Within each single breath their action is highly coordinated with that of the inspiratory rib cage muscles. What muscles are involved in quiet.
Which Muscles Are Activated During Forced Expiration. These muscles also contract forcefully during coughing, vomiting, and defecation. During forced inspiration, muscles of the neck, including the scalenes, contract and lift the thoracic wall, increasing lung volume. During forced inspiration the diaphragm pulls down as normal but to maximise increase the size of the thoracic cavity and suck in extra air the the external intercostals are activated. Additional muscles are recruited to.
 Mechanics Of Breathing - Ppt Download From slideplayer.com
Mechanics Of Breathing - Ppt Download From slideplayer.com
Related Post Mechanics Of Breathing - Ppt Download :
Anterior muscles used in expiration. During quiet breathing, the diaphragm and external intercostals must contract. During forced expiration, the internal intercostal muscles (excluding the interchondral part) contract and depress the rib cage. Abdominal muscle control during forced expiration forced expiration is driven primarily by the abdominal muscles.
Internal and external oblique abdominus, transverse abdominus, rectus abdominus.
During forced expiration, the internal intercostal muscles (excluding the interchondral part) contract and depress the rib cage. During forced exhalation, as when blowing out a candle, expiratory muscles including the abdominal muscles and internal intercostal muscles generate abdominal and thoracic pressure, which forces air out of the lungs. Forced inspiration and expiration require muscular contraction, and therefore, they�re both active processes. During forced expiration, the internal intercostal muscles (excluding the interchondral part) contract and depress the rib cage. What muscles are involved in quiet. Which muscles are activated during forced expiration?
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Abdominal muscles (d) a and c only (e) none of the above: During inspiration, while the rib cage muscles contract, the abdominal muscles gradually relax, and vice versa during expiration Anterior muscles used in expiration.
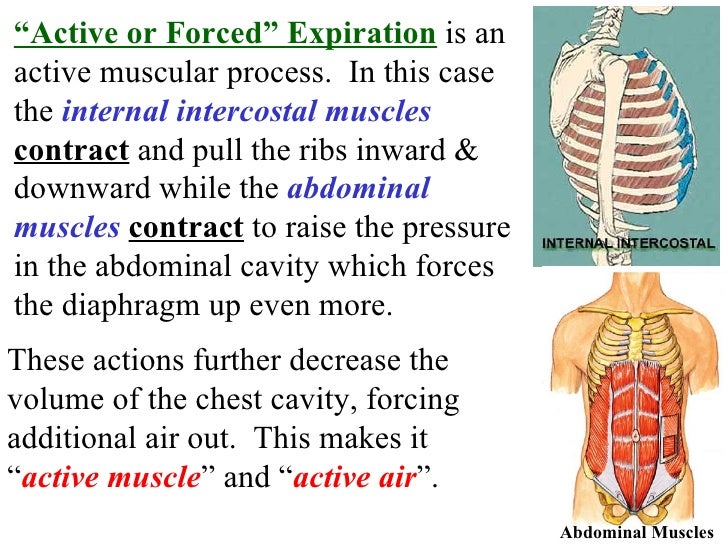 Source: pt.slideshare.net
Source: pt.slideshare.net
During forced inspiration, muscles of the neck, including the scalenes, contract and lift the thoracic wall, increasing lung volume. Internal intercostals muscles, innermost intercostals muscles, and tranverses thoracis muscles. During forced breathing, inspiration and expiration both occur due to muscle contractions.

Posterior muscles used in expiration. Consequently, which muscles are used when inspiration is forced? The abdominal muscles also aid expiration because, when they contract, they force abdominal organs up against the diaphragm and further decrease the volume of the thorax.
![Solved] Which Muscles Are Activated During Forced Expiration? | Course Hero](https://www.coursehero.com/qa/attachment/15017218/ “Solved] Which Muscles Are Activated During Forced Expiration? | Course Hero”) Source: coursehero.com
Which of the following muscles is (are) activated during forceful expiration. The most important contribution that the abdominal wall muscles make to the movements of respiration is in the powerful action of forced expiration, as in coughing or sneezing. As the diaphragm relaxes, air passively leaves the lungs.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
The most important muscles of forced expiration are those of the abdominals. During forced exhalation, as when blowing out a candle, expiratory muscles including the abdominal muscles and internal intercostal muscles generate abdominal and thoracic pressure, which forces air out of the lungs. The abdominal muscles also aid expiration because, when they contract, they force abdominal organs up against the diaphragm and further decrease the volume of the thorax.
 Source: virtualhomeschoolgroup.org
Source: virtualhomeschoolgroup.org
Depress ribs during expiration accessory muscles of expiration rectus abdominus, external obliques, internal obliques, transversus thoracis, serratus posterior inferior, quadratus lumborum During forced expiration, accessory muscles of the abdomen, including the obliques, contract, forcing abdominal organs upward against the diaphragm. Adequate control over these muscles is important for physiologic functions such as coughing and adequately responding to a gag reflex.
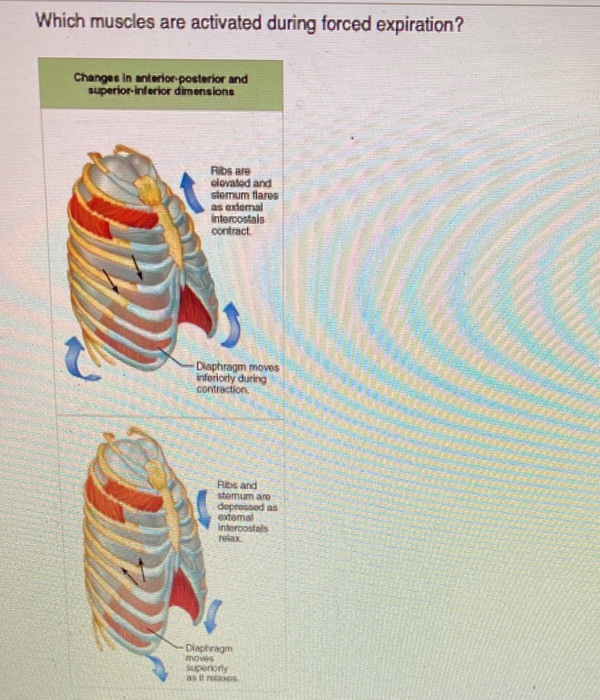 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Anterior muscles used in expiration. Adequate control over these muscles is important for physiologic functions such as coughing and adequately responding to a gag reflex. A deep breath, called diaphragmatic breathing, requires the diaphragm to contract.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
The internal intercostal, oblique, and transversus muscles which of the following is an organ shared by the respiratory system and the digestive system? As the diaphragm relaxes, air passively leaves the lungs. In addition to the muscles of respiration that we�ve seen, there are some minor ones that we�re going to leave out, since they�re unimportant.
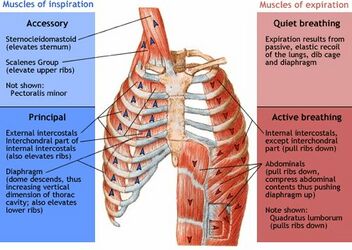 Source: physio-pedia.com
Source: physio-pedia.com
During forced inspiration, muscles of the neck, including the scalenes, contract and lift the thoracic wall, increasing lung volume. Thursday, january 1, 2015 last updated: Abdominal muscle control during forced expiration forced expiration is driven primarily by the abdominal muscles.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Depress ribs during expiration accessory muscles of expiration rectus abdominus, external obliques, internal obliques, transversus thoracis, serratus posterior inferior, quadratus lumborum During inspiration, while the rib cage muscles contract, the abdominal muscles gradually relax, and vice versa during expiration Rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis, external oblique, internal oblique muscles airways conducting airways:
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
When forceful exhalation is required, or when the elasticity of the lungs is reduced (as in emphysema), active exhalation can be achieved by contraction of the abdominal wall muscles (rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis, external oblique muscle and internal oblique muscle). During quiet breathing, the diaphragm and external intercostals must contract. Which muscles are activated during forced expiration?
 Source: 78stepshealth.us
Source: 78stepshealth.us
During forced expiration, accessory muscles of the abdomen, including the obliques, contract, forcing abdominal organs upward against the diaphragm. When forceful exhalation is required, or when the elasticity of the lungs is reduced (as in emphysema), active exhalation can be achieved by contraction of the abdominal wall muscles (rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis, external oblique muscle and internal oblique muscle). During forced inspiration, muscles of the neck, including the scalenes, contract and lift the thoracic wall, increasing lung volume.
 Source: ib.bioninja.com.au
Source: ib.bioninja.com.au
During inspiration, while the rib cage muscles contract, the abdominal muscles gradually relax, and vice versa during expiration Nose, nasopharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchiles, terminal bronchioles Thursday, january 1, 2015 last updated:
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis, external oblique, internal oblique muscles airways conducting airways: Adequate control over these muscles is important for physiologic functions such as coughing and adequately responding to a gag reflex. Nose, nasopharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchiles, terminal bronchioles
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The abdominal muscles also aid expiration because, when they contract, they force abdominal organs up against the diaphragm and further decrease the volume of the thorax. In addition to the muscles of respiration that we�ve seen, there are some minor ones that we�re going to leave out, since they�re unimportant. During forced breathing, inspiration and expiration both occur due to muscle contractions.
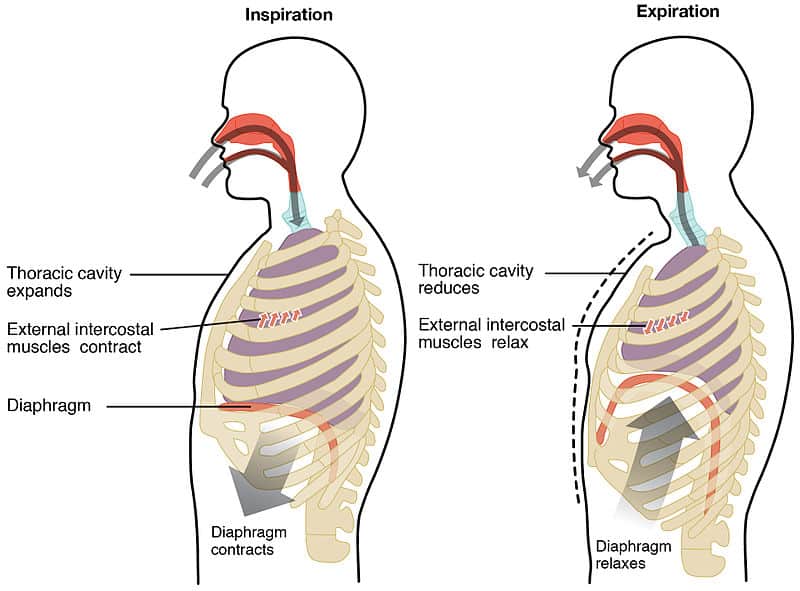 Source: teachmephysiology.com
Source: teachmephysiology.com
Internal and external oblique abdominus, transverse abdominus, rectus abdominus. Expiratory muscles (used in forced expirium): As the diaphragm relaxes, air passively leaves the lungs.
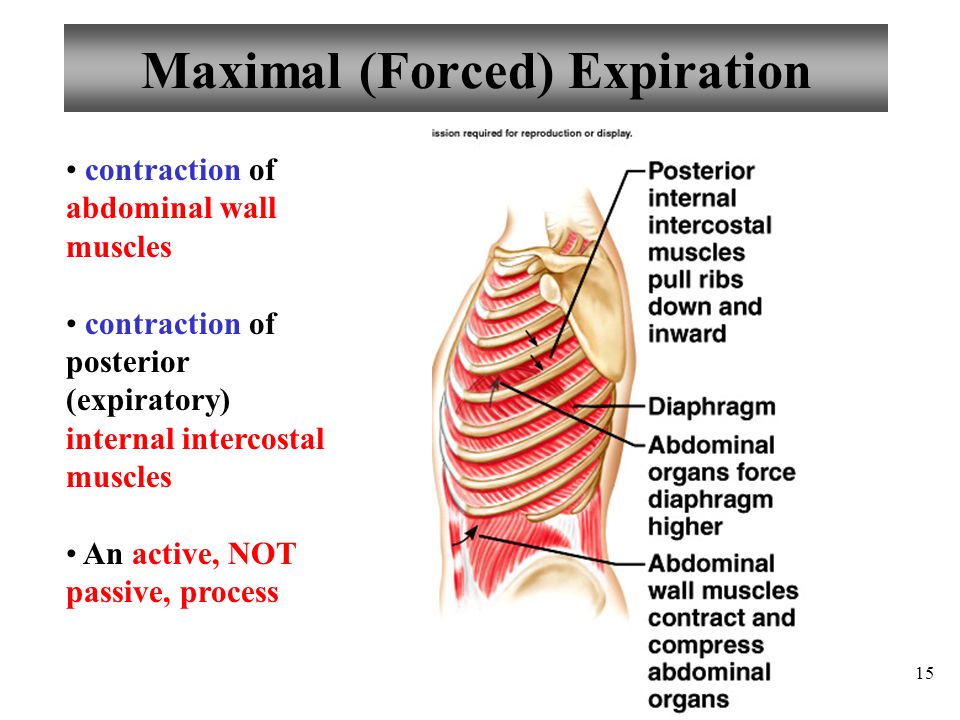 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
These muscles also contract forcefully during coughing, vomiting, and defecation. Consequently, which muscles are used when inspiration is forced? Additional muscles are recruited to.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Adequate control over these muscles is important for physiologic functions such as coughing and adequately responding to a gag reflex. During forced expiration, the internal intercostal muscles (excluding the interchondral part) contract and depress the rib cage. Differently than rest, during exercise the expiratory muscles play an active role in breathing.
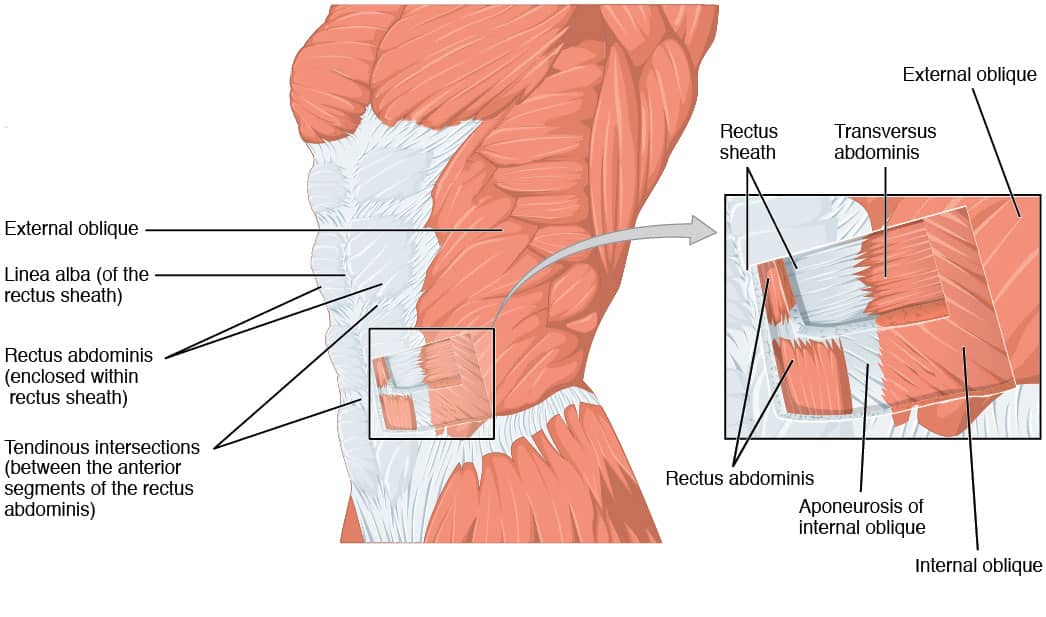 Source: teachmephysiology.com
Source: teachmephysiology.com
Expiratory muscles (used in forced expirium): When forceful exhalation is required, or when the elasticity of the lungs is reduced (as in emphysema), active exhalation can be achieved by contraction of the abdominal wall muscles (rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis, external oblique muscle and internal oblique muscle). In this activity, you will follow oxygen on its path from the lungs to the body tissues.

Anterior muscles used in expiration. Which muscles are activated during forced expiration? During forced breathing, inspiration and expiration both occur due to muscle contractions.
Also Read :




