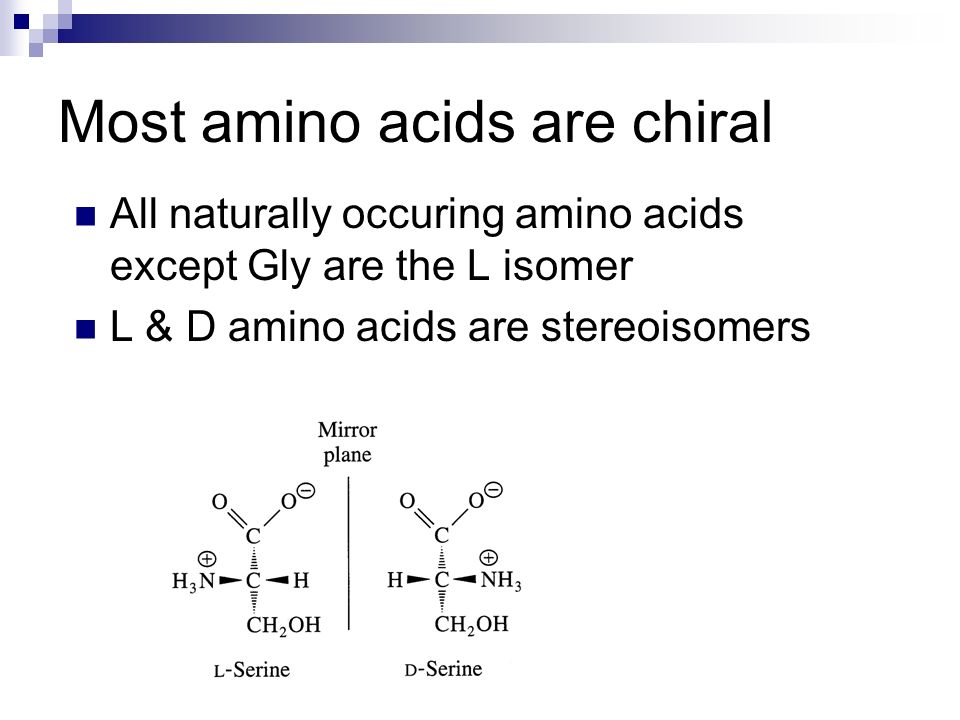
Only glycine, which contains hydrogen as its r‐group does not have chirality. Objects are chiral when they cannot be superposed on their mirror images.
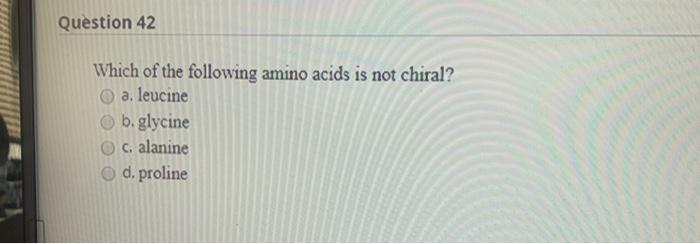
Which Amino Acid Is Not Chiral. Which of the following amino acids is not chiral? The simplest amino acid is glycine, where the r is an h nh2 ch2 co2h some amino acids have an extra carboxylic acid or an amine group on the r group. Let�s look at chirality in proteins and dna. As noted above, since r is just a hydrogen, glycine is the only natural amino acid that is not chiral at the alpha carbon.
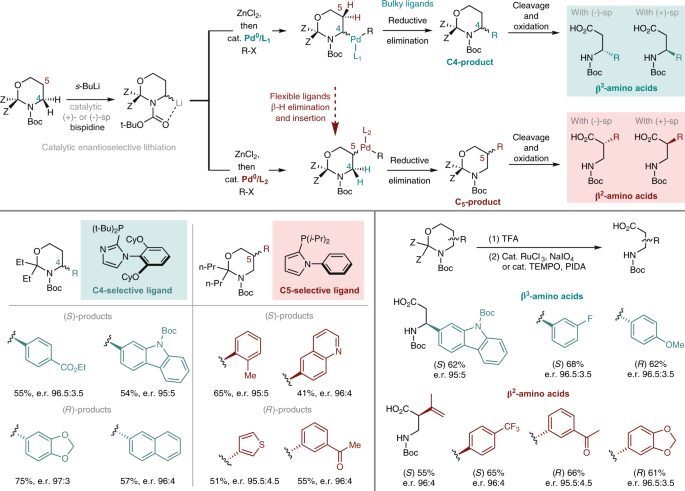 Facile Access To Chiral Non-Natural Amino Acids | Nature Catalysis From nature.com
Facile Access To Chiral Non-Natural Amino Acids | Nature Catalysis From nature.com
Related Post Facile Access To Chiral Non-Natural Amino Acids | Nature Catalysis :
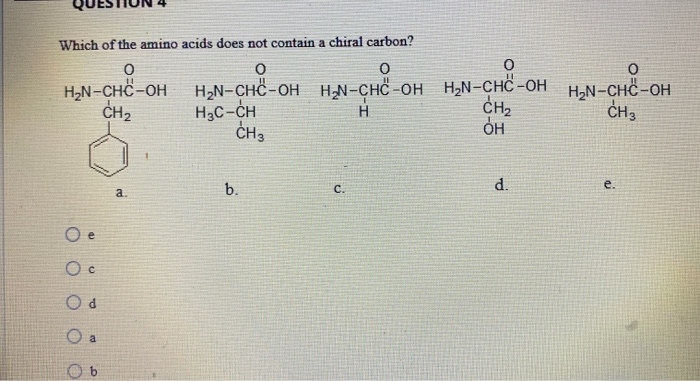
Glycine is not chiral because it has 2 hydrogens attached to its central alpha carbon. The reason cysteine is different is that it has a sulfur atom at the second position of the side chain, which has a larger atomic number than that of the groups at the first carbon. A leucine b isoleucine c glycine d alanine e threonine. Stereochemistry of amino acids other terms you may encounter:
The reason cysteine is different is that it has a sulfur atom at the second position of the side chain, which has a larger atomic number than that of the groups at the first carbon.
So the compound can exist as a pair of nonsuperimposable mirror images. So the compound can exist as a pair of nonsuperimposable mirror images. Which amino acid does not have a chiral alpha carbon? Nature uses almost exclusively l. Objects are chiral when they cannot be superposed on their mirror images. Chiral recognition and quantification of amino acid (aa) enantiomers are of great significance in many fields such as biology and biomedicine.
Polar and has sulfur atom. These are classed as acidic. Regarding the (s) and (r) nomenclature, nearly all amino acids in proteins are (s) at the alpha carbon.
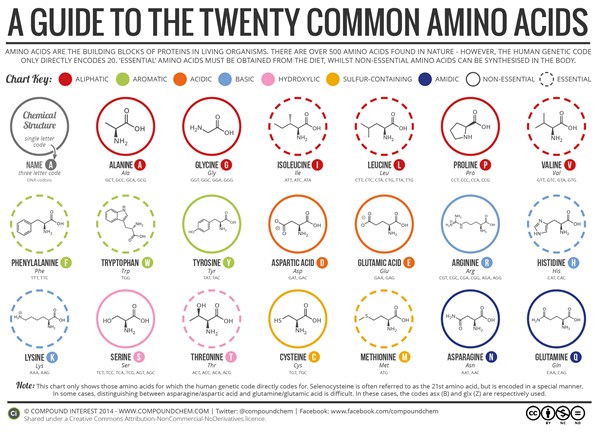 Source: alevelchemistry.co.uk
Source: alevelchemistry.co.uk
L amino acids are a subcategory of amino acids. Regarding the (s) and (r) nomenclature, nearly all amino acids in proteins are (s) at the alpha carbon. Which amino acid does not have a chiral alpha carbon?
 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
The general formula for an amino acid is. The designed fluorescent probes consist of three components: Chiral recognition and quantification of amino acid (aa) enantiomers are of great significance in many fields such as biology and biomedicine.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
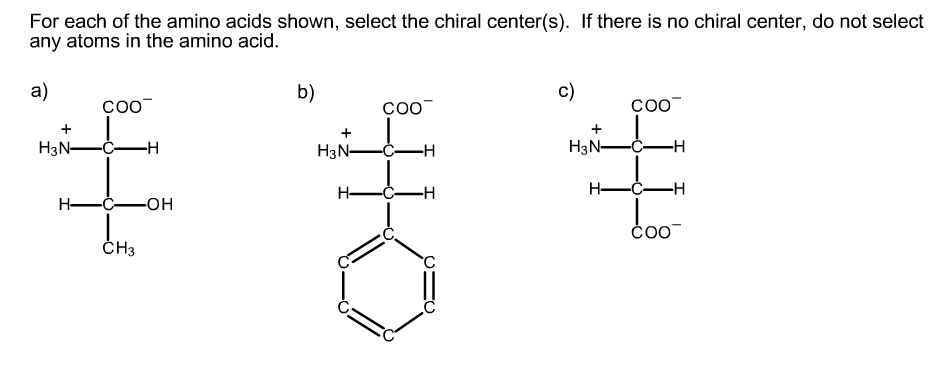
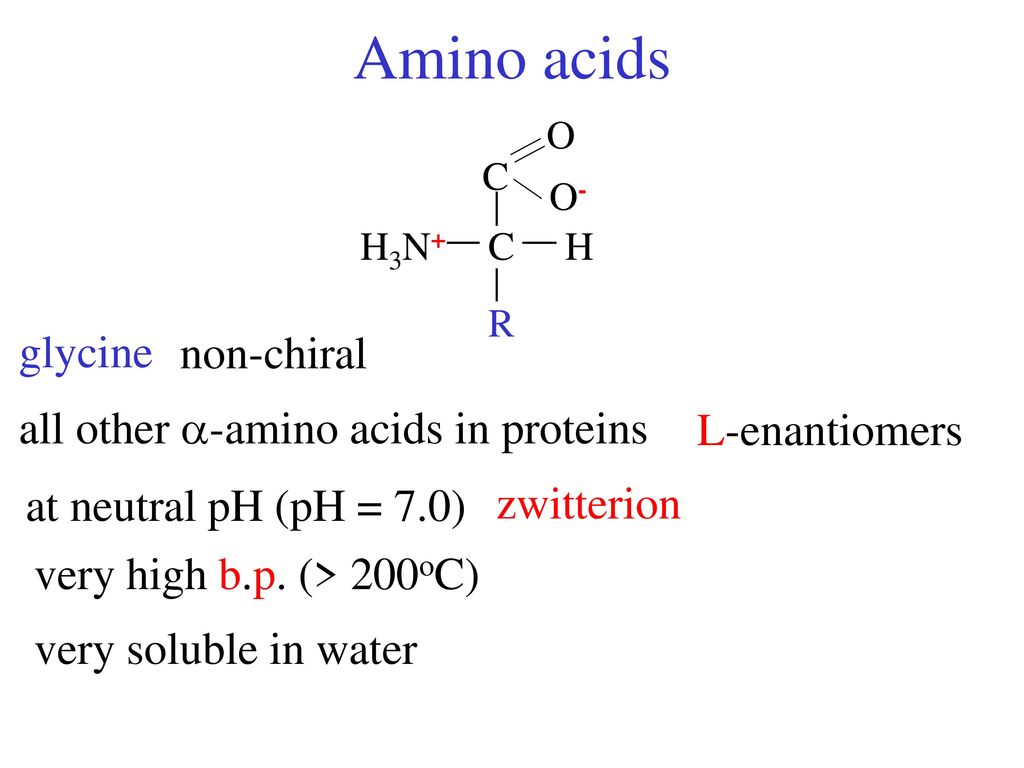
6.2.2 amino acids and chirality general structure of an α amino acid nh2 ch co2h r the r group can be a variety of different things depending on what amino acid it is. The simplest amino acid glycine (gly or g), has h as an r group, meaning that it has only 3 different groups (carboxylate, amine, but 2 hydrogens) there are no 4 different groups attached to the alpha carbon and therefore glycine is not chiral and cannot be optically active (possess optical chirality). Experts are tested by chegg as specialists in their subject area.
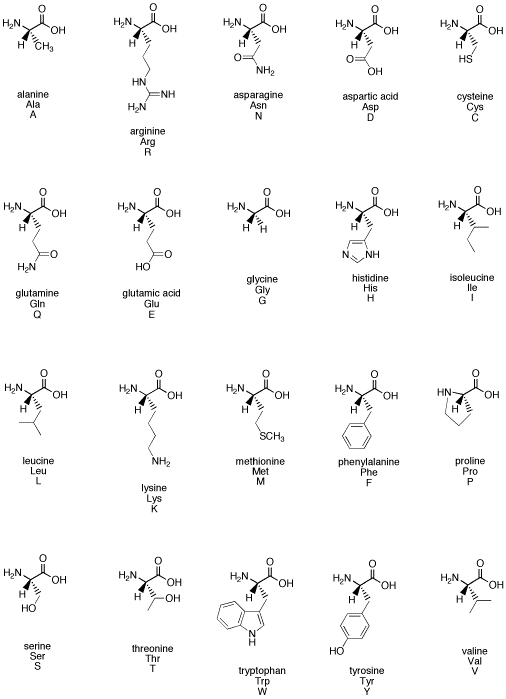 Source: employees.csbsju.edu
Source: employees.csbsju.edu
As noted above, since r is just a hydrogen, glycine is the only natural amino acid that is not chiral at the alpha carbon. Objects are chiral when they cannot be superposed on their mirror images. Glycine is not chiral because it has 2 hydrogens attached to its central alpha carbon.
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Racemic mixtures (or solutions) of molecules do not exhibit optical activity because there are So the compound can exist as a pair of nonsuperimposable mirror images. Although in some classification schemes, glycine is considered nonpolar, hydrogen is so small that it contributes negligibly to nonpolar surface area.

In the past they were often called imino acids, a misnomer because they do not contain an imine grouping hn=c. Chirality is a property that only a few scientists would even recognize as a problem. All amino acids except glycine are chiral because they all contain at least one chiral centre.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
The central carbon has four different groups attached. The central carbon has four different groups attached. And, finally, the possibility that chiral selection might have occurred on solid surfaces is mentioned.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Glycine is not chiral because it has 2 hydrogens attached to its central alpha carbon. The central carbon has four different groups attached. Which amino acid does not have a chiral alpha carbon?
 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
With the exception of glycine, which is not chiral, these amino acids have an s configuration and are designated as l using the fischer configurational system. Which amino acid is not chiral? These are classed as acidic.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
A carboxyl group, an amino group, an r group, and a hydrogen atom (in case of glycine, the r group is another hydrogen atom). Chiral recognition and quantification of amino acid (aa) enantiomers are of great significance in many fields such as biology and biomedicine. As noted above, since r is just a hydrogen, glycine is the only natural amino acid that is not chiral at the alpha carbon.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
So the compound can exist as a pair of nonsuperimposable mirror images. Nature uses almost exclusively l. Objects are chiral when they cannot be superposed on their mirror images.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The simplest amino acid is glycine, where the r is an h nh2 ch2 co2h some amino acids have an extra carboxylic acid or an amine group on the r group. Which of the following amino acids is not chiral? As noted above, since r is just a hydrogen, glycine is the only natural amino acid that is not chiral at the alpha carbon.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
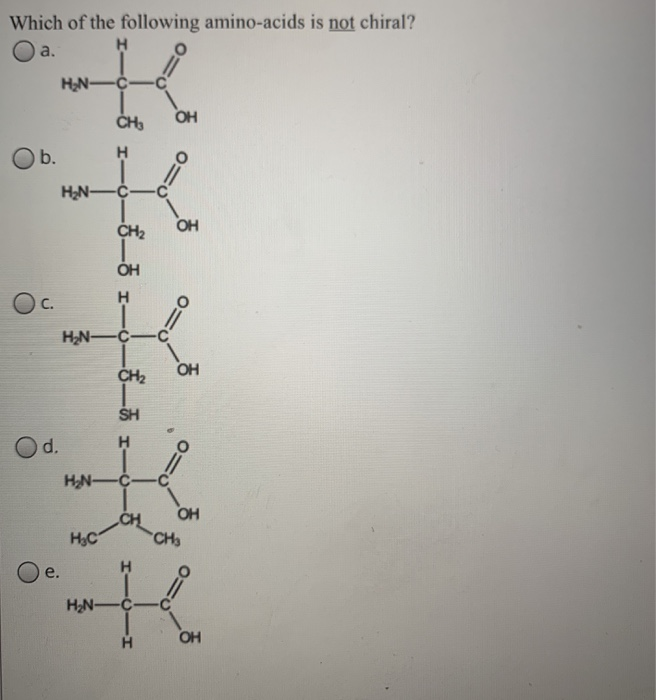
A leucine b isoleucine c glycine d alanine e threonine. Which amino acid does not have a chiral alpha carbon? These are classed as acidic.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
In general, there are a variety of amino acids that are not chiral (achiral). As noted above, since r is just a hydrogen, glycine is the only natural amino acid that is not chiral at the alpha carbon. The obsolete term remains frequent.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
The reason cysteine is different is that it has a sulfur atom at the second position of the side chain, which has a larger atomic number than that of the groups at the first carbon. So the compound can exist as a pair of nonsuperimposable mirror images. Homochirality is a uniformity of chirality, or handedness.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
As noted above, since r is just a hydrogen, glycine is the only natural amino acid that is not chiral at the alpha carbon. Glycine is not chiral, e.g. A leucine b isoleucine c glycine d alanine e threonine.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
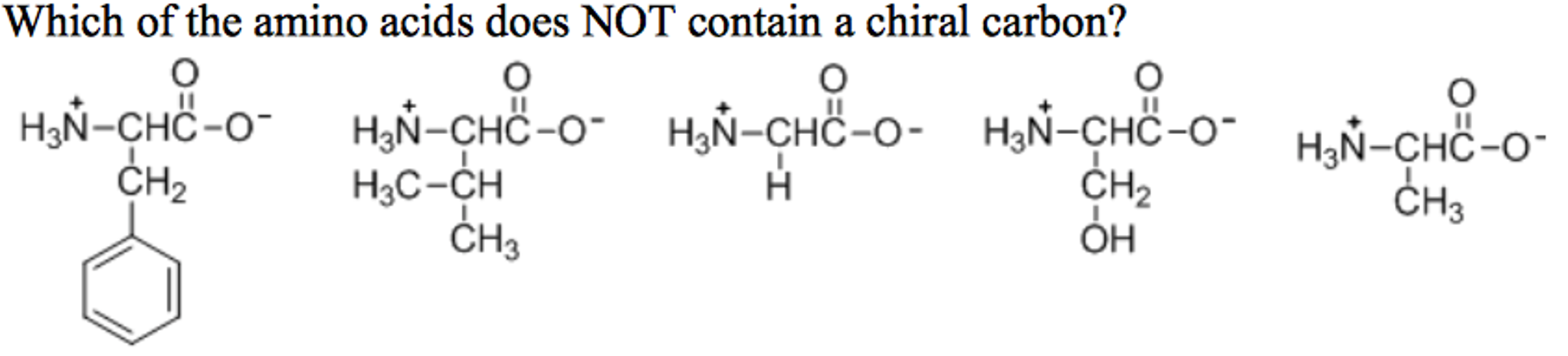
The designed fluorescent probes consist of three components: And, finally, the possibility that chiral selection might have occurred on solid surfaces is mentioned. Experts are tested by chegg as specialists in their subject area.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
The central carbon has four different groups attached. Which amino acid is not chiral? The simplest amino acid glycine (gly or g), has h as an r group, meaning that it has only 3 different groups (carboxylate, amine, but 2 hydrogens) there are no 4 different groups attached to the alpha carbon and therefore glycine is not chiral and cannot be optically active (possess optical chirality).

Specifically, the means by which circularly polarized light could create chiral amino acids, both on earth and in outer space, are detailed. So the compound can exist as a pair of nonsuperimposable mirror images. 100% (1 rating) previous question next question.
Also Read :





