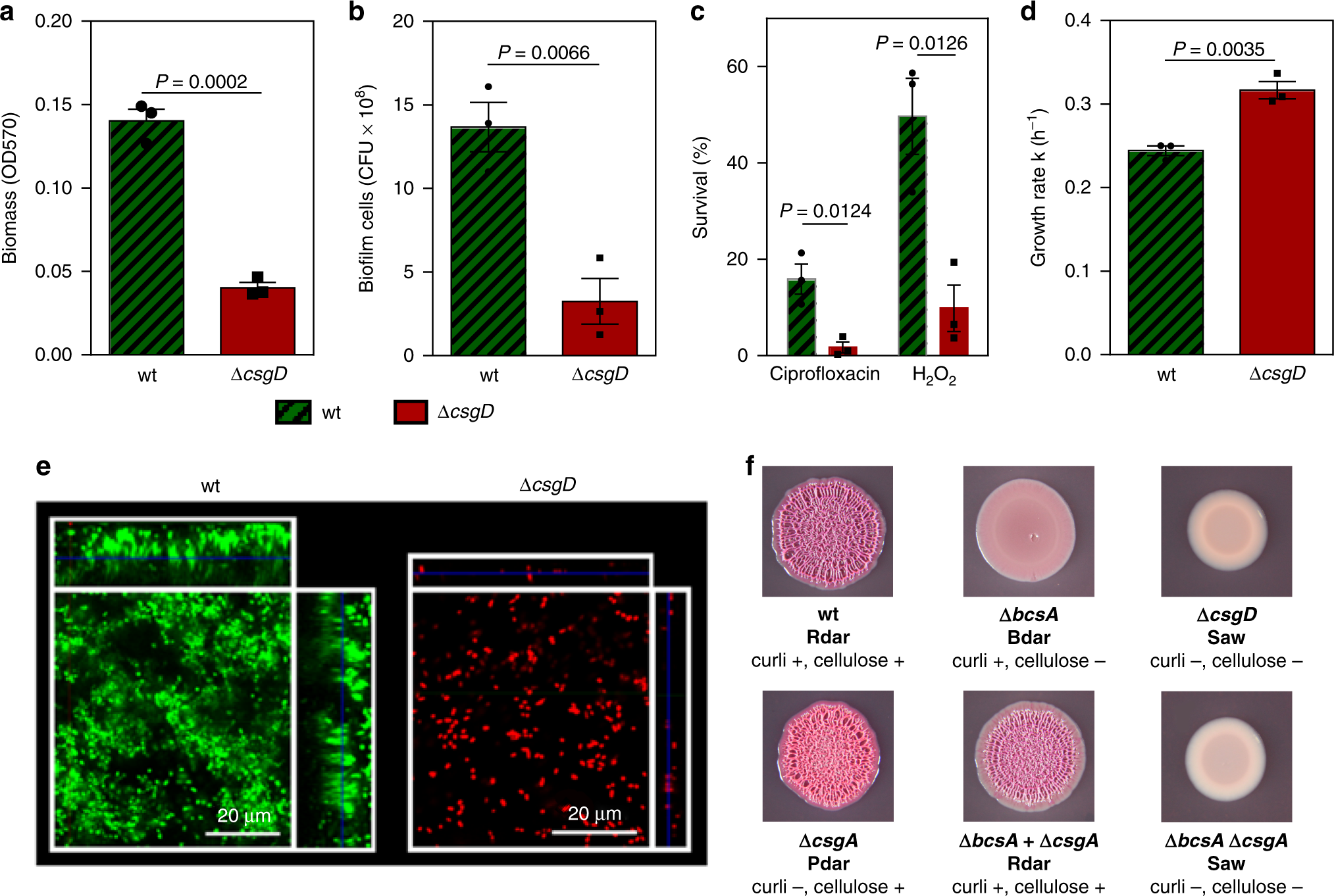
Describe the myelinated and unmyelinated nerve fibers. Nerve fibers are found in the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system.
Where Are Unmyelinated Nerve Fibers Surrounded By Schwann Cells. The nerve fiber consists of a neuron�s axon and its myelin sheath, if present. Unmyelinated nerve fibers conduct impulses at low velocities. In the pns and cns d. Unmyelinated nerve fibres is enveloped by a schwann cell that doesn�t form a myelin sheath around the axon, and found in autonomous and the somatic neural systems.
 Histology Of The Peripheral Nerves And Light Microscopy - Nysora From nysora.com
Histology Of The Peripheral Nerves And Light Microscopy - Nysora From nysora.com
Related Post Histology Of The Peripheral Nerves And Light Microscopy - Nysora :
(l) schwann cell nuclei (sc) with associated unmyelinated axons surrounded by collagen fibers. Axons or nerve fibers may be myelinated or unmyelinated. Unmyelinated nerve fibers conduct impulses at low velocities. Abutting schwann cells are tightly joined and nodes of ranvier do not form.
First, generation of new, noninnervated schwann cells, either free within the endoneurial space or arranged around nerve fibers in “onion bulbs” of the type seen in some demyelinating disorders of peripheral nerve;
In central nervous system the myelin is formed by oligodendrocytes and in peripheral nervous sytem by schwann cells. Explore the role of all three in the development of ms and the action. Where are unmyelinated nerve fibers surrounded by schwann cells? Myelinated nerve fibers usually range 2 to 14 µm while unmyelinated fibers range 0.2 to 3. On the contrary, one to four unmyelinated axons are normally included in one schwann cell subunit. Each schwann cell typically contains several axons (up to 20), which are often brought into the cell by.
 Source: nysora.com
Source: nysora.com
Myelinated nerve fibers usually range 2 to 14 µm while unmyelinated fibers range 0.2 to 3. A series of schwann cells covers the length of each axon. Therefore, each unmyelinated fiber is not completely covered by the myelin sheath formed by the schwann cell.
 Source: getbodysmart.com
Source: getbodysmart.com
Inner aspect of a cell showing a nucleus, golgi complex and a centrioles. In the pns and cns d. The axon, its sheath of schwann cells and the surrounding basal lamina form the impulse conducting structures, the nerve fibres, classified in myelinated.
 Source: doctorlib.info
Source: doctorlib.info
First, generation of new, noninnervated schwann cells, either free within the endoneurial space or arranged around nerve fibers in “onion bulbs” of the type seen in some demyelinating disorders of peripheral nerve; In the pns and cns d. [ nerv ] a macroscopic cordlike structure of the body, comprising a collection of nerve fibers that convey impulses between a part of the central nervous system and some other body region.
 Source: getbodysmart.com
Source: getbodysmart.com
They are also found in the spinal cord. The myelin sheet of myelinated nerve fiber was varied in thickness and diameter. However, in autopsy materials, the axoplasm sometimes shrinks and becomes as dense as schwann cell cytoplasm (fig.
 Source: quora.com
Source: quora.com
Each axon has a thin lamina of schwann cell sheets enveloping both myelinated and unmyelinated nerve fibers (figs. In central nervous system the myelin is formed by oligodendrocytes and in peripheral nervous sytem by schwann cells. They are also found in the spinal cord.
 Source: intechopen.com
Source: intechopen.com
Nerve fibers are found in the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system. (l) schwann cell nuclei (sc) with associated unmyelinated axons surrounded by collagen fibers. Where are unmyelinated nerve fibers surrounded by schwann cells?
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Myelinated nerve fibers usually range 2 to 14 µm while unmyelinated fibers range 0.2 to 3. The myelinated nerve fibres are enveloped with schwann cells, it form a myelin sheath around the axon. The basement membrane of perineural cell was noted (fig.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Similarly to the organization of the cns tracts, both myelinated and unmyelinated fibers occur peripherally too. Explore the role of all three in the development of ms and the action. Note basal lamina (arrows) outlining the cell membrane of each schwann cell.
 Source: doubtnut.com
Source: doubtnut.com
Where are unmyelinated nerve fibers surrounded by schwann cells? Abutting schwann cells are tightly joined and nodes of ranvier do not form. In unmyelinated fibers, the nerve impulse is like a grasshopper walking while in a myelinated fiber, the nerve impulse is like grasshopper jumping.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Axons or nerve fibers may be myelinated or unmyelinated. Myelinated nerve fibers usually range 2 to 14 µm while unmyelinated fibers range 0.2 to 3. Depending on their function, nerves are known as sensory, motor, or mixed.
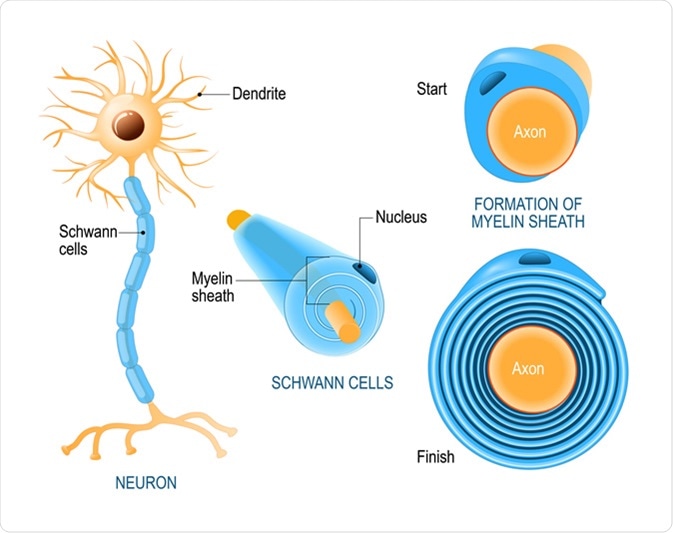 Source: news-medical.net
Source: news-medical.net
In the pns and cns d. In unmyelinated fibers, the nerve impulse is like a grasshopper walking while in a myelinated fiber, the nerve impulse is like grasshopper jumping. Describe the myelinated and unmyelinated nerve fibers.
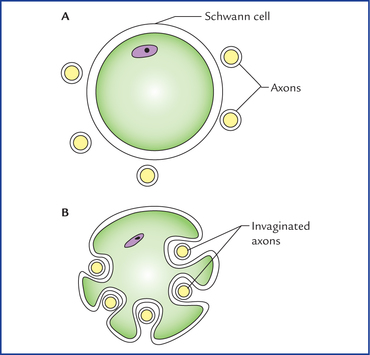 Source: neupsykey.com
Source: neupsykey.com
In both myelinated and unmyelinated nerve fibers, schwann cells are surrounded by an associated basal lamina. Myelin sheath originated by a multilayered spiral wrapping of schwann cell membrane mitochondria and synaptic vesicles in a axonal termination. (l) schwann cell nuclei (sc) with associated unmyelinated axons surrounded by collagen fibers.

They are also found in the spinal cord. In both myelinated and unmyelinated nerve fibers, schwann cells are surrounded by an associated basal lamina. Nerve fibers are found in the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Inner aspect of a cell showing a nucleus, golgi complex and a centrioles. They are also found in the spinal cord. Blood vessels run longitudinally within compartments formed by epineurium and perineurium.
 Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Unmyelinated nerve fibres is enveloped by a schwann cell that doesn�t form a myelin sheath around the axon, and found in autonomous and the somatic neural systems. They lack the myelin envelope completely, with schwann cells surrounding them forming the remak fibers in bundles within peripheral nerves. The myelin sheath, schwann cells, and nodes of ranvier are all related to the nervous system and multiple sclerosis (ms).

Describe the myelinated and unmyelinated nerve fibers. Nerve fibers are found in the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system. In the pns and cns d.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
The schwann cells wrap tightly around the nerve axon and form the myelin sheath. 5) are enveloped by perineural cell cytoplasmic laminae. Due to presence of nodes of ranvier on myelinated nerve fibers, the speed of transmission of nerve impulses is high in myelinated nerve fibers.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
First, generation of new, noninnervated schwann cells, either free within the endoneurial space or arranged around nerve fibers in “onion bulbs” of the type seen in some demyelinating disorders of peripheral nerve; The myelin sheath, schwann cells, and nodes of ranvier are all related to the nervous system and multiple sclerosis (ms). The nonmyelinating schwann cells (nmscs) include the schwann cells of remak fibers, the specialized terminal schwann cells (tscs) at neuromuscular junctions, and those in some sensory transducers, including in pacinian corpuscles and meissner�s corpuscles.

Due to presence of nodes of ranvier on myelinated nerve fibers, the speed of transmission of nerve impulses is high in myelinated nerve fibers. Myelinated nerve fibers usually range 2 to 14 µm while unmyelinated fibers range 0.2 to 3. In central nervous system the myelin is formed by oligodendrocytes and in peripheral nervous sytem by schwann cells.
 Source: intechopen.com
Source: intechopen.com
The myelin sheet of myelinated nerve fiber was varied in thickness and diameter. The myelinated nerve fibres are enveloped with schwann cells, it form a myelin sheath around the axon. Where are unmyelinated nerve fibers surrounded by schwann cells?
Also Read :