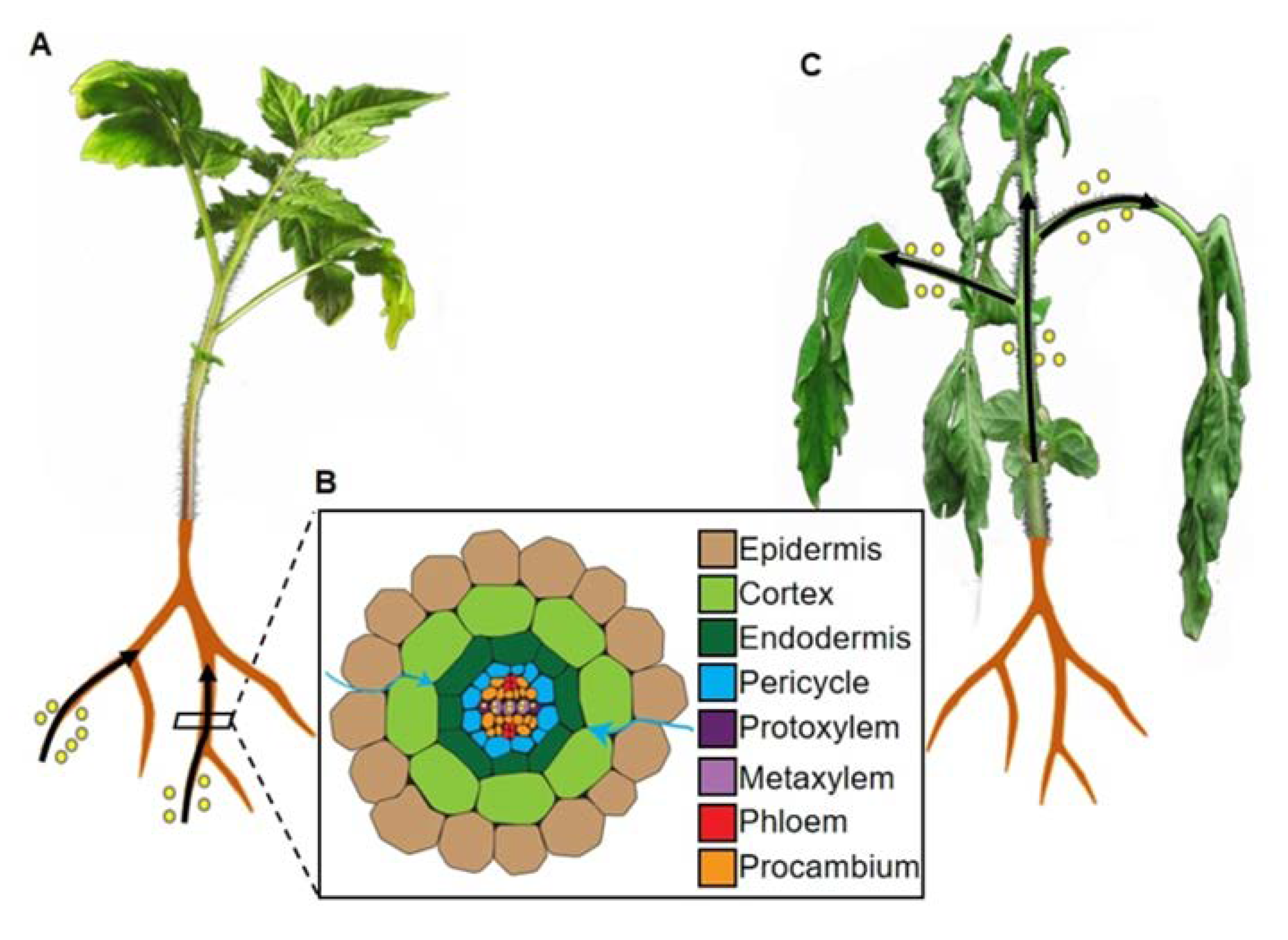
Originating from procambium, further divided into protoxylem and metaxylem The xylem transports water and minerals from the roots up the plant stem and into the leaves.
Which Is Transported In The Xylem Of A Plant Apex. 2 get other questions on the subject: Plants have tissues to transport water, nutrients and minerals. It later appeared in the leaves. Hormones and other small molecules also travel through the xylem as they are moved throughout the plant.

Related Post Smarteduhub.com :
Xylem transport water up the plant (from root to leaf), and phloem transports the food and sugar materials. Xylem cells form long tubes that transport materials, and the mixture of water and nutrients that flows through the xylem cells is called xylem sap. Hormones and other small molecules also travel through the xylem as they are moved throughout the plant. Although aba is produced in both roots and leaves, it is accepted that root tips are the major source of aba produced in response to drying soil.
Plants have tissues to transport water, nutrients and minerals.
In land plants, water and minerals are taken up from the soil by the roots and transported through the xylem network to the leaves. The plant cell can move substances into cells using proton pumps that work against a gradient. True active transport in plants works against a concentration gradient and this allows for substances to pass through plant cells without an energy input. The initiation of fascicular and interfascicular cambia is believed to be. In a mature flowering plant or tree, most of the cells that make up the xylem are specialised cells called vessels. Xylem is a type of vascular tissue present in plants, which primarily transports water and nutrients from roots to stem and leaves.

The main function of the xylem is to transport water and some soluble nutrients, including minerals and inorganic ions, upwards from the roots to. The main function of xylem is to transport water, and some soluble nutrients including minerals and inorganic ions, upwards from the roots to the rest of the plant. Transpiration is the process by which water evaporates from the leaves, which results in more water being drawn up from the roots.
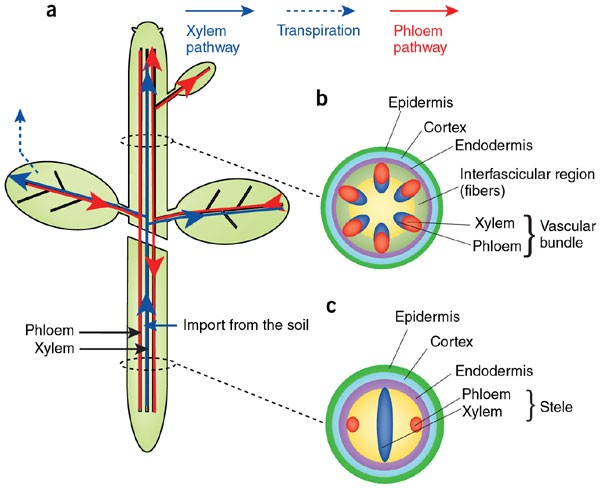 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Auxin is basipetally transported from leaf primordia to the shoot apex and is believed to be the major factor involved in the process of vasculature patterning and differentiation. In land plants, water and minerals are taken up from the soil by the roots and transported through the xylem network to the leaves. True active transport in plants works against a concentration gradient and this allows for substances to pass through plant cells without an energy input.
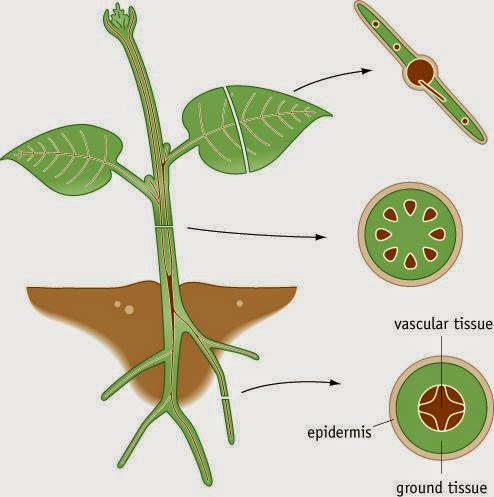 Source: msseconisseniorbiology.blogspot.com
Source: msseconisseniorbiology.blogspot.com
The initiation of fascicular and interfascicular cambia is believed to be. These two parts of the plant work in unison to transport nutrients. Neonicotinoid insecticide molecules are absorbed by the roots and leaves of maize plants.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Plants have tissues to transport water, nutrients and minerals. The initiation of fascicular and interfascicular cambia is believed to be. These mineral nutrients are subsequently transported in the xylem into the ears (martin, 1982).
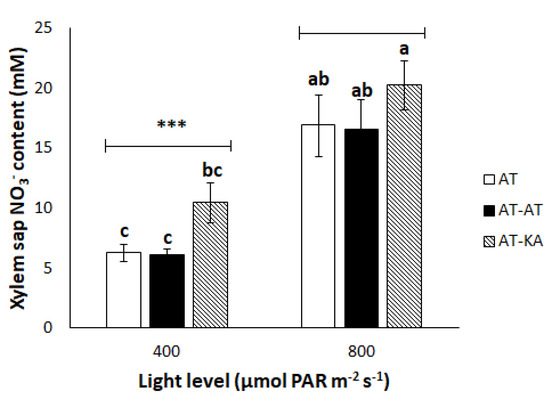 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
The main function of xylem is to transport water, and some soluble nutrients including minerals and inorganic ions, upwards from the roots to the rest of the plant. Xylem is a type of tissue in vascular plants that transports water and some nutrients from the roots to the leaves. Originating from procambium, further divided into protoxylem and metaxylem
 Source: jagranjosh.com
Source: jagranjosh.com
Water in plants are transported by tubes called xylem and food is transported by tubes called phloem. In a mature flowering plant or tree, most of the cells that make up the xylem are specialised cells called vessels. In land plants, water and minerals are taken up from the soil by the roots and transported through the xylem network to the leaves.
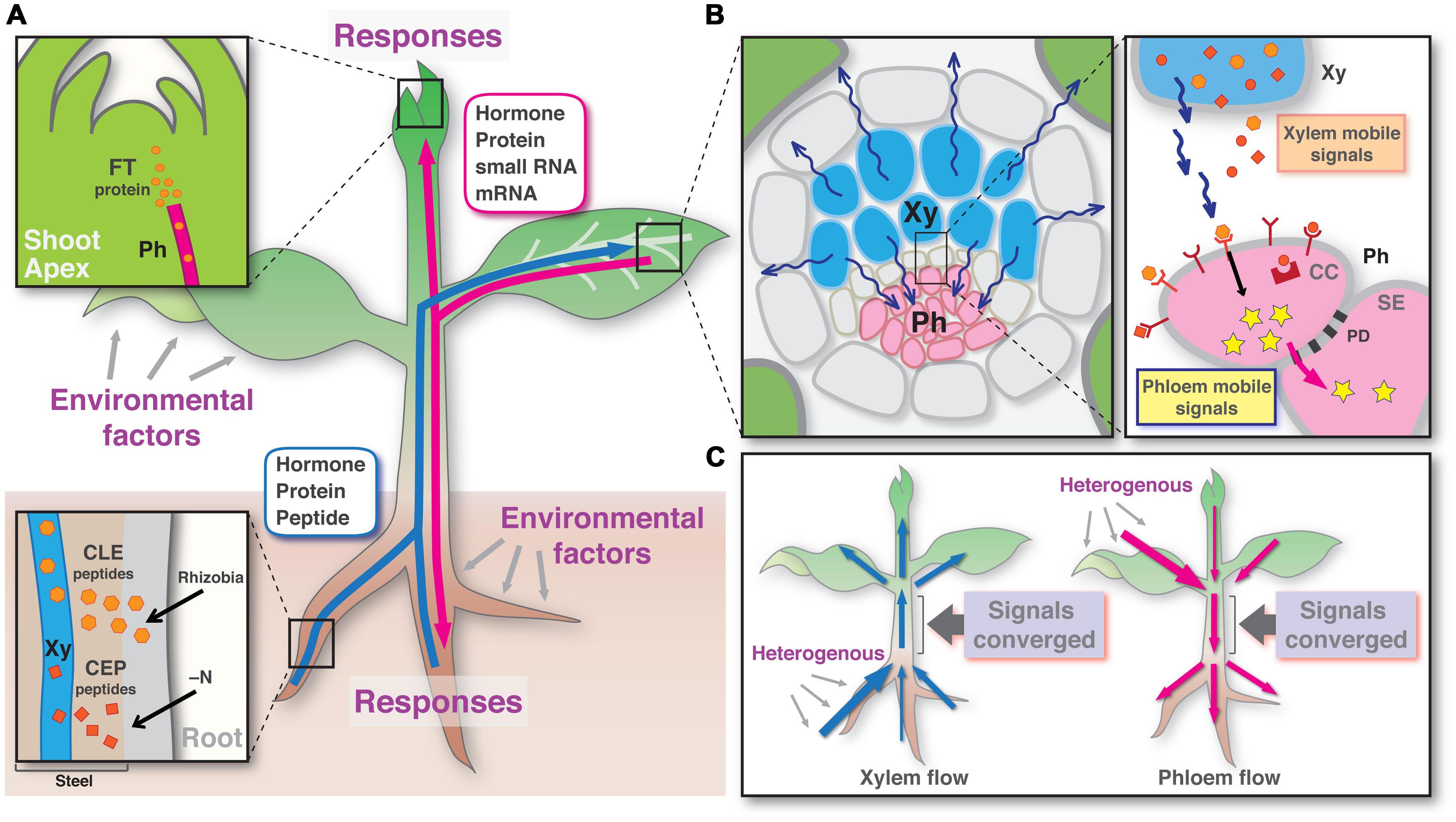 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
The plant cell can move substances into cells using proton pumps that work against a gradient. Xylem is a type of tissue in vascular plants that transports water and some nutrients from the roots to the leaves. In land plants, water and minerals are taken up from the soil by the roots and transported through the xylem network to the leaves.
 Source: sites.google.com
Source: sites.google.com
The main function of xylem is to transport water, and some soluble nutrients including minerals and inorganic ions, upwards from the roots to the rest of the plant. Salts from soil to roots markscheme c Cloned plant is transferred to soil.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
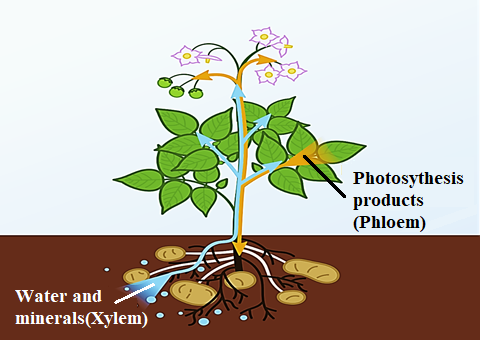
Xylem is a type of vascular tissue present in plants, which primarily transports water and nutrients from roots to stem and leaves. Xylem transports water and minerals, while phloem transports a variety of dissolved substances, including sugars and amino acids, throughout the plant. In phloem (by), translocation / mass flow ;
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Water is transported through xylem and food is transported through phloem. Cloned plant is transferred to soil. Water from roots to leaves d.
 Source: sites.google.com
Source: sites.google.com
On the basis of origin, there are two types of xylem cells: Salts from soil to roots markscheme c The main function of xylem is to transport water, and some soluble nutrients including minerals and inorganic ions, upwards from the roots to the rest of the plant.

Although aba is produced in both roots and leaves, it is accepted that root tips are the major source of aba produced in response to drying soil. Water in the xylem always moves up , in the direction from the roots to the leaves. Xylem transports water and mineral salts from the roots up to other parts of the plant,.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Correct answer to the question which is transported in the xylem of a plant? These substances are transported through passive. In phloem (by), translocation / mass flow ;

Plants have two different types of transport tissue. Cloned plant is transferred to soil. Neonicotinoid insecticide molecules are absorbed by the roots and leaves of maize plants.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
On the basis of origin, there are two types of xylem cells: On the basis of origin, there are two types of xylem cells: Plants have two different types of transport tissue.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
What is transported in xylem tissue? The evidence to date suggests that a chemical signal, abscisic acid (aba), is produced in roots in drying soil and is transported to leaves in the xylem sap, where it induces stomatal closure before reductions in leaf water potential occur. Just as animals, plants also contain vascular tissues (xylem), which transports water and minerals up from the roots to the leaves, and phloem, which transports sugar molecules, amino acids, and hormones both up and down through the plant.
 Source: vedantu.com
Source: vedantu.com
Sap is the mix of water and minerals that move through the xylem. Xylem transports water and mineral salts from the roots up to other parts of the plant,. Water in the xylem always moves up , in the direction from the roots to the leaves.

On the basis of origin, there are two types of xylem cells: Xylem transports water and mineral salts from the roots up to other parts of the plant,. What is transported in xylem tissue?
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
These two parts of the plant work in unison to transport nutrients. Starch from leaves to storage organs c. Originating from procambium, further divided into protoxylem and metaxylem
 Source: shutterstock.com
Source: shutterstock.com
Just as animals, plants also contain vascular tissues (xylem), which transports water and minerals up from the roots to the leaves, and phloem, which transports sugar molecules, amino acids, and hormones both up and down through the plant. Xylem transports water and solutes from the roots to the leaves, phloem transports food from the leaves to the rest of the plant. Plants have two different types of transport tissue.
Also Read :





