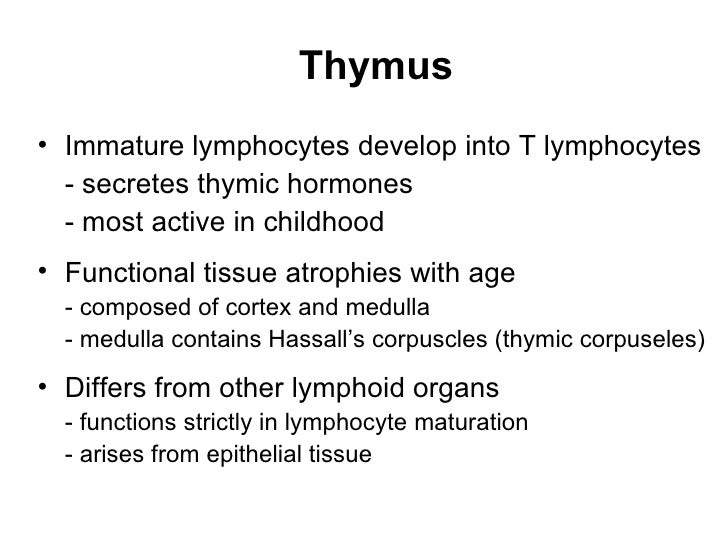
Secretes hormones that stimulate development off other lymphatic organs and activity of t lymphocytes; Plays a role in the endocrine, lymphatic, and immune systems;
Which Cells Become Immunocompetent Due To Thymic Hormones. While thymic tb is an infrequent manifestation of the disease, several pieces of experimental and clinical evidence point out that the thymus can be Thyroxin in response to a tsh, a hormone released by the 40 rows which cells become immunocompetent due to thymic hormones: T helper cells (th) have a wide range of effector functions and can differentiate into many different subtypes, such as th1, th2, th17, tfh cells and regulatory t cells.
 The Immune System: Innate And Adaptive Body Defenses - Ppt Download From slideplayer.com
The Immune System: Innate And Adaptive Body Defenses - Ppt Download From slideplayer.com
Related Post The Immune System: Innate And Adaptive Body Defenses - Ppt Download :
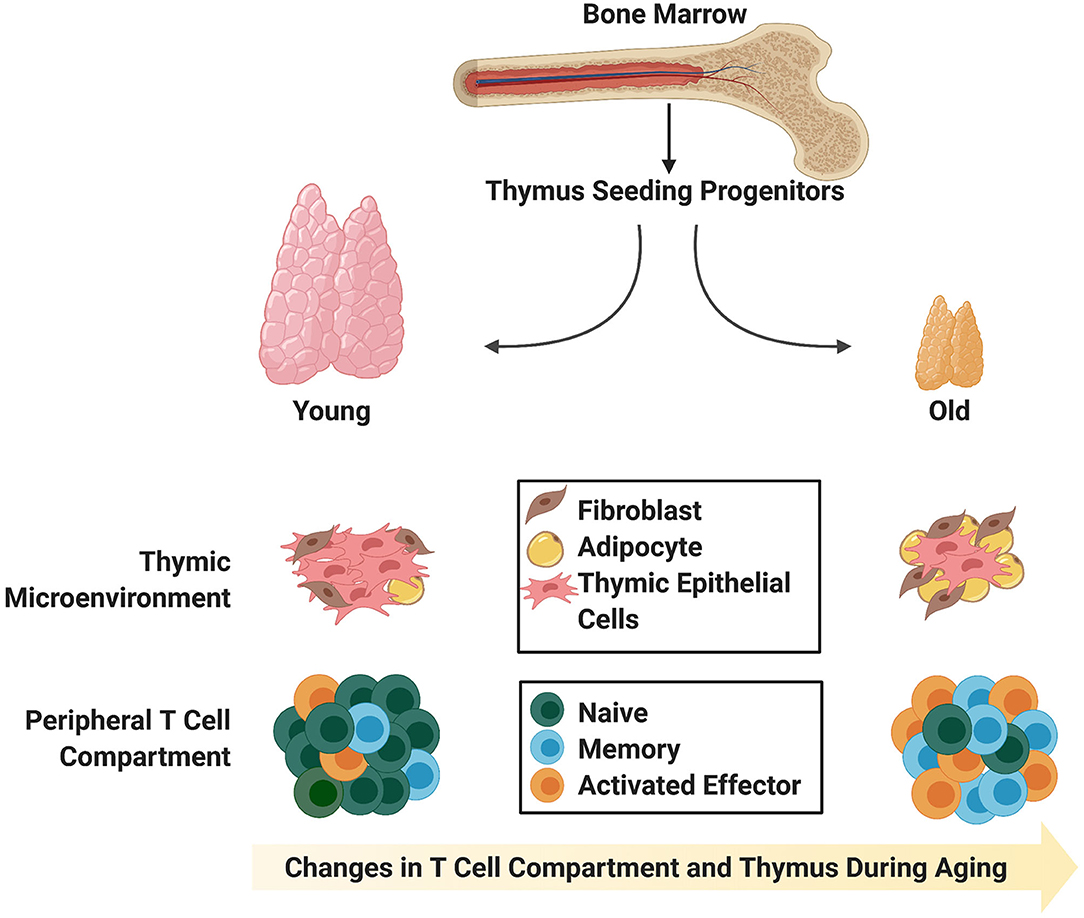
T lymphocyte differentiation, maturation, and proliferation occur as developing cells traffic through the thymic cortex and medulla in response to a 40 rows which cells become immunocompetent due to thymic hormones: D) t cells are the only form of lymphocyte found in lymphoid tissue. Sex hormones such as estrogen and testosterone enhance involution, and the hormonal changes in pregnant women cause a temporary thymic involution that reverses itself, when the size of the thymus and its hormone levels return to normal, usually after lactation ceases.
Small gland resting atop kidneyy;
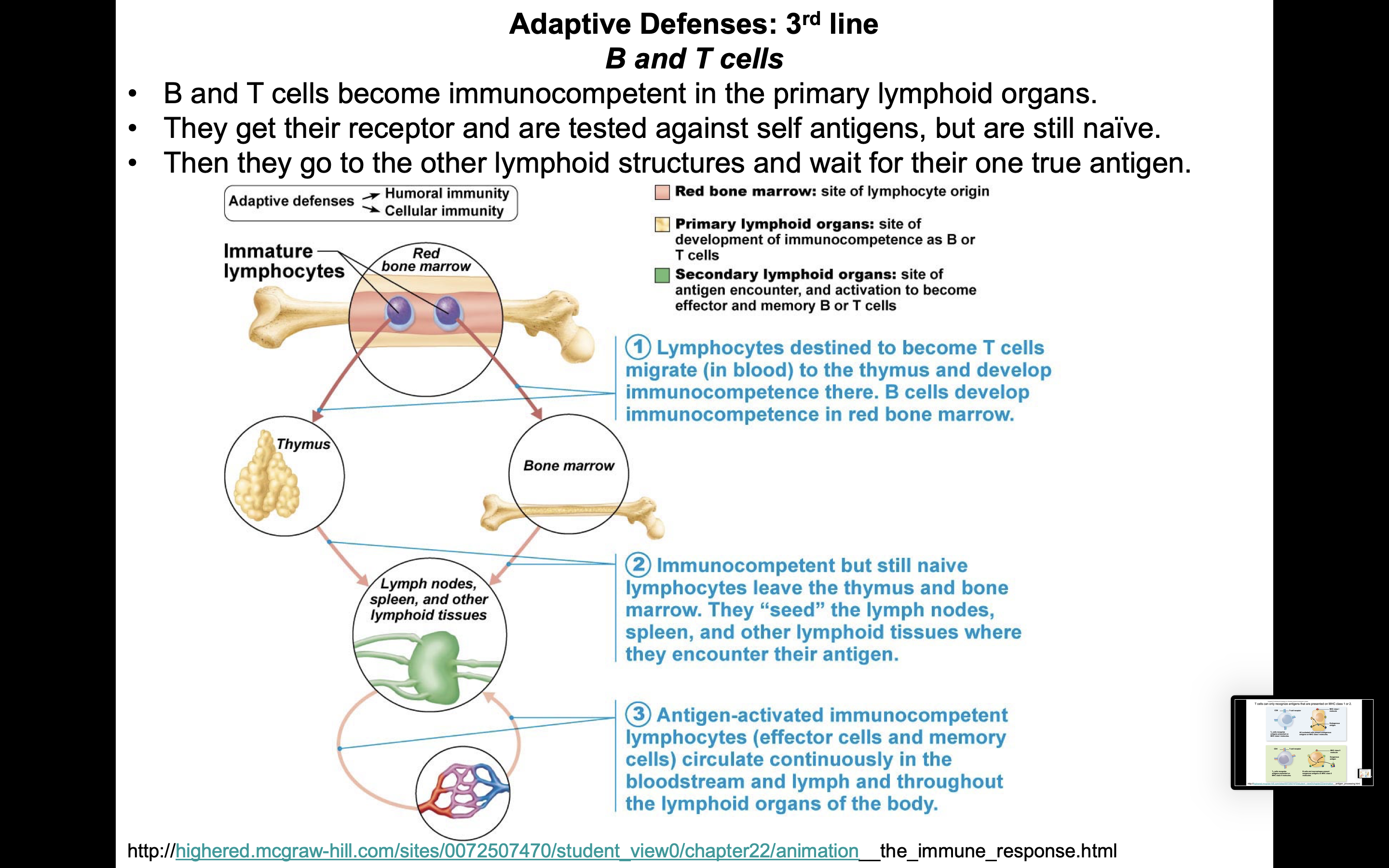
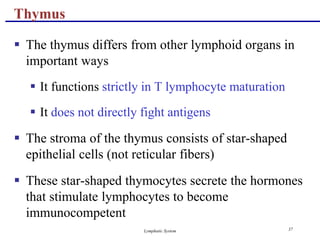
Population of developing t cells (thymocytes) lies between processes of these cells, and constitute up to 90% of the weight of the thymus. One that is being challenged in the secondary lymphoid tissues/organs Secretes hormones that stimulate development off other lymphatic organs and activity of t lymphocytes; Cells settling in the thymus proliferate under thymic control. T lymphocyte differentiation, maturation, and proliferation occur as developing cells traffic through the thymic cortex and medulla in response to a Cytoplasmic extensions are connected to other cells by desmosomes.
 Source:
Source:
Thymus a bilobed organ that secretes hormones (thymosin and thymopoietin) that cause t lymphocytes (t cells) to become immunocompetent (functional) size of the thymus varies with age: T cells are one of two primary types of lymphocytes — b cells being the second type—that determine the specificity of immune response to antigens (foreign substances) in the body. T helper cells (th) have a wide range of effector functions and can differentiate into many different subtypes, such as th1, th2, th17, tfh cells and regulatory t cells.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
The thymic epithelial cells have a stellate shape (fig. T cells are one of two primary types of lymphocytes — b cells being the second type—that determine the specificity of immune response to antigens (foreign substances) in the body. 40 rows which cells become immunocompetent due to thymic hormones:
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Naive t or b cell: Some of these cells leave the thymus and migrate to the spleen and lynph nodes. Thymus a bilobed organ that secretes hormones (thymosin and thymopoietin) that cause t lymphocytes (t cells) to become immunocompetent (functional) size of the thymus varies with age:
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
These cells contain a large, pale, oval However, cells derived from the thymus do participate in the immune response to some Population of developing t cells (thymocytes) lies between processes of these cells, and constitute up to 90% of the weight of the thymus.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
40 rows which cells become immunocompetent due to thymic hormones: 40 rows which cells become immunocompetent due to thymic hormones: The lymphatic organ(s) where b cells and t cells are born, and where b cells become immunocompetent
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
One that is undergoing immunocompetency processing in the bone marrow or thymus. 40 rows which cells become immunocompetent due to thymic hormones: The size of the thymus increases continuously from birth to death
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
However, cells derived from the thymus do participate in the immune response to some Nevertheless, it remains unclear to what degree sex steroids’ impact on thymic cellularity may reflect the influence of hormones on thymic epithelial cells. Thyroxin in response to a tsh, a hormone released by the
 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
The lymphatic organ(s) where b cells and t cells are born, and where b cells become immunocompetent 40 rows which cells become immunocompetent due to thymic hormones: One that is being challenged in the secondary lymphoid tissues/organs
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Thymus a bilobed organ that secretes hormones (thymosin and thymopoietin) that cause t lymphocytes (t cells) to become immunocompetent (functional) size of the thymus varies with age: The thymic epithelial cells have a stellate shape (fig. In infants, it is found in the inferior neck and extends into the mediastinum where it partially overlies the heart it increases in size and is most active during
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
C) t cells are the precursors of b cells. A) the two main types are t cells and macrophages. 40 rows which cells become immunocompetent due to thymic hormones:
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Population of developing t cells (thymocytes) lies between processes of these cells, and constitute up to 90% of the weight of the thymus. Small gland resting atop kidneyy; One that is undergoing immunocompetency processing in the bone marrow or thymus.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
Some of these cells leave the thymus and migrate to the spleen and lynph nodes. Cytoplasmic extensions are connected to other cells by desmosomes. Thymus a bilobed organ that secretes hormones (thymosin and thymopoietin) that cause t lymphocytes (t cells) to become immunocompetent (functional) size of the thymus varies with age:
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
T cells are one of two primary types of lymphocytes — b cells being the second type—that determine the specificity of immune response to antigens (foreign substances) in the body. The size of the thymus increases continuously from birth to death The b cells have the ability to transform into plasmocytes and are responsible for producing antibodies (abs).
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
The b cells have the ability to transform into plasmocytes and are responsible for producing antibodies (abs). T lymphocyte differentiation, maturation, and proliferation occur as developing cells traffic through the thymic cortex and medulla in response to a Small gland resting atop kidneyy;
 Source: studylib.net
Source: studylib.net
C) t cells are the precursors of b cells. Thyroxin in response to a tsh, a hormone released by the While thymic tb is an infrequent manifestation of the disease, several pieces of experimental and clinical evidence point out that the thymus can be
 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
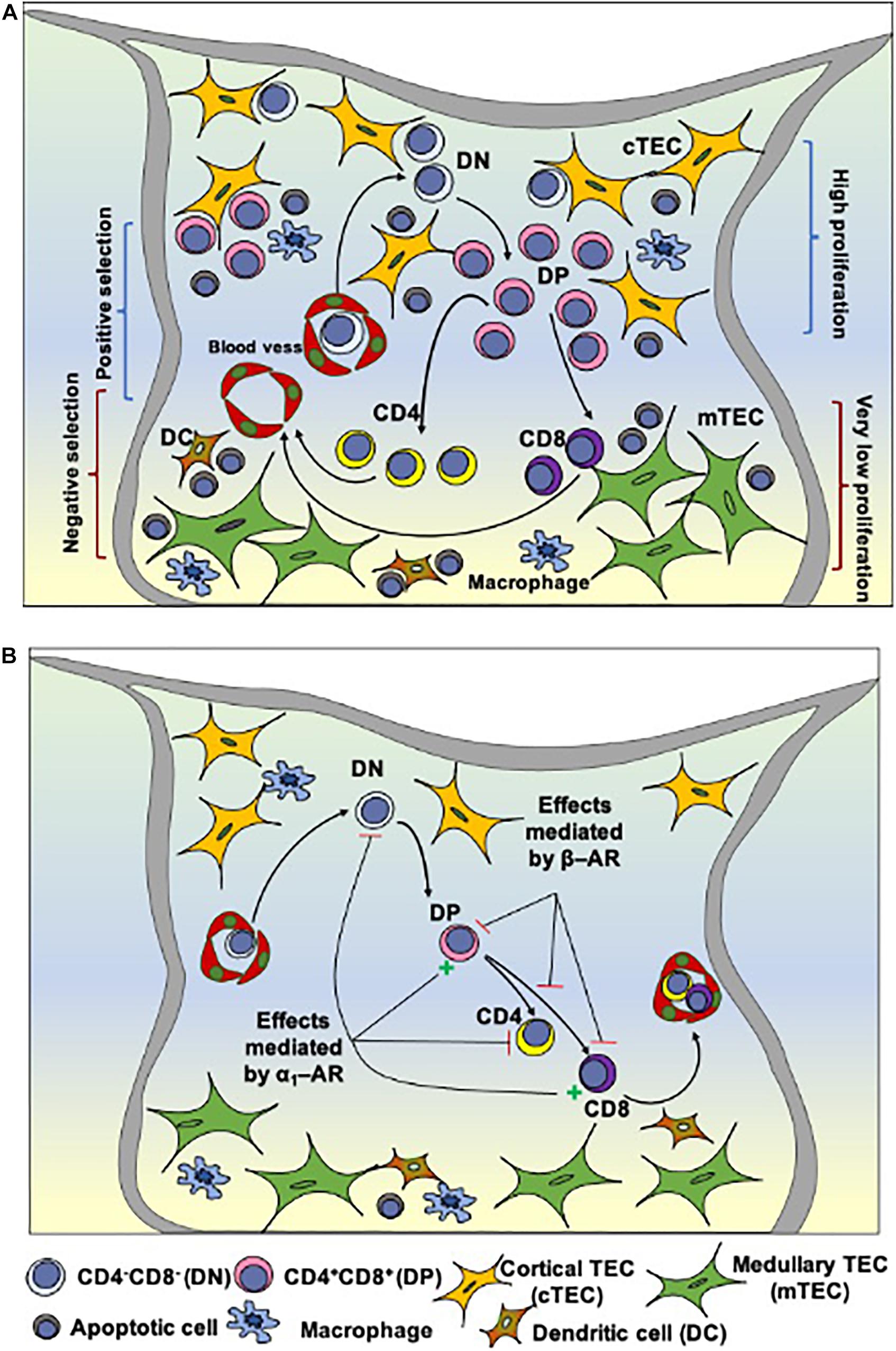
Site of maturation of t cells which are important in immune defense; It is also known that thymic involution can be altered by hormone levels. Males, females and males castrated at four weeks of age.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Sex hormones such as estrogen and testosterone enhance involution, and the hormonal changes in pregnant women cause a temporary thymic involution that reverses itself, when the size of the thymus and its hormone levels return to normal, usually after lactation ceases. Some function as antigen receptors, molecules capable of recognizing specific antigens. Males, females and males castrated at four weeks of age.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Sex hormones such as estrogen and testosterone enhance involution, and the hormonal changes in pregnant women cause a temporary thymic involution that reverses itself, when the size of the thymus and its hormone levels return to normal, usually after lactation ceases. Nevertheless, it remains unclear to what degree sex steroids’ impact on thymic cellularity may reflect the influence of hormones on thymic epithelial cells. T helper cells (th) have a wide range of effector functions and can differentiate into many different subtypes, such as th1, th2, th17, tfh cells and regulatory t cells.
 Source:
Source:
D) t cells are the only form of lymphocyte found in lymphoid tissue. (thymosin, thymulin and thymopoietin ) hormones are produced by reticular epithelial cells in the cortex. These are expressed on the surface of apcs.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Thymus a bilobed organ that secretes hormones (thymosin and thymopoietin) that cause t lymphocytes (t cells) to become immunocompetent (functional) size of the thymus varies with age: Small gland resting atop kidneyy; The thymus initially increases in size and then decreases in size from adolescence through old age c.
Also Read :





