During this process, the dna sequence of a gene is copied into rna. Our immune system recognizes that.
Where Does Rna Polymerase Begin Transcribing A Gene Into Mrna. It has become clear that cotranscriptional splicing is spatially and temporally linked to transcription, and a key player in coordinating transcription with splicing is the rna polymerase itself. ↑ large molecule that accelerate chemical reactions that take place in the body or inside the cell. Rna polymerase iii is also located in the nucleus. This mature mrna is ready for translation.
 Dna To Rna Transcription From hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu
Dna To Rna Transcription From hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu
Related Post Dna To Rna Transcription :
Once a gene is transcribed, the rna polymerase needs to be instructed to dissociate from the dna template and liberate the newly made mrna. The rna transcript carries the information used to encode a protein. This mature mrna is ready for translation. It looks for the aug start codon.
Once a gene is transcribed, the rna polymerase needs to be instructed to dissociate from the dna template and liberate the newly made mrna.
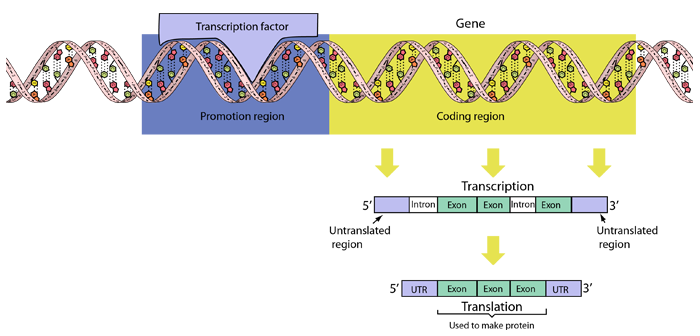
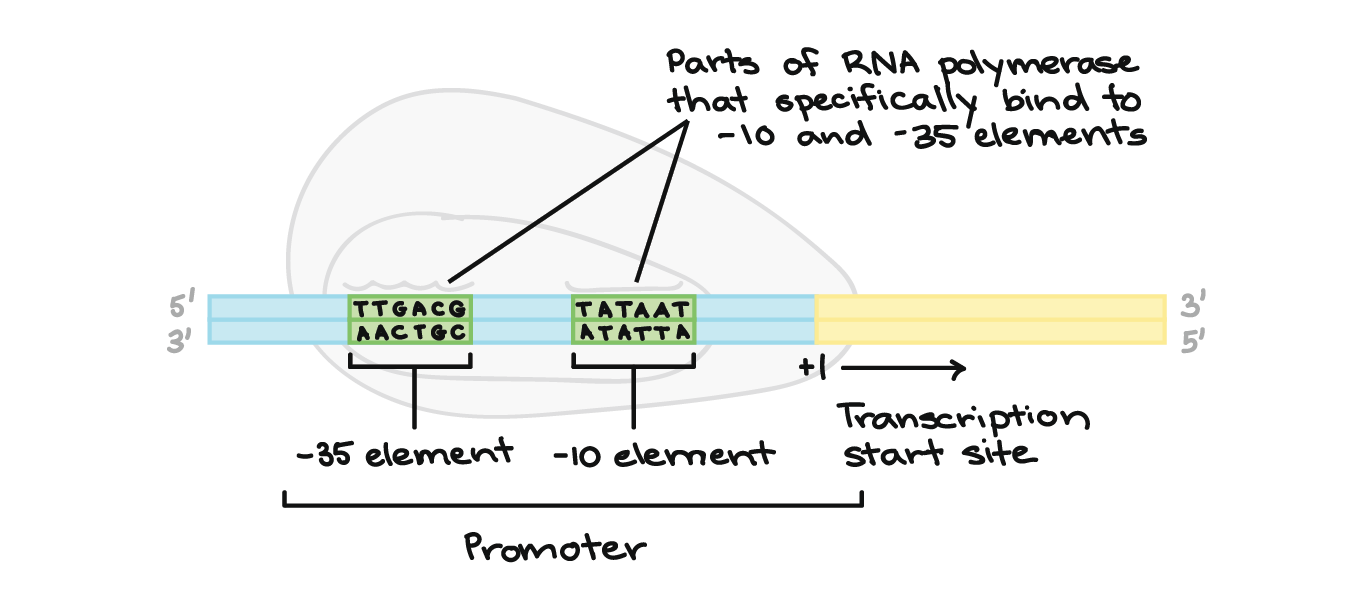
After the protein piece is made, our cells break down the mrna and remove it. After the protein piece is made, our cells break down the mrna and remove it. It starts after a certain nucleotide sequence called a promoter. The main motive of transcription is to make a copy of rna from the dna sequence. During the process of rna splicing, introns are removed and exons joined to form a contiguous coding sequence. A generalized promoter of a gene transcribed by rna polymerase ii is shown.
 Source: technologynetworks.com
Source: technologynetworks.com
Only one strand of dna is copied during the process of transcription known as the template strand and the rna formed is called the mrna. The main motive of transcription is to make a copy of rna from the dna sequence. Because bacterial mrna does not need to be processed and is accessible to ribosomes while it is being made, ribosomes can attach to the free end of a bacterial mrna molecule and start translating it even before the transcription of that rna is complete, following closely behind the rna polymerase as it moves along dna.
This mature mrna is ready for translation. Rna polymerase ii is responsible for transcribing the overwhelming majority of eukaryotic genes. It has become clear that cotranscriptional splicing is spatially and temporally linked to transcription, and a key player in coordinating transcription with splicing is the rna polymerase itself.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
↑ large molecule that accelerate chemical reactions that take place in the body or inside the cell. This process involves capping of the 50 end, This mature mrna is ready for translation.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
Turns out things are a hair more complicated. Turns out things are a hair more complicated. The main motive of transcription is to make a copy of rna from the dna sequence.
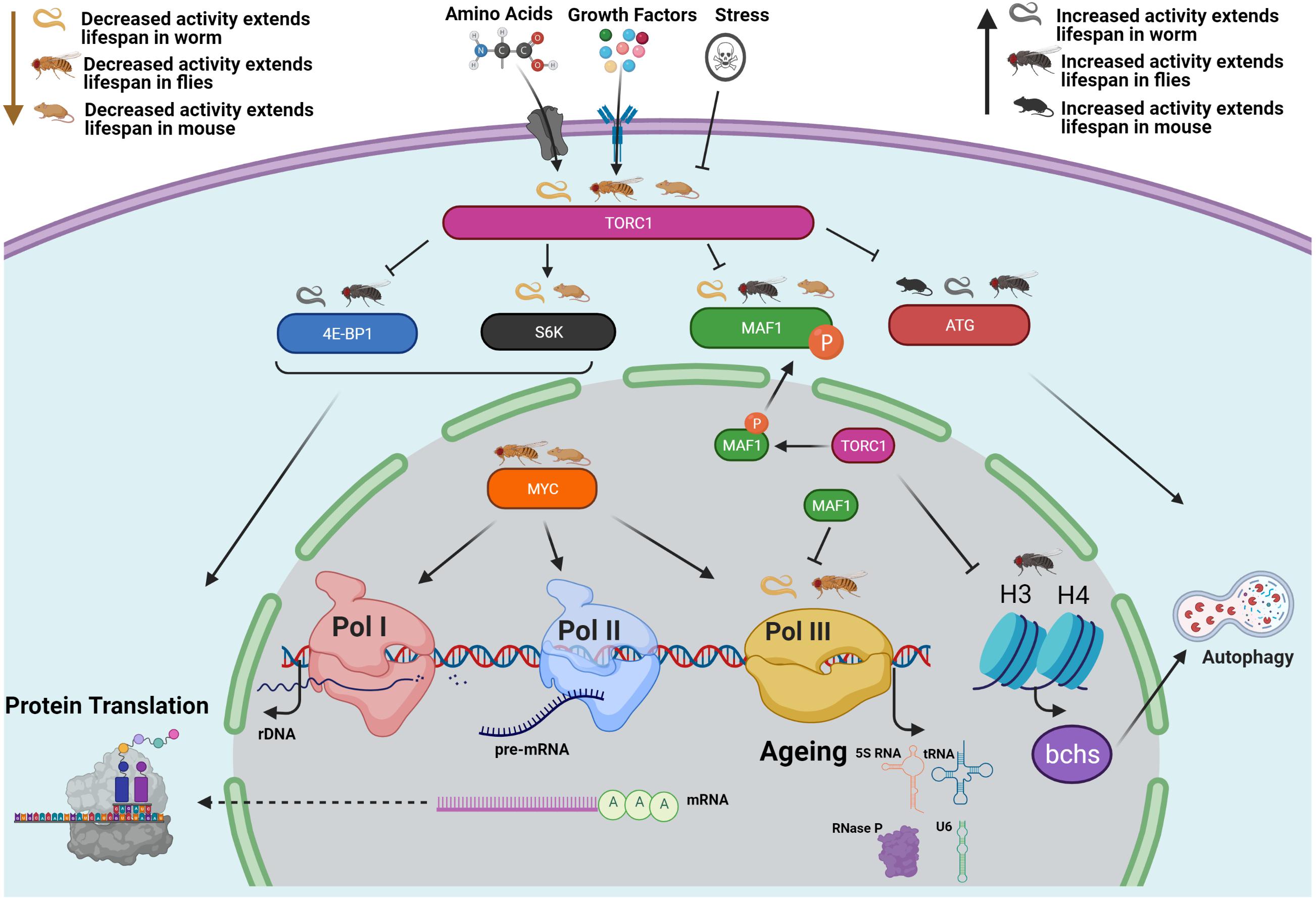 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
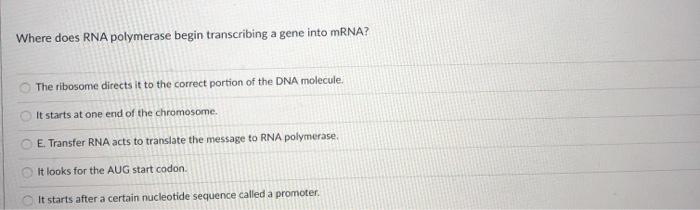
The main motive of transcription is to make a copy of rna from the dna sequence. It starts at one end of the chromosome. Where does rna polymerase begin transcribing a gene into mrna?
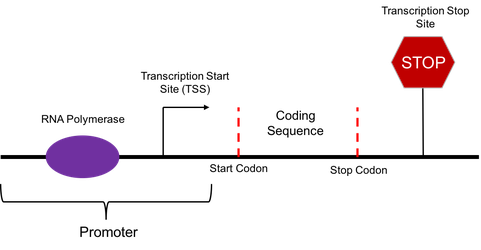 Source: addgene.org
Source: addgene.org
This process involves capping of the 50 end, ↑ a type of rna that is involved in building proteins based on the information stored in the dna. The rna transcript carries the information used to encode a protein.
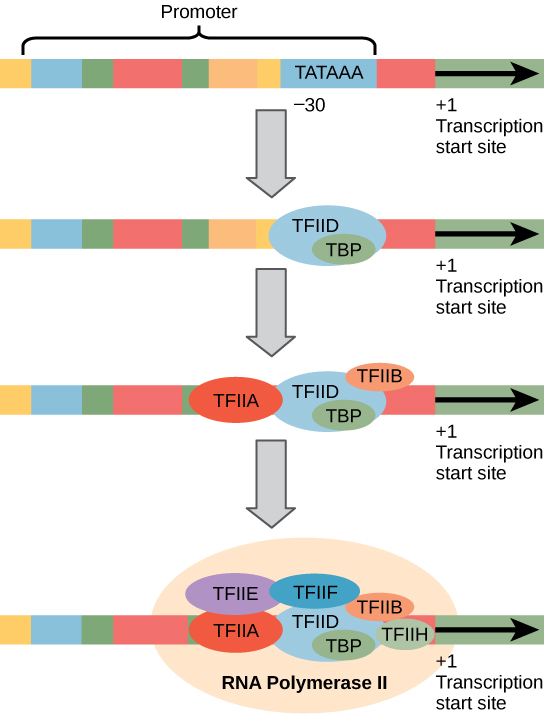 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Transcription is under the control of cell�s metabolic processes which must activate a gene before this process can begin. Once a gene is transcribed, the rna polymerase needs to be instructed to dissociate from the dna template and liberate the newly made mrna. The enzyme that directly controls the process is rna polymerase, which makes a strand of mrna using the single
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
A generalized promoter of a gene transcribed by rna polymerase ii is shown. The paused transcribing complex has two options: Transcription is the process in which a gene�s dna sequence is copied (transcribed) to make an rna molecule.
 Source: hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu
Source: hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu
The enzyme that directly controls the process is rna polymerase, which makes a strand of mrna using the single Because bacterial mrna does not need to be processed and is accessible to ribosomes while it is being made, ribosomes can attach to the free end of a bacterial mrna molecule and start translating it even before the transcription of that rna is complete, following closely behind the rna polymerase as it moves along dna. It starts after a certain nucleotide sequence called a promoter.
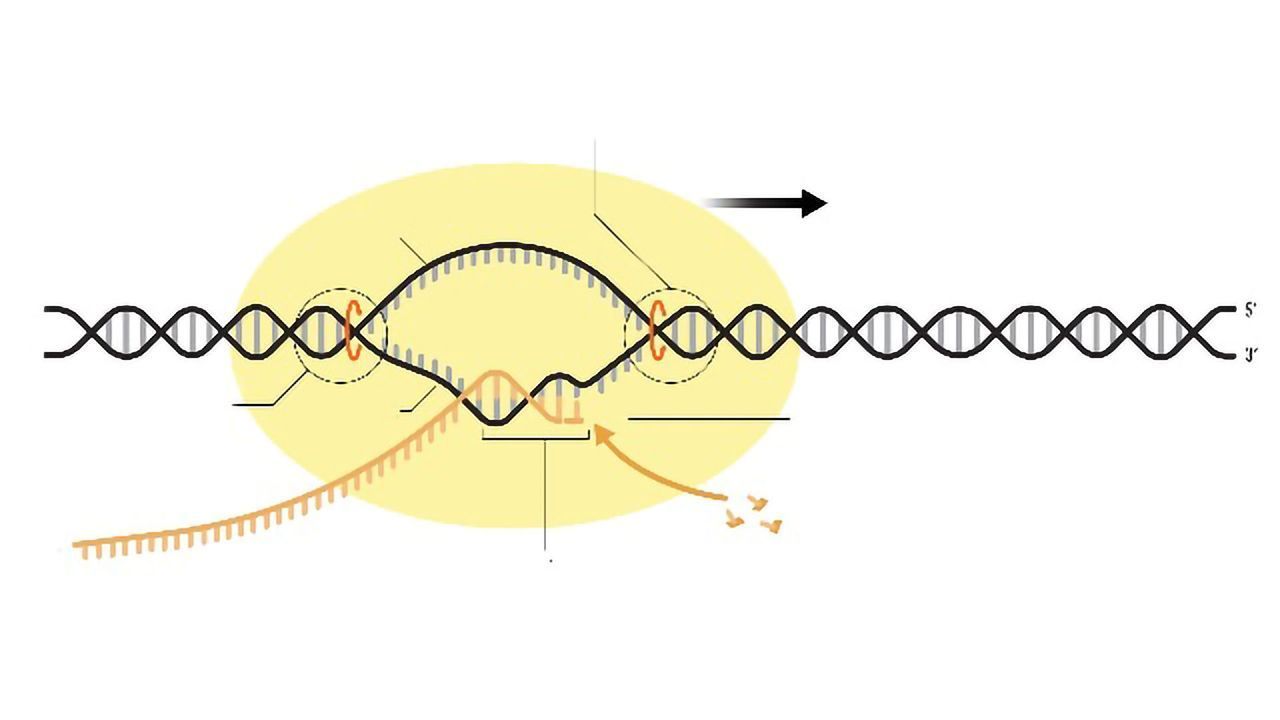
An enzyme called rna polymerase proceeds along the dna template adding nucleotides by base pairing with the dna template in a manner similar to dna replication. Where does rna polymerase begin transcribing a gene into mrna? The rna polymerase must then add new nucleotides to the 3′ end of the growing rna strand in a phase called transcription elongation.
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
This process involves capping of the 50 end, During elongation, rna polymerase tracks along the dna template, synthesizes mrna in the 5′ to 3′ direction, and unwinds then rewinds the dna as it is read. This mature mrna is ready for translation.
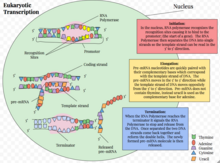 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
In a prokaryotic cell, by the time transcription ends, the transcript would already have been used to begin making copies of the encoded protein because the processes of transcription and translation can. In the basic model, rna polymerase pulls apart a gene’s two strands, then slithers down one of them to make an mrna copy of it. Before transcription can take place, the dna double helix must unwind near the gene that is getting transcribed.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
In the basic model, rna polymerase pulls apart a gene’s two strands, then slithers down one of them to make an mrna copy of it. First, they conclude that only a surprisingly small fraction of rna polymerases that bind the promoter, ∼ 1%, actually go on to transcribe the gene and. The mrna is an rna version of the gene that leaves the cell nucleus and moves to the cytoplasm where proteins are made.

Transcription is the first step of gene expression. Rna polymerase iii is also located in the nucleus. In a prokaryotic cell, by the time transcription ends, the transcript would already have been used to begin making copies of the encoded protein because the processes of transcription and translation can.
 Source: jackwestin.com
Source: jackwestin.com
The rna polymerase must then add new nucleotides to the 3′ end of the growing rna strand in a phase called transcription elongation. In a prokaryotic cell, by the time transcription ends, the transcript would already have been used to begin making copies of the encoded protein because the processes of transcription and translation can. Turns out things are a hair more complicated.
 Source: britannica.com
Source: britannica.com
This mature mrna is ready for translation. Transcription is the first step of gene expression. During this process, the dna sequence of a gene is copied into rna.
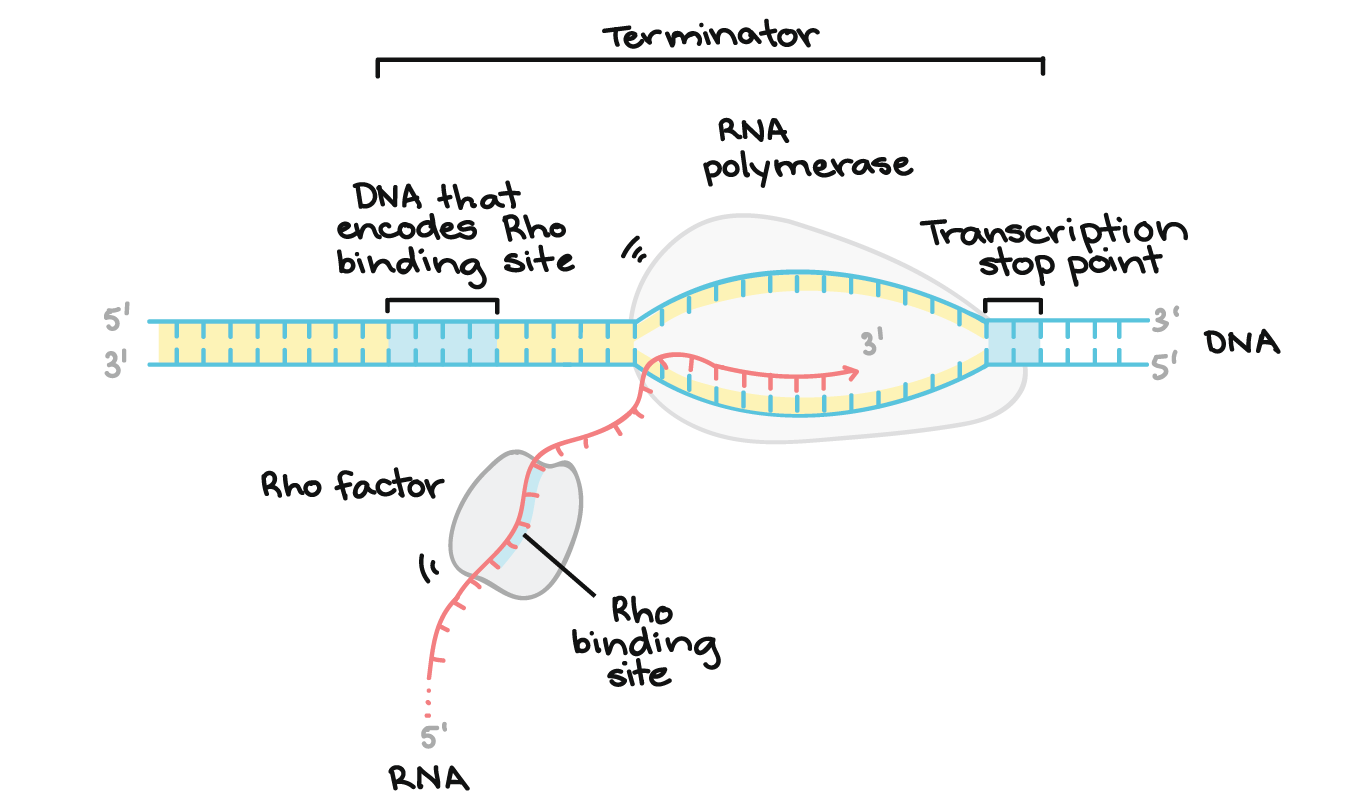 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
In a prokaryotic cell, by the time transcription ends, the transcript would already have been used to begin making copies of the encoded protein because the processes of transcription and translation can. ↑ the first step in gene expression, in which a segment of the dna is copied into an mrna molecule. Our immune system recognizes that.
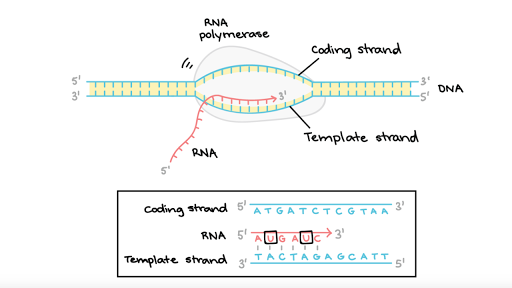
An enzyme called rna polymerase proceeds along the dna template adding nucleotides by base pairing with the dna template in a manner similar to dna replication. Next, our cells display the spike protein piece on their surface. This mature mrna is ready for translation.
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
If transcription factors are the gas pedal and brakes, the engine is rna polymerase. Turns out things are a hair more complicated. Polyadenylation (poly(a)) site after transcribing through the whole transcription unit, which can span hundreds of kilobases.
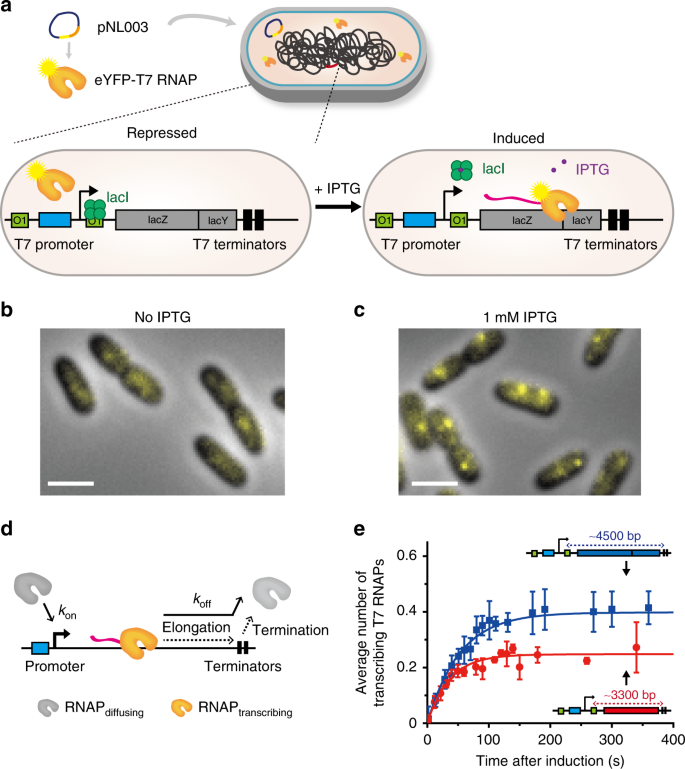 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
↑ large molecule that accelerate chemical reactions that take place in the body or inside the cell. ↑ the first step in gene expression, in which a segment of the dna is copied into an mrna molecule. An enzyme called rna polymerase proceeds along the dna template adding nucleotides by base pairing with the dna template in a manner similar to dna replication.
Also Read :





