1 dimers. Which of the following are examples of heterochromatin? Some regions in the chromosomes belong to the constitutive heterochromatin;
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
Centromeric dna telomeric dna barr body repetitive dna nucleosome x chromosome y chromosome attention: I have chosen centromeric dna, telomeric dna, barr body, and repetitive dna the answer was A) the addition of methyl groups to cytosine bases of dna b) the binding of transcription factors to a promoter c) the removal of introns and alternative splicing of exons d) gene amplification contributing to cancer e) the folding of dna to form.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Which of the following are examples of heterochromatin? Heterochromatin is found in the telomere and the centromere. In heterochromatin formation, which of the following are responsible for recruiting histone deacetylases and histone methyltransferases to a nucleation site?
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Which of the following are examples of heterochromatin in a mammalian chromosome? Centromeric dna telomeric dna barr body repetitive dna nucleosome x chromosome y chromosome attention: Which of the following are examples of heterochromatin in a mammalian chromosome?
 Source: coredifferences.com
Source: coredifferences.com
I have chosen centromeric dna, telomeric dna, barr body, and repetitive dna the answer was Which of the following are examples of heterochromatin in a mammalian chromosome? These regions, which are known as constitutive heterochromatin, remain condensed throughout the cell cycle and are not actively transcribed.
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
The organization of heterochromatin is so highly compact in the way that these are inaccessible to the protein which is engaged in gene. Facultative heterochromatin, which can be unwound to form euchromatin, on the other hand, is more dynamic in nature and can form and change in response to cellular signals and gene activity. Heterochromatin replicates early in s phase.
 Source: jbc.org
Source: jbc.org
Chromatin is a macro molecule which consist of dna (deoxyribonucleic acid), rna (ribonucleic acid) and protein and this chromatin is results in the formation of the chromosomes. In heterochromatin formation, which of the following are responsible for recruiting histone deacetylases and histone methyltransferases to a nucleation site? Heterochromatin protein 1 (hp1) causes changes in heterochromatin structure when hp1 dimers.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Heterochromatin remains relatively condensed throughout the cell cycle and condenses early in cell division. Facultative heterochromatin facultative heterochromatin contains the inactive genes in the genome; At centromeres, heterochromatin formation is directed by rna interference (rnai) a naturally occurring process in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells that silences gene expression (figure 2).
 Source: numerade.com
Source: numerade.com
Facultative heterochromatin, which can be unwound to form euchromatin, on the other hand, is more dynamic in nature and can form and change in response to cellular signals and gene activity. Sumner, in encyclopedia of genetics, 2001 facultative heterochromatin. Heterochromatin protein 1 (hp1) causes changes in heterochromatin structure when hp1 dimers.
 Source: nyaspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: nyaspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Which of the following are examples of heterochromatin in a mammalian chromosome? In heterochromatin formation, which of the following are responsible for recruiting histone deacetylases and histone methyltransferases to a nucleation site? Facultative heterochromatin, which can be unwound to form euchromatin, on the other hand, is more dynamic in nature and can form and change in response to cellular signals and gene activity.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Some regions in the chromosomes belong to the constitutive heterochromatin; The process of dna to protein development is a complicated one! Heterochromatin is observed both on the outer edge of the nucleus or buried withinside the indoors of a chromosomal domain.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
A) heterochromatin of eukaryotic nucleus stains densely with simpler dyes than euchromatin. For example, most of the regions of y chromosome is constitutionally heterochromatic. Heterochromatin is found in the telomere and the centromere.
Also Read :