See the answer see the answer see the answer done loading The ventricles begin to slow down and stop producing that much pressure.
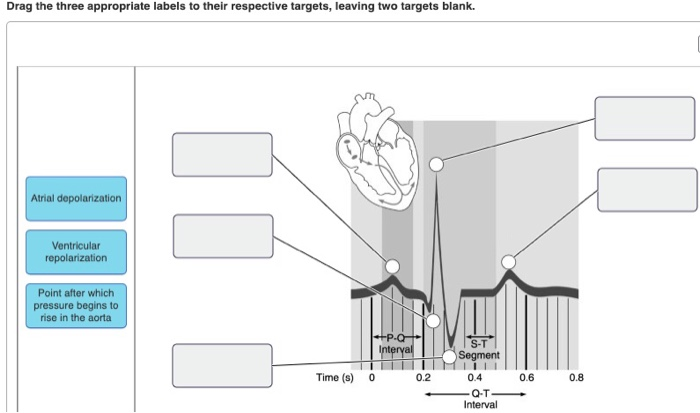
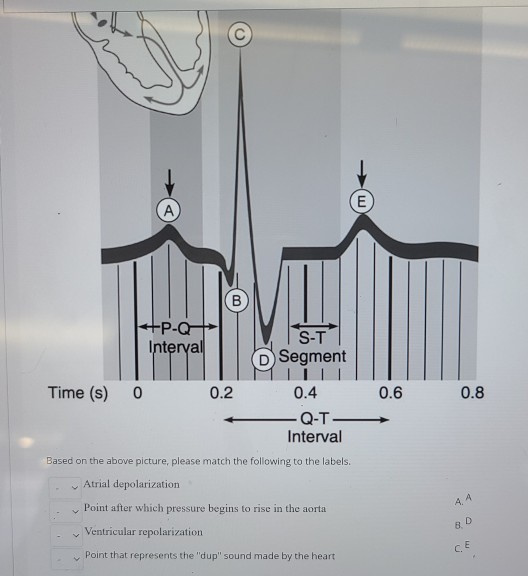
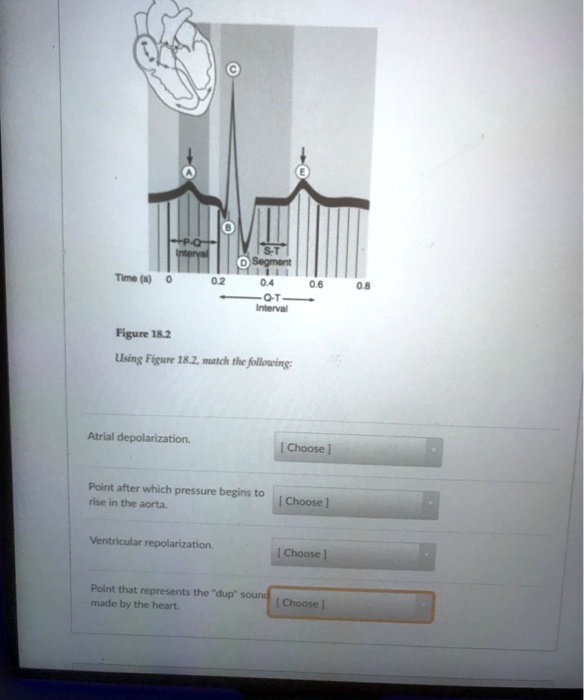
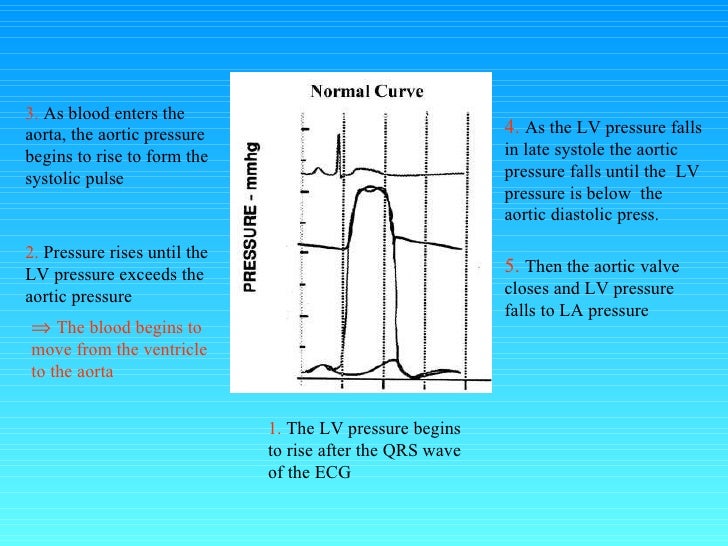
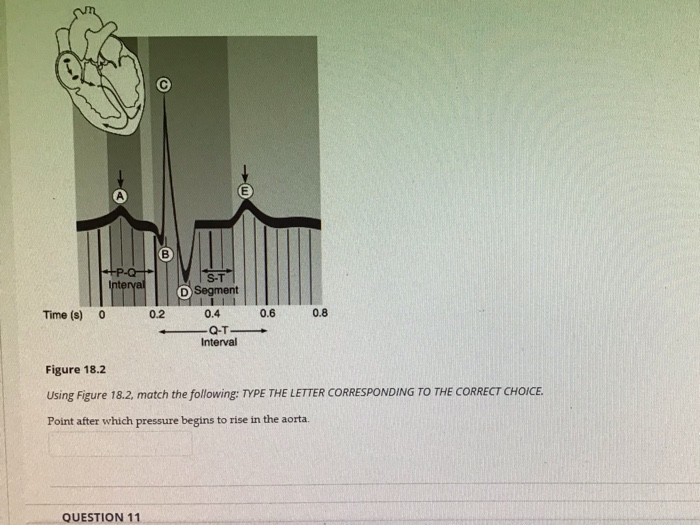
Point After Which Pressure Begins To Rise In The Aorta. The av valve will only open again when the ventricular pressure is below the atrial. At point “a” is when ventricular diastole ends, the mitral valve closes and phase 2 of the cardiac cycle or isovolumetric contraction begins. Pressure in the pulmonary artery (and all pressures on the right side of the heart) are much lower than their counterparts on the left side of the heart. Because the aorta is the most compliant portion of the human arterial system, the pulse pressure is the lowest.
 Chapter 18-Cardiovascular System Images And T/F Flashcards | Quizlet From quizlet.com
Chapter 18-Cardiovascular System Images And T/F Flashcards | Quizlet From quizlet.com
Related Post Chapter 18-Cardiovascular System Images And T/F Flashcards | Quizlet :
(iii) soon after the left ventricle begins to contract, the pressure in the left atrium begins to increase. At point “a” is when ventricular diastole ends, the mitral valve closes and phase 2 of the cardiac cycle or isovolumetric contraction begins. When the right ventricular pressure rises above the pulmonary pressure (~8 mmhg), pulmonary valve opens and there is rapid ejection (70% ejection) of blood into the pulmonary trunk. In the systemic circulation, pressure is actually slightly higher in the downstream arteries (e.g., renal artery) than in the aorta because of the reflection of pressure waves at branch points.
Stroke volume is the amount ejected in each beat.
State why the pressure in the left atrium increases. Ventricularization, during which aortic and systolic pressures mildly decrease while diastolic pressure significantly lowers. True proxysmal atrial tachycardia is characterized by bursts of atrial contractions with little pause Blood is pumped from the heart, pushing open the pulmonary and aortic semilunar valves. In the second phase of ventricular systole, the ventricular ejection phase, the contraction of the ventricular muscle has raised the pressure within the ventricle to the point that it is greater than the pressures in the pulmonary trunk and the aorta. Last updated on sun, 21 feb 2021 | medical physiology.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Compliance progressively decreases until it reaches a minimum in the femoral and saphenous arteries, and then it begins to increase again. Shortly after ejection begins, the active state of ventricular myocardium. Ventricular ejection begins when the semilunar valves open.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
In the systemic circulation, pressure is actually slightly higher in the downstream arteries (e.g., renal artery) than in the aorta because of the reflection of pressure waves at branch points. Ventricles after systole and it is about 50 ml (point a) 14. Even though the valve is opening, the ventricle is still contracting and pushing on the blood that�s present there.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
In early left heart ejection, blood enters the aorta rapidly and causes the pressure within it to rise. In the second phase of ventricular systole, the ventricular ejection phase, the contraction of the ventricular muscle has raised the pressure within the ventricle to the point that it is greater than the pressures in the pulmonary trunk and the aorta. Left ventricular pressure is continuing to climb because the left ventricle is continuing to contract, right?

The semilunar valves are closed because the ventricular pressure is lower than that in the aorta and the pulmonary artery (fig. The pressure drops in both the aorta and the ventricles. During life the size of the aorta increases.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Left ventricular volume decreases as the ventricle contracts and pumps blood into the aorta. This is represented on the aortic pressure graph by a sharp decline or ‘incisura’ and then a sharp increase. Because the aorta is the most compliant portion of the human arterial system, the pulse pressure is the lowest.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
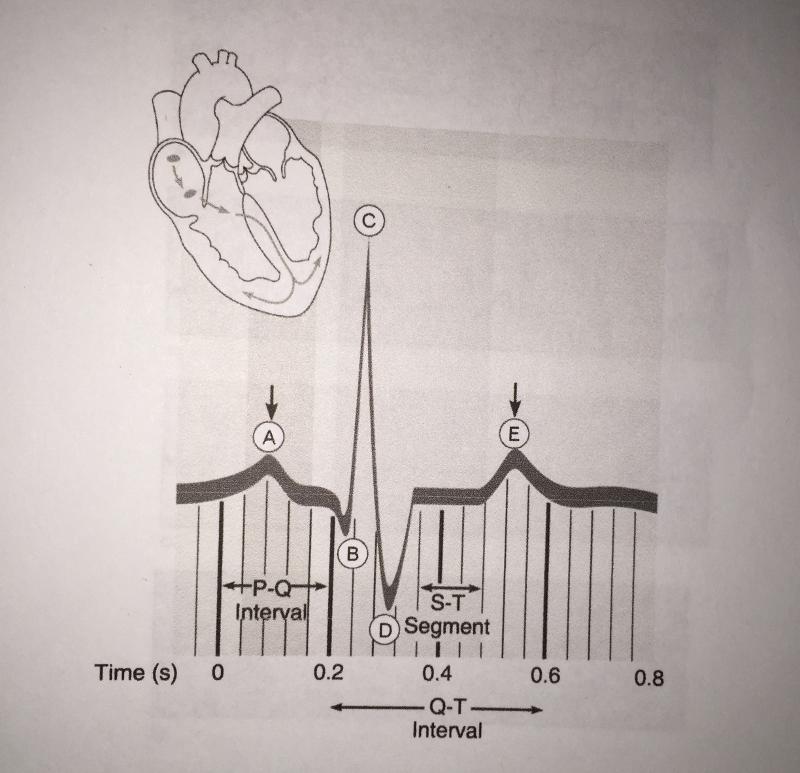
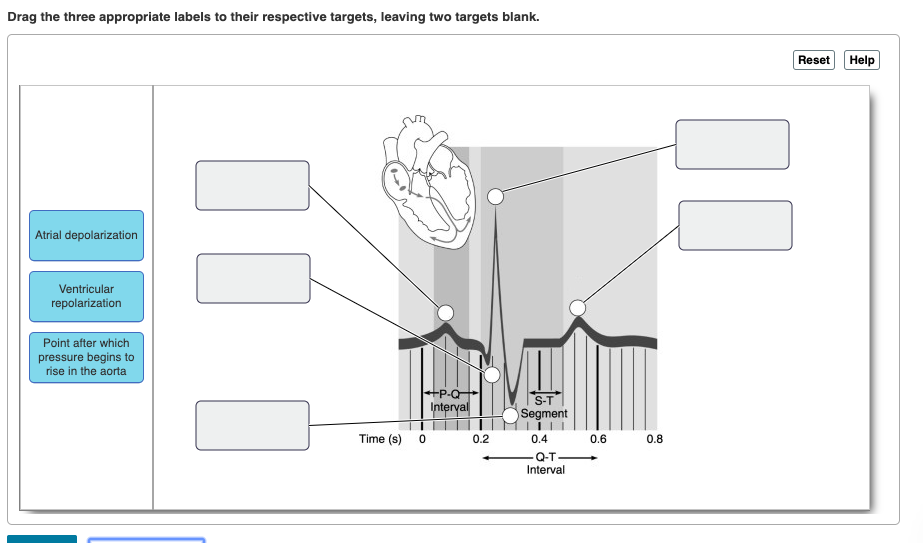
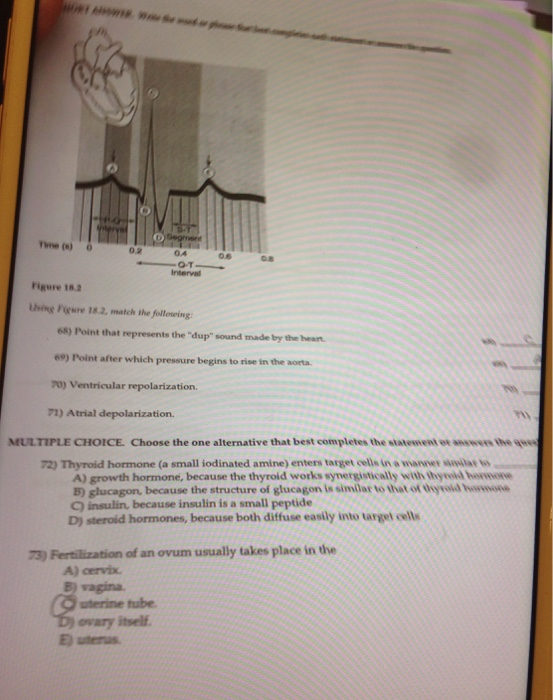
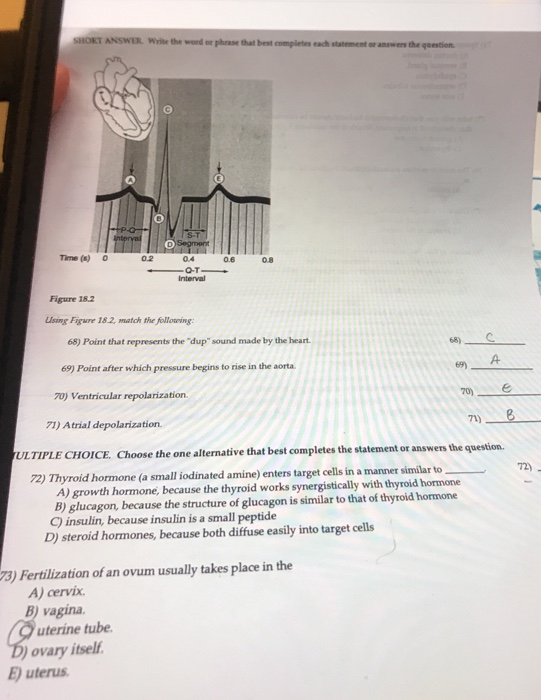
So, you know as more blood gets injected into the. Compliance progressively decreases until it reaches a minimum in the femoral and saphenous arteries, and then it begins to increase again. Figure 18.2using figure 18.2, match the following:
 Source: easynotecards.com
Source: easynotecards.com
At the time of valve closure, the pressure increases by approximately 5 to 10 mmhg as a result of aortic elastic recoil and blood passing from the apex. The semilunar valves are closed because the ventricular pressure is lower than that in the aorta and the pulmonary artery (fig. Blood is pumped from the heart, pushing open the pulmonary and aortic semilunar valves.
 Source: numerade.com
Source: numerade.com
Shortly after ejection begins, the active state of ventricular myocardium. Pressure in the aorta is increasing during this phase, because the left ventricle is pushing blood out into the aorta. Because the aorta is the most compliant portion of the human arterial system, the pulse pressure is the lowest.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
The semilunar valves are closed because the ventricular pressure is lower than that in the aorta and the pulmonary artery (fig. The aortic valve opens and the mitral valve remains closed. The sudden change in the pressure gradient results in a small backflow of blood into the left ventricle just before the aortic valves close.
 Source: aulad.org
Source: aulad.org
In early left heart ejection, blood enters the aorta rapidly and causes the pressure within it to rise. The left ventricle contracts isovolumetrically until the ventricular pressure exceeds the systemic pressure, which opens the aortic valve and results in ventricular ejection. See the answer see the answer see the answer done loading
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Stroke volume is the amount ejected in each beat. Blood is pumped from the heart, pushing open the pulmonary and aortic semilunar valves. 13.13) when ejection begins and the ventricular volume decreases.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
After the maximum pressure is reached, the ventricle relaxes, which results in diminished left ventricular pressure. Last updated on sun, 21 feb 2021 | medical physiology. The left ventricle contracts isovolumetrically until the ventricular pressure exceeds the systemic pressure, which opens the aortic valve and results in ventricular ejection.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Figure 18.2using figure 18.2, match the following: The ventricles begin to slow down and stop producing that much pressure. The pressure in the left ventricle and aorta rises to about 120 mmhg (fig.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Even though the valve is opening, the ventricle is still contracting and pushing on the blood that�s present there. Even though the valve is opening, the ventricle is still contracting and pushing on the blood that�s present there. The pressure drops in both the aorta and the ventricles.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
The aortic valve opens and the mitral valve remains closed. (iii) soon after the left ventricle begins to contract, the pressure in the left atrium begins to increase. Importantly, pressure builds simultaneously in both the left ventricle and the aorta as the ventricular myocardium continues to contract.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Three conditions increasing afterload are: Bulging of the mitral valve into the left atrium during isovolumetric contraction causes a slight increase in left atrial pressure (c wave). Figure 18.2using figure 18.2, match the following:
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
3 in adulthood the aortic size is related to exercise and workload.the ageing of the aorta is accompanied by a loss of. At the time of valve closure, the pressure increases by approximately 5 to 10 mmhg as a result of aortic elastic recoil and blood passing from the apex. Because the aorta is the most compliant portion of the human arterial system, the pulse pressure is the lowest.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
During life the size of the aorta increases. Shortly after ejection begins, the active state of ventricular myocardium. The pressure at the point of measurement reaches its peak (systolic pressure) after the pumping pulse is completed, and then begins to drop.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
Left ventricular pressure is continuing to climb because the left ventricle is continuing to contract, right? See the answer see the answer see the answer done loading Figure 18.2using figure 18.2, match the following:
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
The aortic valve opens and the mitral valve remains closed. 13.13) when ejection begins and the ventricular volume decreases. The ventricles begin to slow down and stop producing that much pressure.
Also Read :





