This is consistent with the. Now while human stem cells are powerful for skin regeneration… the problem is it’s extremely expensive.
Which Layer Is Consistently Renewing Epidermal Cells. It is the deepest layer of epidermis. This layer is mostly comprised of keratinocytes. Keratin and the thickened plasma membranes of cells in this strata protect the skin from abrasion, penetration, and the glycolipids between its cells waterproofs this layer. The rapidly renewing epidermis of the human skin undergoes cell replacement in intimate association with its immediate dermal mesenchymal microenvironment.
 Epidermis - An Overview | Sciencedirect Topics From sciencedirect.com
Epidermis - An Overview | Sciencedirect Topics From sciencedirect.com
Related Post Epidermis - An Overview | Sciencedirect Topics :
How do epidermal cells grow? Bottom layer of the epidermis responsible for constantly renewing epidermal cells. Epidermal stem cells are indispensable for epithelialization, and they are regulated by. This is also called stratum germinativum;
Monkey palm epidermis provides a model system for further studies of primate epidermal stem cells.
Even though individual cells within the skin periodically die and are replaced with new cells, the scar collagen remains. Monkey palm epidermis provides a model system for further studies of primate epidermal stem cells. It is the layer we see with our eyes. There are five main layers of the epidermis; While some basal cells are dividing, adding to the population in the basal layer, others (their sisters or cousins) are slipping out of the basal cell layer into the prickle cell layer, taking the first step on their outward journey. The rapidly renewing epidermis of the human skin undergoes cell replacement in intimate association with its immediate dermal mesenchymal microenvironment.
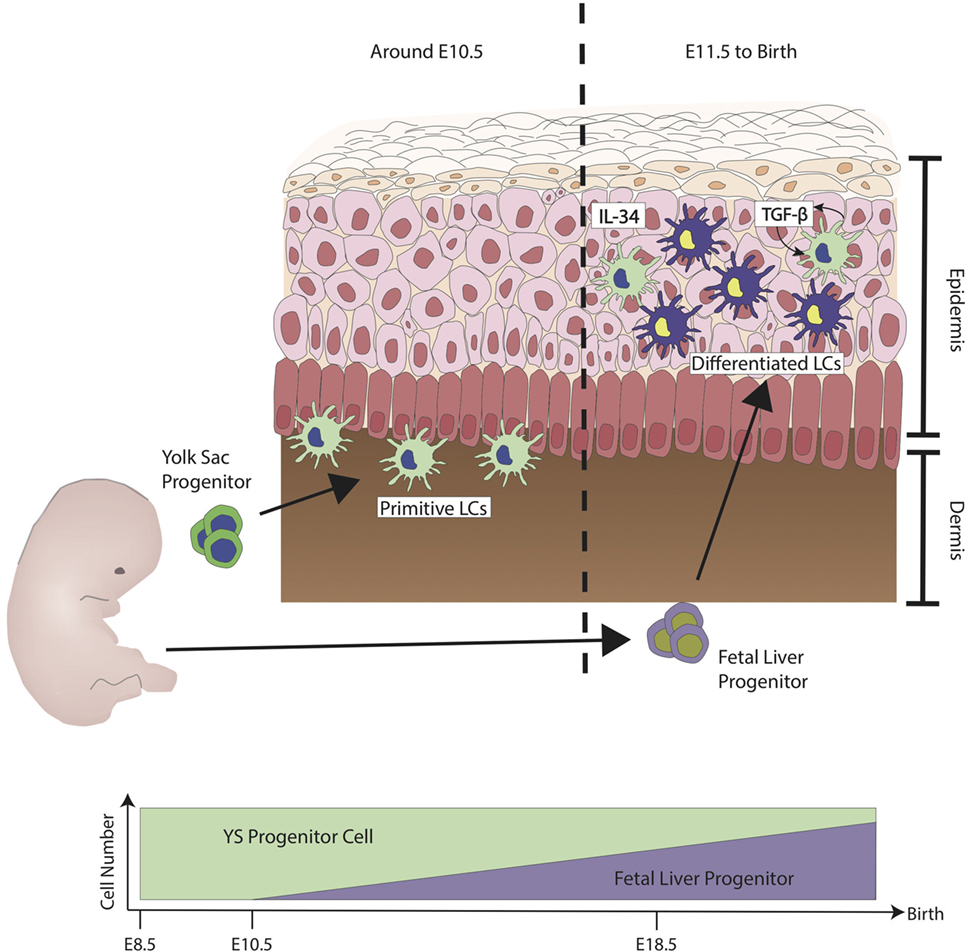 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
Bottom layer of the epidermis responsible for constantly renewing epidermal cells. Bottom layer of the epidermis responsible for constantly renewing epidermal cells. Now while human stem cells are powerful for skin regeneration… the problem is it’s extremely expensive.
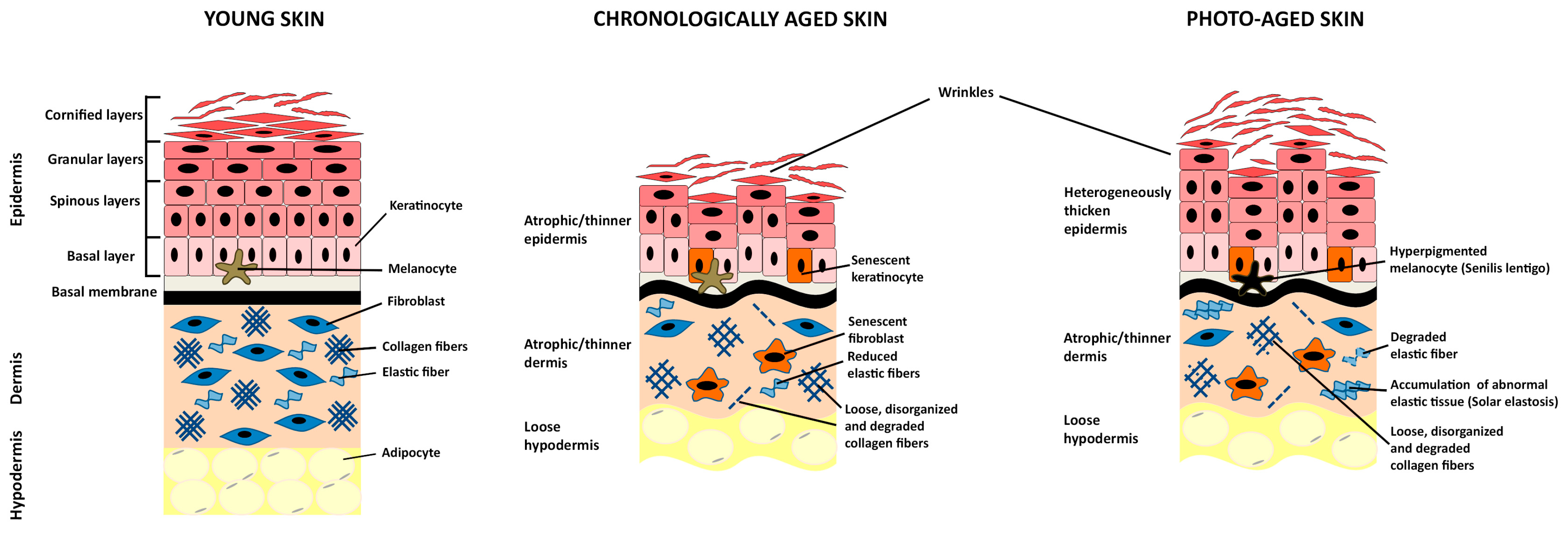 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
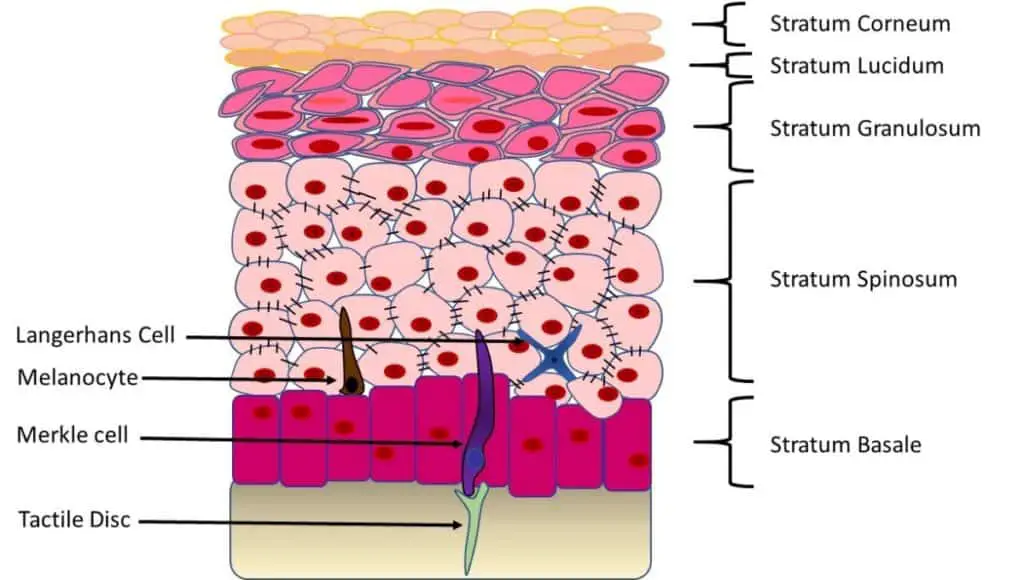
In mammals the epidermis consists of fourto five separate layers, the top layer is made up of cornifiedcells, which form the primary protective layer. The physiological process that maintains a constant number of cells in renewing organs is called tissue homeostasis. They include the stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, and stratum corneum.
 Source: skinpen.com
Source: skinpen.com
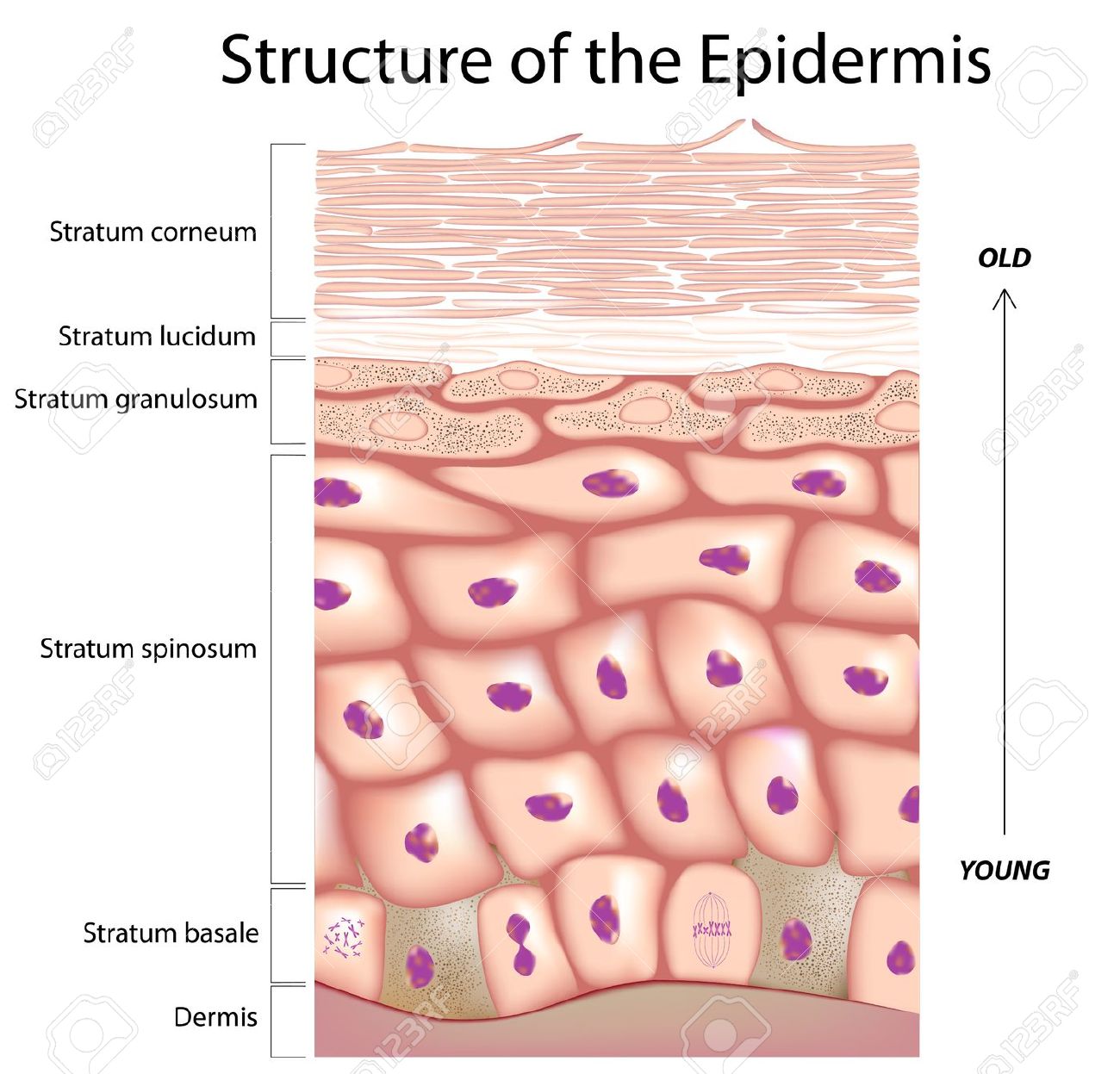
The epidermis has four layers that perform different functions: The epidermis has four layers that perform different functions: A single layer of epidermal cells forms and.
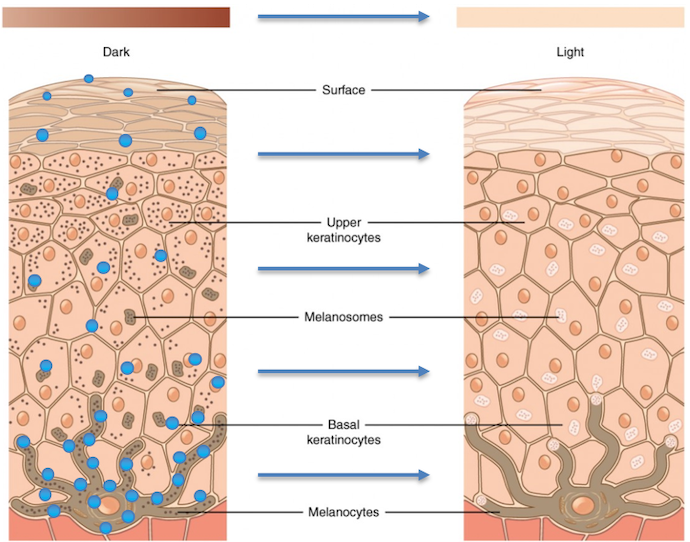 Source: 28cubed.com
Source: 28cubed.com
Epidermal stem cells residing in specific niches are self renewing, and give rise to transit amplifying that are responsible for the majority of the proliferative activity in. It is the deepest layer of epidermis. How do epidermal cells grow?
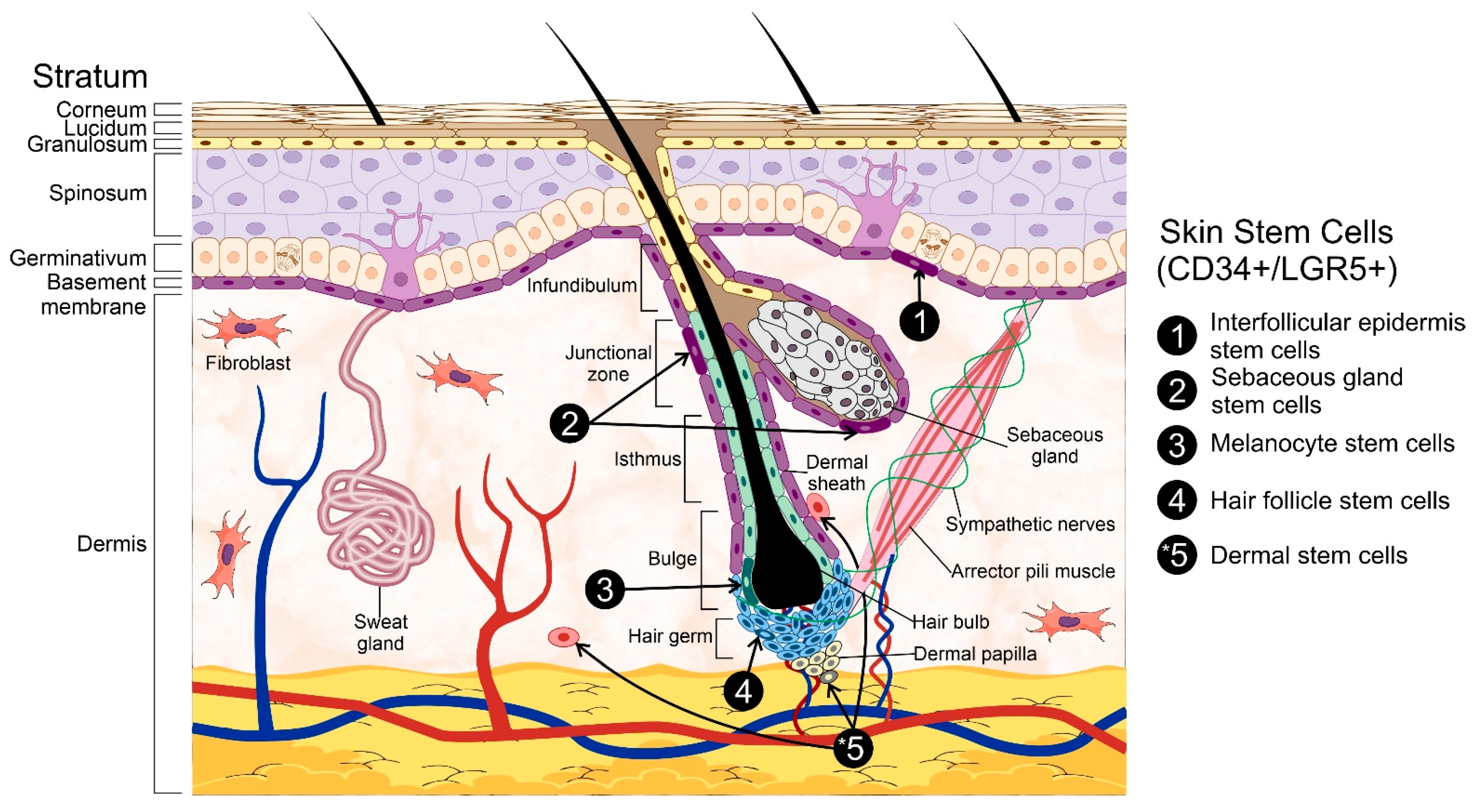 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
In mammals the epidermis consists of fourto five separate layers, the top layer is made up of cornifiedcells, which form the primary protective layer. These cells are young and healthy, formed from dividing keratinocyte stem cells. The deepest layer of the epidermis is called the stratum basale, sometimes called the stratum germinativum.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Even though individual cells within the skin periodically die and are replaced with new cells, the scar collagen remains. Much remains to be known about how epithelial stem cells are generated and maintained. This is also called stratum germinativum;
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Purpose of the stratum corneum? About half the cells begin to flatten and move to the next layer in the maturation process. In mammals the epidermis consists of fourto five separate layers, the top layer is made up of cornifiedcells, which form the primary protective layer.
 Source: jacionline.org
Source: jacionline.org
This is consistent with the. This layer is mostly comprised of keratinocytes. A single layer of epidermal cells forms and.
 Source: microscopeclarity.com
Source: microscopeclarity.com
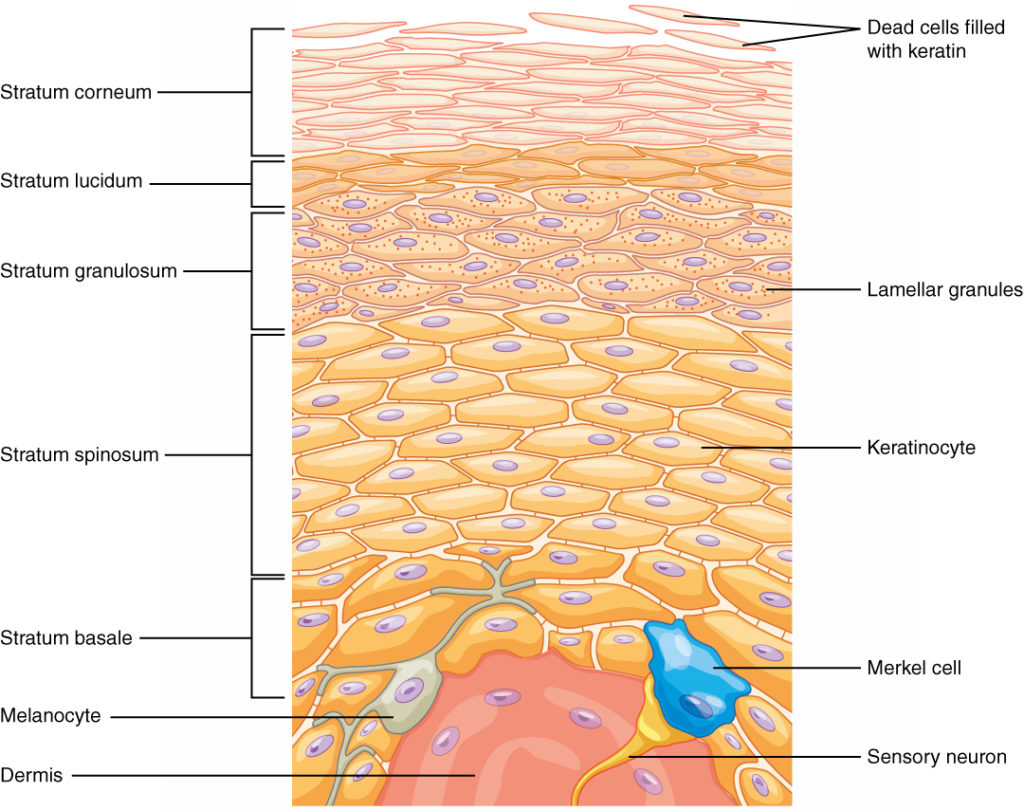
Much remains to be known about how epithelial stem cells are generated and maintained. As more cells are made, they push upwards, and all the cells move up. The skin is composed of two major layers, an upper multilayer of cells (epidermis) consisting primarily of keratinocytes of varying stages of differentiation attached to one another by desmosomes and an underlying connective tissue layer (dermis) separated from the epidermis by a basal membrane.
 Source: theecowell.com
Source: theecowell.com
Keratin and the thickened plasma membranes of cells in this strata protect the skin from abrasion, penetration, and the glycolipids between its cells waterproofs this layer. The skin is composed of two major layers, an upper multilayer of cells (epidermis) consisting primarily of keratinocytes of varying stages of differentiation attached to one another by desmosomes and an underlying connective tissue layer (dermis) separated from the epidermis by a basal membrane. In normal human epidermis, lrig1+ cells form clusters located in the basal layer in which cd44 expression is downregulated and lef1 expression reflects an active wnt signaling.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
This is the deepest layer of the epidermis, and it’s responsible for renewing the skin. Even though individual cells within the skin periodically die and are replaced with new cells, the scar collagen remains. Indeed, its dependency on mesenchymal factors was evident from studies demonstrating that a feeder layer of embryonic fibroblasts was essential for epidermal
 Source: socratic.org
Source: socratic.org
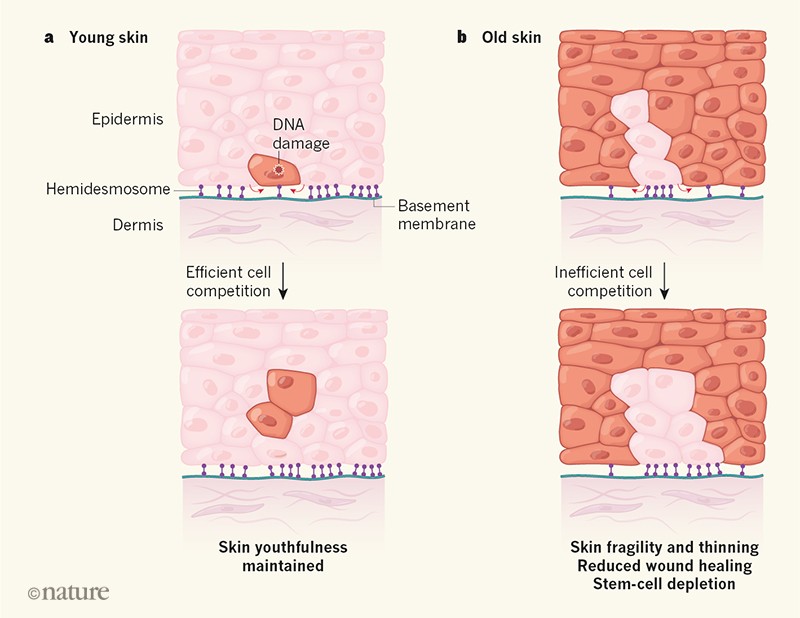
The physiological process that maintains a constant number of cells in renewing organs is called tissue homeostasis. These cells are young and healthy, formed from dividing keratinocyte stem cells. That’s the only layer we see when we look in the mirror.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The other half remain in the basal layer and divide over and over. The epidermis forms columnar cells in the base layer, furthest away from the surface. In mammals the epidermis consists of fourto five separate layers, the top layer is made up of cornifiedcells, which form the primary protective layer.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
The rapidly renewing epidermis of the human skin undergoes cell replacement in intimate association with its immediate dermal mesenchymal microenvironment. Much remains to be known about how epithelial stem cells are generated and maintained. Bottom layer of the epidermis responsible for constantly renewing epidermal cells.
 Source: shutterstock.com
Source: shutterstock.com
They’re called epidermal stem cells… and in case you didn’t know, these cells are found in the epidermis which is the outer layer of the skin. The physiological process that maintains a constant number of cells in renewing organs is called tissue homeostasis. These cells are young and healthy, formed from dividing keratinocyte stem cells.
 Source: theecowell.com
Source: theecowell.com
Even though individual cells within the skin periodically die and are replaced with new cells, the scar collagen remains. How do epidermal cells grow? In mammals the epidermis consists of fourto five separate layers, the top layer is made up of cornifiedcells, which form the primary protective layer.

They’re called epidermal stem cells… and in case you didn’t know, these cells are found in the epidermis which is the outer layer of the skin. This layer isconstantly renewed by releasing. It contains no blood supply of its own —which is why you can shave your skin and not cause any bleeding despite losing many cells in the process.

Much remains to be known about how epithelial stem cells are generated and maintained. In mammals the epidermis consists of fourto five separate layers, the top layer is made up of cornifiedcells, which form the primary protective layer. How do epidermal cells grow?
 Source: tokopedia.com
Source: tokopedia.com
That’s the only layer we see when we look in the mirror. While some basal cells are dividing, adding to the population in the basal layer, others (their sisters or cousins) are slipping out of the basal cell layer into the prickle cell layer, taking the first step on their outward journey. As more cells are made, they push upwards, and all the cells move up.
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
This layer contains a single row of columnar stem cells that divide very frequently. Monkey palm epidermis provides a model system for further studies of primate epidermal stem cells. Now while human stem cells are powerful for skin regeneration… the problem is it’s extremely expensive.
Also Read :





