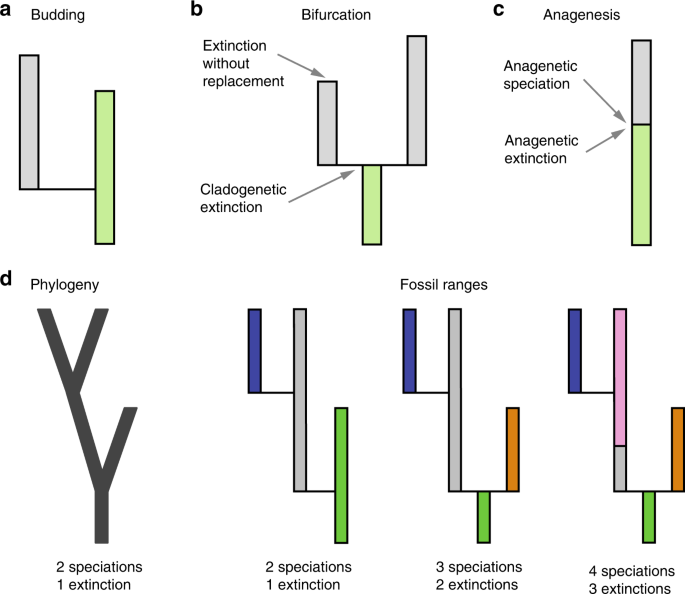
The evolutionary rates of speciation and extinction, their difference being diversification rate, shape current patterns of diversity across the tree of life. At equilibrium these three processes balance ( m + g = d ).
Which Increases The Rate Of Speciation. C) the rate increases as the extent of geographic barriers separating the two subsets increases. However, recent phylogenetic studies have found. Increased instances of hybrid formation d. Longer distance between divided groups.
 Sxsnqktq332Bem From
Sxsnqktq332Bem From
Related Post Sxsnqktq332Bem :
Allopatric speciation, meaning speciation in “other homelands,” involves a geographic separation of populations from a parent species and subsequent evolution. It refers to the evolution of new species from the surviving ancestral species in which both the species continue to live in the same geographical region. Several evolutionary theories predict that rates of morphological change should be positively associated with the rate at which new species arise. Over time, it leads to arise of new and different.
Which variable increases the likelihood of allopatric speciation taking place more quickly?
Likewise, the number of species will decrease when extinction rates begin to overtake speciation rates. Longer distance between divided groups. Under some conditions, selection occurs quickly or radically. An increased mutation rate results in a no effect on the rate of speciation b decreases the rate of speciation c increases the rate of speciation Consider a species of snails that had been living with the same basic form for many thousands of years. Likewise, the number of species will decrease when extinction rates begin to overtake speciation rates.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
It refers to the evolution of new species from the surviving ancestral species in which both the species continue to live in the same geographical region. Which increases the rate of speciation? D) the rate increases as negative selective pressures decrease in both subsets.
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Consider a species of snails that had been living with the same basic form for many thousands of years. Equivalent numbers of individuals in each population. When the rate of speciation is higher than the rate of extinction, then the number of languages is increasing and when the opposite is true, then the number of languages is decreasing.
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Longer distance between divided groups. Such speciation could eventually happen via hybridization of existing languages. Rate of speciation increases due to reproductive isolation, which prevents mating between members of different species to accumulate genetic differences in the population.
 Source: methodsblog.com
Source: methodsblog.com
Predictions are supported by global datasets from planktonic foraminifera for rates of dna evolution and speciation spanning 30 million years. C) the rate increases as the extent of geographic barriers separating the two subsets increases. Predictions are supported by global datasets from planktonic foraminifera for rates of dna evolution and speciation spanning 30 million years.
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Such speciation could eventually happen via hybridization of existing languages. As predicted by the model, rates of speciation increase toward the tropics even after controlling for the greater ocean coverage at tropical latitudes. Lower rate of mutation b.
 Source: bio.libretexts.org
Source: bio.libretexts.org
Theory predicts that, under warmer temperatures, fish grow to a smaller size, undergo a reduction in dispersal ability and increase speciation rates. Predictions are supported by global datasets from planktonic foraminifera for rates of dna evolution and speciation spanning 30 million years. Over time, it leads to arise of new and different.
 Source:
Source:
Equivalent numbers of individuals in each population. C) the rate increases as the extent of geographic barriers separating the two subsets increases. Which variable increases the likelihood of allopatric speciation taking place more quickly?
 Source:
Source:
A low gene flow would increase speciation. Colonization from the mainland ( m) and in situ speciation ( g) increase the number of species, while extinction ( d) decreases the number of species. A low gene flow would increase speciation.
 Source: numerade.com
Source: numerade.com
D) the rate increases as negative selective pressures decrease in both subsets. The evolutionary rates of speciation and extinction, their difference being diversification rate, shape current patterns of diversity across the tree of life. An increased mutation rate results in a no effect on the rate of speciation b decreases the rate of speciation c increases the rate of speciation
 Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Lower rate of mutation b. Theory predicts that, under warmer temperatures, fish grow to a smaller size, undergo a reduction in dispersal ability and increase speciation rates. Population bottlenecks reproductive isolation niche availability speciation caused by change in the course of a river is an example pf divergent speciation?
 Source: royalsocietypublishing.org
Source: royalsocietypublishing.org
B) the rate increases as the rate of genetic change increases in both subsets. Theory predicts that, under warmer temperatures, fish grow to a smaller size, undergo a reduction in dispersal ability and increase speciation rates. Factors affecting speciation there are several factors that lead to speciation.
 Source: pnas.org
Source: pnas.org
Rate of speciation increases due to reproductive isolation, which prevents mating between members of different species to accumulate genetic differences in the population. Colonization from the mainland ( m) and in situ speciation ( g) increase the number of species, while extinction ( d) decreases the number of species. Which variable increases the likelihood of allopatric speciation taking place more quickly?
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
B) the rate increases as the rate of genetic change increases in both subsets. The diversification rate hypothesis holds that tropical regions diversify faster due to higher rates of speciation (caused by increased opportunities for the evolution of reproductive isolation, or faster molecular evolution, or the increased importance of biotic interactions), or due to lower extinction rates. Lower rate of mutation b.
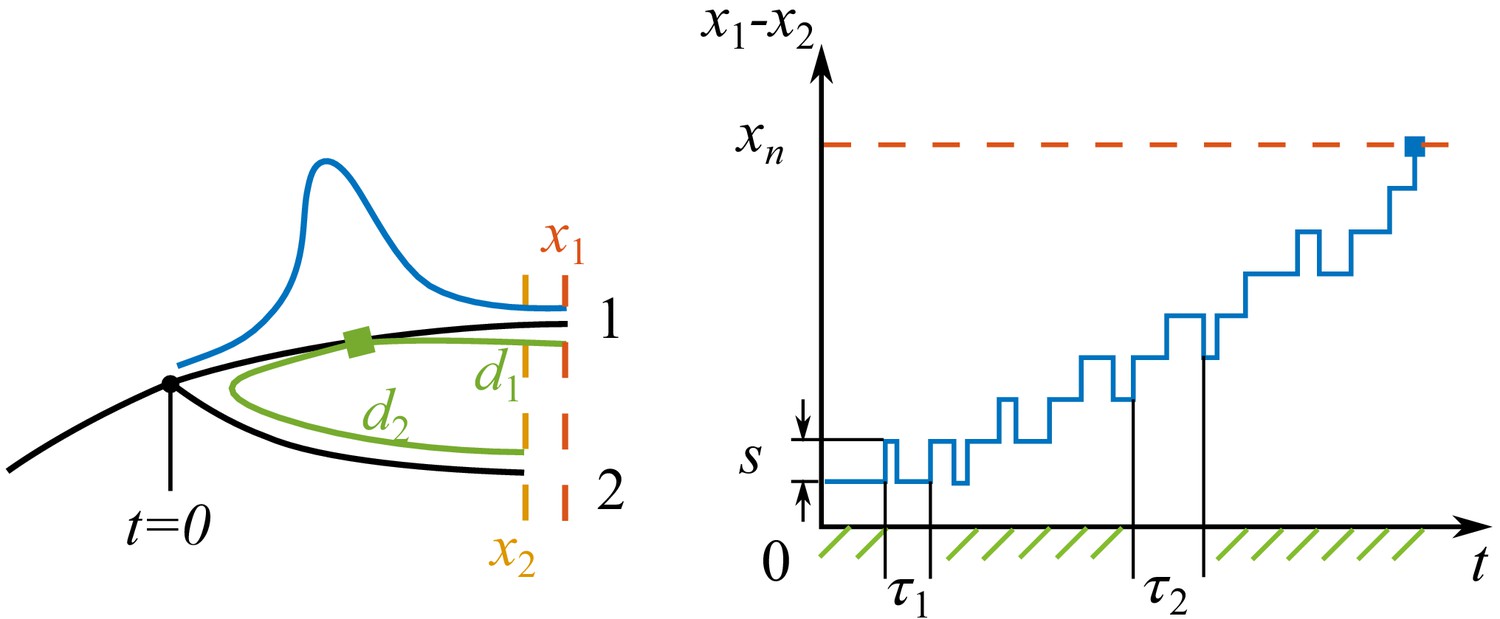 Source: elifesciences.org
Source: elifesciences.org
Lower rate of mutation b. A) the rate increases as the distance separating the two subsets increases. Population bottlenecks reproductive isolation niche availability speciation caused by change in the course of a river is an example pf divergent speciation?
 Source: royalsocietypublishing.org
Source: royalsocietypublishing.org
Colonization from the mainland ( m) and in situ speciation ( g) increase the number of species, while extinction ( d) decreases the number of species. As predicted by the model, rates of speciation increase toward the tropics even after controlling for the greater ocean coverage at tropical latitudes. Several evolutionary theories predict that rates of morphological change should be positively associated with the rate at which new species arise.
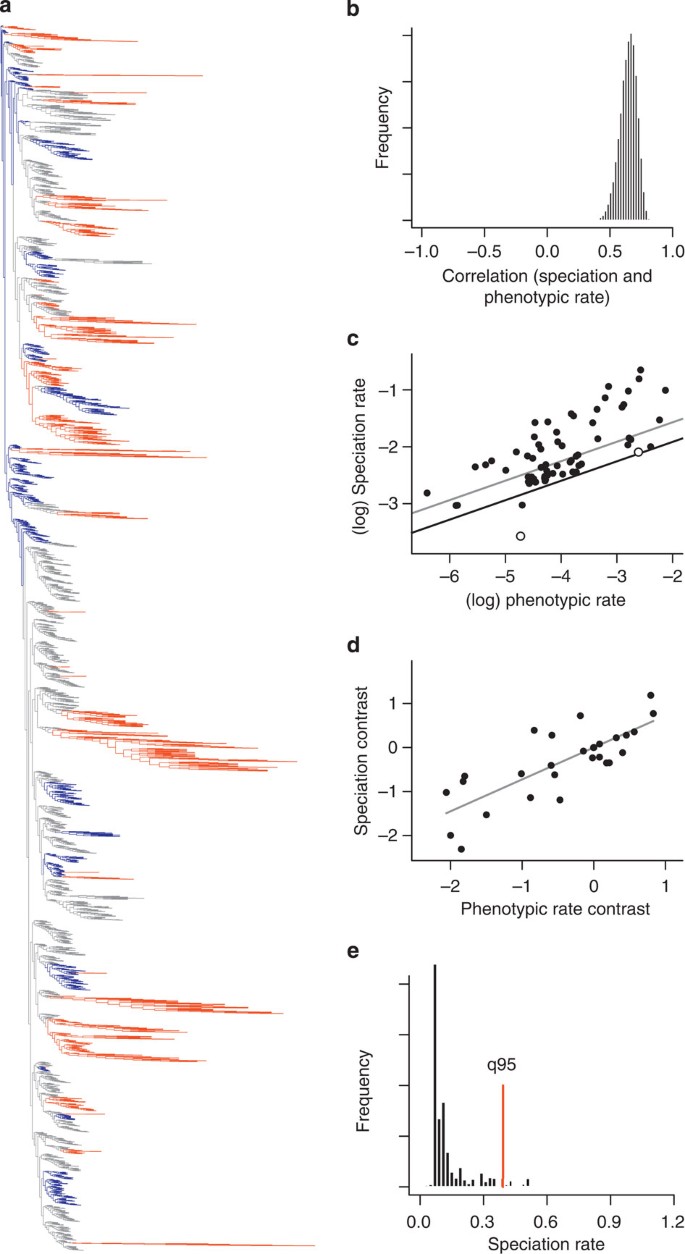 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
It refers to the evolution of new species from the surviving ancestral species in which both the species continue to live in the same geographical region. As predicted by the model, rates of speciation increase toward the tropics even after controlling for the greater ocean coverage at tropical latitudes. Factors affecting speciation there are several factors that lead to speciation.
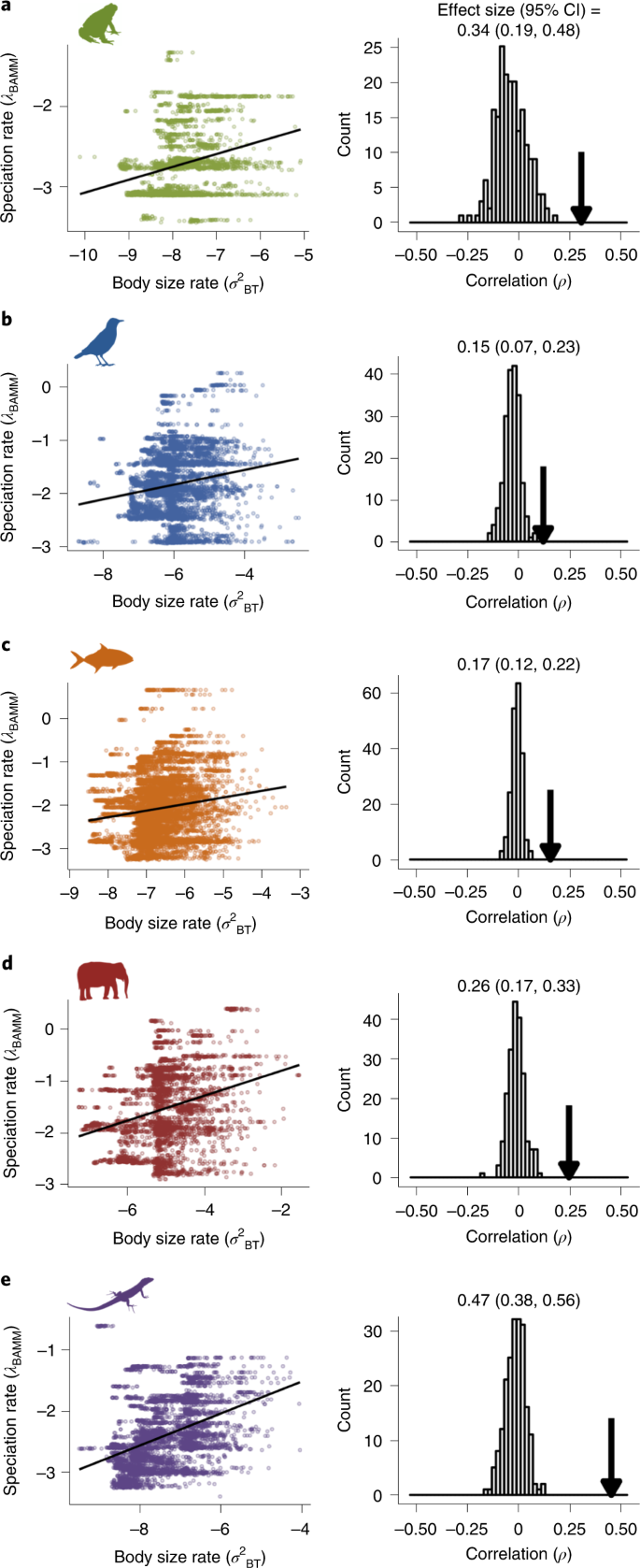 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
A low gene flow would increase speciation. Biology concepts of biology which variable increases the likelihood of allopatric speciation taking place more quickly? The solid blue line and blue region represent the mean and 95% credibility interval (ci) over 100 trees for the estimated speciation rate main effect of trait a, which increases speciation rates (true value is 0·1, indicated by the grey dotted line).
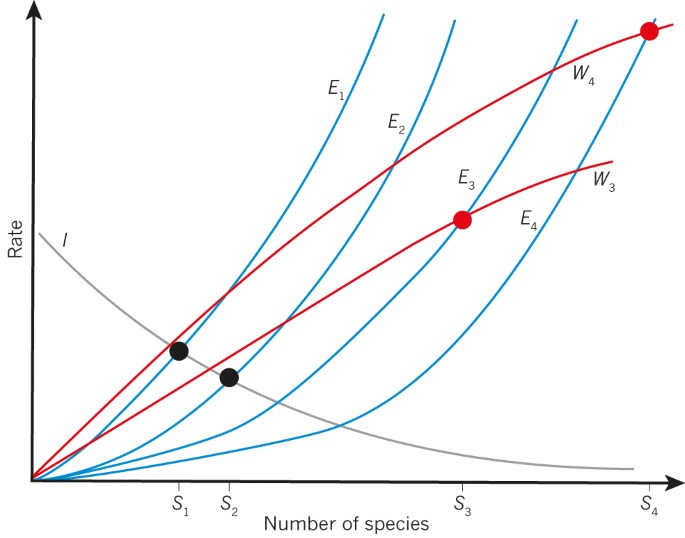 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Sympatric speciation, meaning speciation in the “same homeland,” involves speciation occurring within a parent species while remaining in one location. However, recent phylogenetic studies have found. Under some conditions, selection occurs quickly or radically.
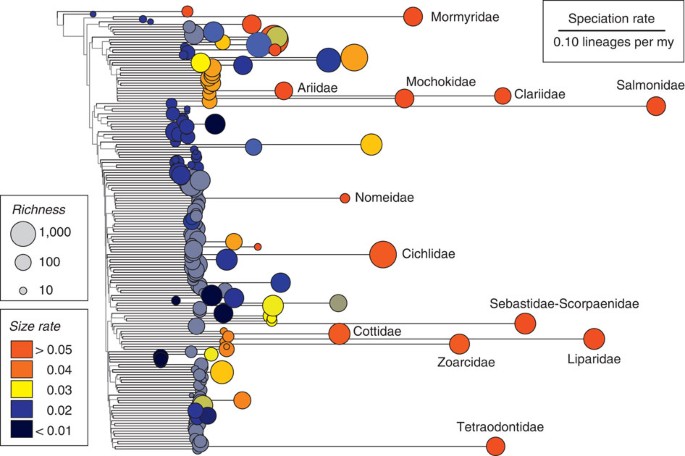 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Equivalent numbers of individuals in each population. Likewise, the number of species will decrease when extinction rates begin to overtake speciation rates. Lower rate of mutation b.
 Source: besjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: besjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
However, recent phylogenetic studies have found. Predictions are supported by global datasets from planktonic foraminifera for rates of dna evolution and speciation spanning 30 million years. An increased mutation rate results in a no effect on the rate of speciation b decreases the rate of speciation c increases the rate of speciation
Also Read :





