Group 2 correct the matrix produced by bacteria that grow in a biofilm can slow down the diffusion of antibiotics into the biofilm. This work suggests that inhibition of biofilm formation should be considered in pgpr mixture development.
Which Of The Bacterial Mixtures S Grow As A Biofilm. Biofilms develop from bacteria bound on surfaces that grow into structured communities (microcolonies). Group 2 correct the matrix produced by bacteria that grow in a biofilm can slow down the diffusion of antibiotics into the biofilm. Over 500 bacterial species have been identified in typical dental plaque biofilms. The characteristic of biofilm bacteria of most importance to the food hygienist is their high resistance to antimicrobial agents.
 Mastering Micro Chapter 6 Exam 2 Flashcards | Quizlet From quizlet.com
Mastering Micro Chapter 6 Exam 2 Flashcards | Quizlet From quizlet.com
Related Post Mastering Micro Chapter 6 Exam 2 Flashcards | Quizlet :
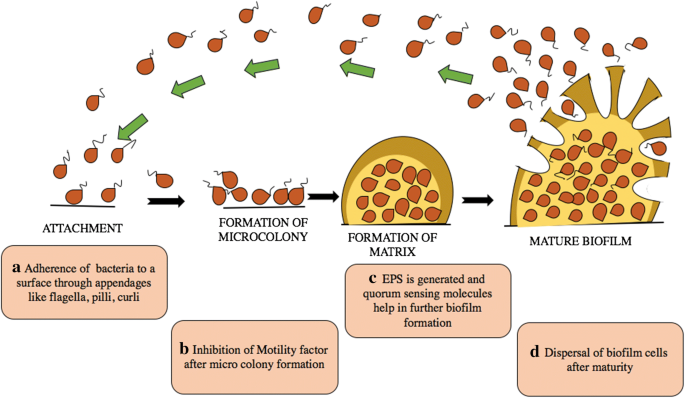
Biofilm formation can depend on a single kind of microorganism. A biofilm community can be formed by a single bacterial species, but in nature biofilms almost always consist of rich mixtures of many species of bacteria, as well as fungi, algae, yeasts, protozoa, other microorganisms, debris and corrosion products. Download to read the full article text. You include a control mixture in your study that you know does not form biofilms.
However, they almost always consist of mixtures of many bacteria species.
However, they almost always consist of mixtures of many bacteria species. They also commonly contain fungi, algae, yeasts, protozoa, and other microorganisms. Download to read the full article text. Group 2 correct the matrix produced by bacteria that grow in a biofilm can slow down the diffusion of antibiotics into the biofilm. However, they almost always consist of mixtures of many bacteria species. Aeruginosa still exhibiting the stronger growth of both.
 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
Briefly, pcr mixtures were performed in a final volume of 25 µl. Therefore, bacteria in the deeper segments of the biofilm persist and perpetuate the infection. Namely, we evaluated bacterial growth, biofilm production and antimicrobial resistance profiles of aeromonas species in pure and mixed cultures.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
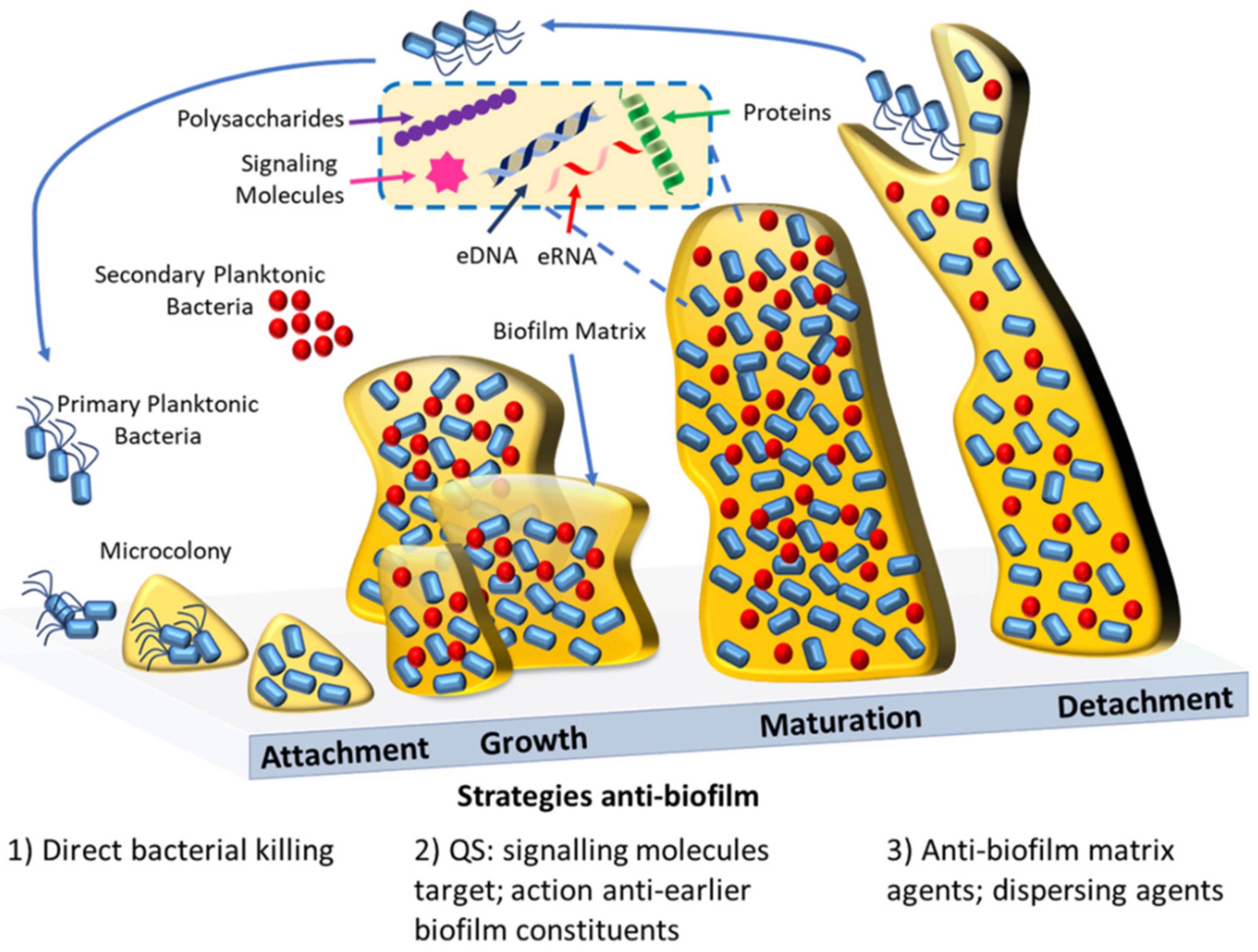
Biofilms are clusters of single or multiple species of bacteria encased in a matrix composed of polysaccharides, proteins, and dna that house and protect the bacteria from environmental pressures. Bacteria frequently grow in communities called biofilms, which are aggregates of cells and polymers. Studied for its role as an inhibitor of bacterial growth and biofilm formation of many clinical bacterial isolates.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Studied for its role as an inhibitor of bacterial growth and biofilm formation of many clinical bacterial isolates. The slides were washed with deionized water three times. Biofilms are medically important as they can allow bacteria to persist in host tissues and on catheters, and confer increased resistance to.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
The bacteria examined were divided into. According to some authors, biofilm bacteria are embedded in a matrix of extracellular polymeric substances (eps). Therefore, bacteria in the deeper segments of the biofilm persist and perpetuate the infection.
 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
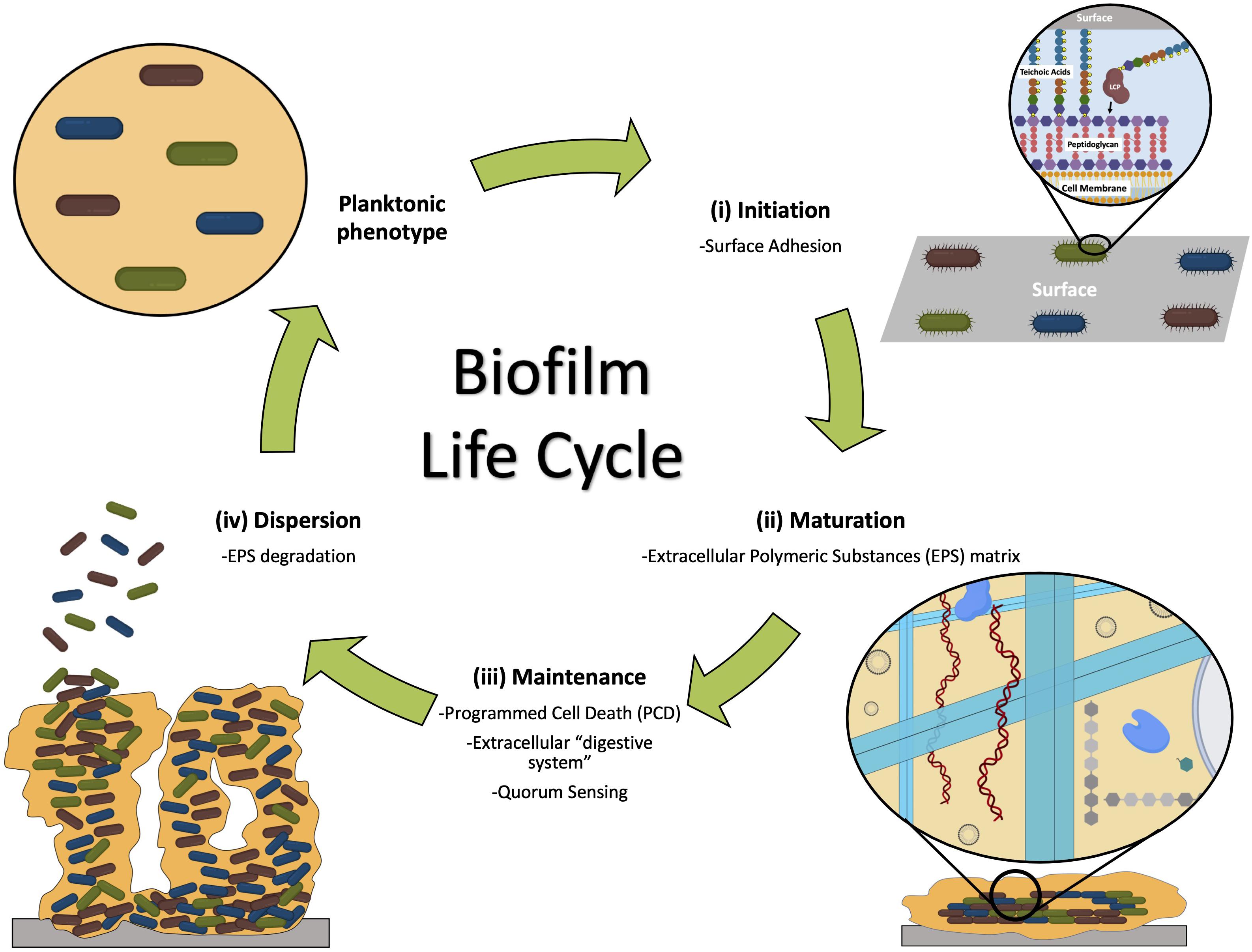
The films can be just a few cells thick. For example, over 500 bacterial species can live on typical dental plaque biofilms. Bacteria suspension and incubated at 37 °c for 24 hours for biofilm growth.
 Source: coursehero.com
Source: coursehero.com
Group 2 correct the matrix produced by bacteria that grow in a biofilm can slow down the diffusion of antibiotics into the biofilm. For example, over 500 bacterial species can live on typical dental plaque biofilms. Download to read the full article text.
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Aeruginosa still exhibiting the stronger growth of both. Biofilm is characterised by heterogenous environment and the presence of a variety of subpopulations. An example of a biofilm is the dental plaque on your teeth.
 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
Cells deep in the biofilm are therefore protected against the antibiotic. Bacteria suspension and incubated at 37 °c for 24 hours for biofilm growth. Biofilms can be described as a group of microorganisms that attach and colonise on any surface that is immersed in an aqueous medium (costerton 1995;
 Source: coursehero.com
Source: coursehero.com
Briefly, pcr mixtures were performed in a final volume of 25 µl. The bacteria examined were divided into. Biofilms are medically important as they can allow bacteria to persist in host tissues and on catheters, and confer increased resistance to.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Biofilms develop from bacteria bound on surfaces that grow into structured communities (microcolonies). Biofilm is characterised by heterogenous environment and the presence of a variety of subpopulations. Biofilm formation can depend on a single kind of microorganism.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Therefore, bacteria in the deeper segments of the biofilm persist and perpetuate the infection. According to others, bacteria form a biofilm even if eps are absent or below a detectable level. A biofilm community can be formed by a single bacterial species, but in nature biofilms almost always consist of rich mixtures of many species of bacteria, as well as fungi, algae, yeasts, protozoa, other microorganisms, debris and corrosion products.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Biofilms can be described as a group of microorganisms that attach and colonise on any surface that is immersed in an aqueous medium (costerton 1995; Bacteria frequently grow in communities called biofilms, which are aggregates of cells and polymers. Bacteria suspension and incubated at 37 °c for 24 hours for biofilm growth.
 Source: microbialcell.com
Source: microbialcell.com
Bacteria frequently grow in communities called biofilms, which are aggregates of cells and polymers. Dimethyl methylene blue (dmmb) dye was used to quantify biofilm matrix colorimetrically. According to some authors, biofilm bacteria are embedded in a matrix of extracellular polymeric substances (eps).
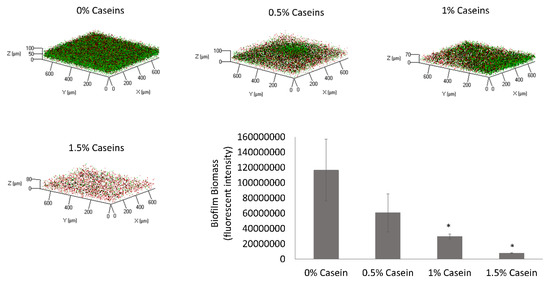 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Biofilms can be described as a group of microorganisms that attach and colonise on any surface that is immersed in an aqueous medium (costerton 1995; They also commonly contain fungi, algae, yeasts, protozoa, and other microorganisms. You know that all your mixtures of bacteria are susceptible to penicillin when they do not grow as a biofilm.
 Source: coursehero.com
Source: coursehero.com
The organisms included in the study were 33 isolates of 11 different bacterial species. Briefly, pcr mixtures were performed in a final volume of 25 µl. Bacteria suspension and incubated at 37 °c for 24 hours for biofilm growth.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
Biofilm is characterised by heterogenous environment and the presence of a variety of subpopulations. In this study, a new microplate model for the detection of staphylococcus aureus biofilms was developed. Briefly, pcr mixtures were performed in a final volume of 25 µl.
 Source: coursehero.com
Source: coursehero.com
An example of a biofilm is the dental plaque on your teeth. Bacteria frequently grow in communities called biofilms, which are aggregates of cells and polymers. Previous studies have demonstrated that edna is a key constituent in the construction and structural integrity of the biofilm matrix in many bacterial species, and the cleaving of edna by nuclease enzymes such as dnase i disintegrates the biofilm matrix, thereby increasing the susceptibility of bacterial cells within the biofilm matrix to antimicrobial agents.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
Download to read the full article text. The films can be just a few cells thick. According to others, bacteria form a biofilm even if eps are absent or below a detectable level.
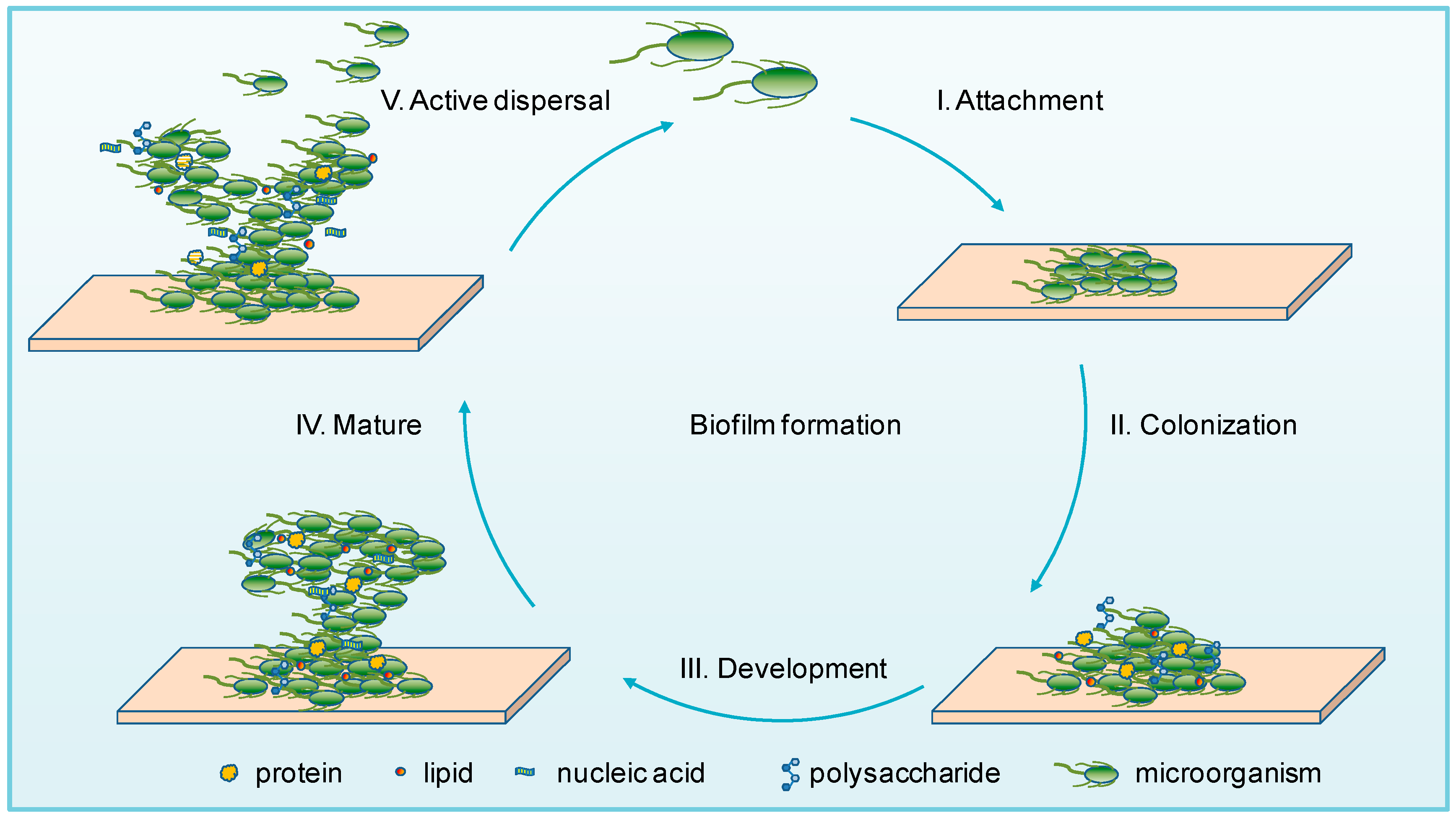 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Group 2 correct the matrix produced by bacteria that grow in a biofilm can slow down the diffusion of antibiotics into the biofilm. However, they almost always consist of mixtures of many bacteria species. Namely, we evaluated bacterial growth, biofilm production and antimicrobial resistance profiles of aeromonas species in pure and mixed cultures.
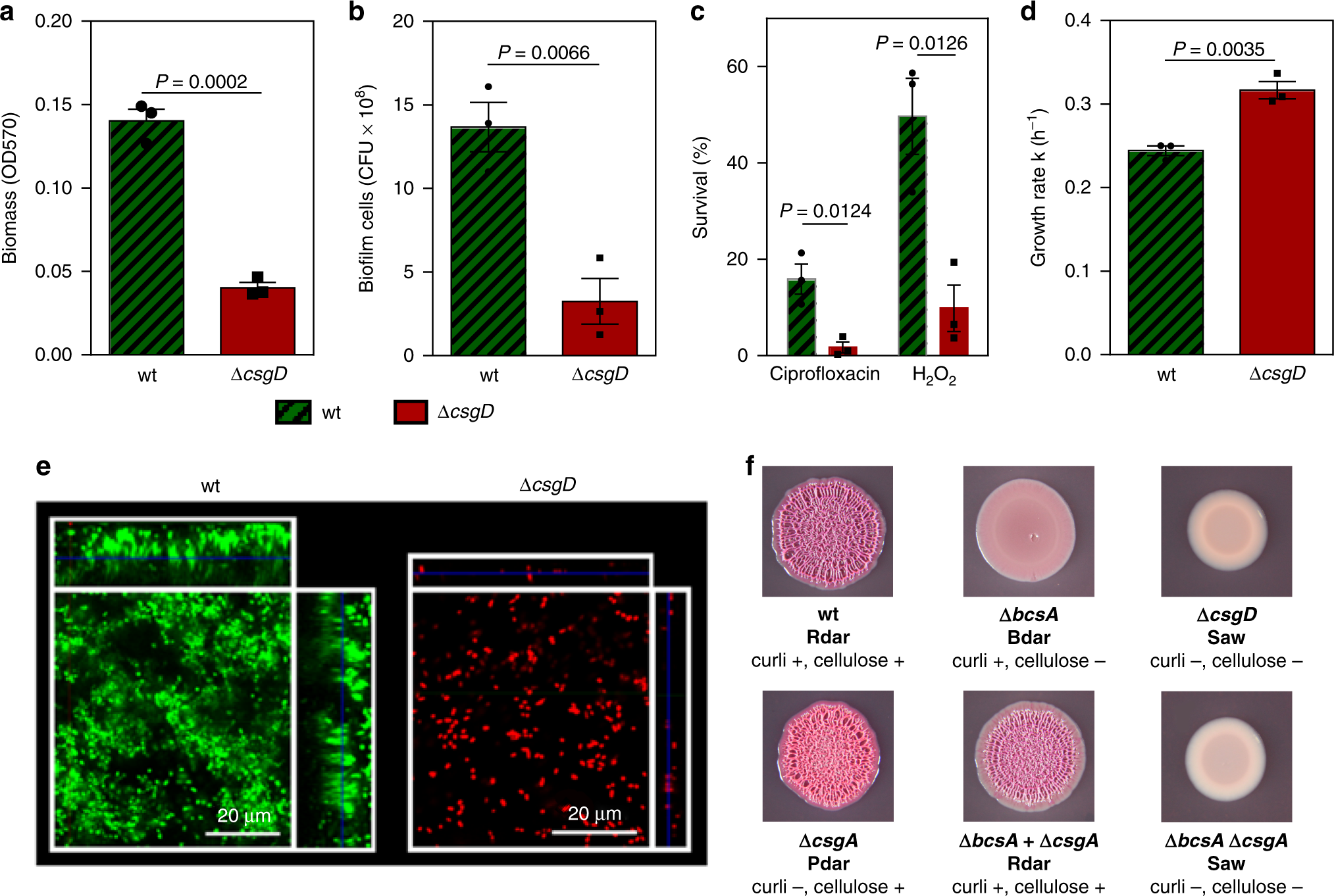 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Therefore, bacteria in the deeper segments of the biofilm persist and perpetuate the infection. You know that all your mixtures of bacteria are susceptible to penicillin when they do not grow as a biofilm. A biofilm community can be formed by a single bacterial species, but in nature biofilms almost always consist of rich mixtures of many species of bacteria, as well as fungi, algae, yeasts, protozoa, other microorganisms, debris and corrosion products.
Also Read :