Definition function f is differentiable at x=a if and only if f'(a) exists. Hence, |x| is not differentiable at x=0.
Describe The X Values At Which The Function Is Differentiable. Function g below is not differentiable at x = 0 because there is no tangent to the graph at x = 0.(try to draw a tangent at x=0!) function h below is not differentiable at x = 0 because there is a jump in the value of the function and also the function is not defined therefore not continuous at x = 0. More generally, a function is said to be differentiable on if it is differentiable at every point in an open set , and a differentiable function is one in. Let’s consider some piecewise functions first. F(x) is differentiable everywhere except at x = 0.
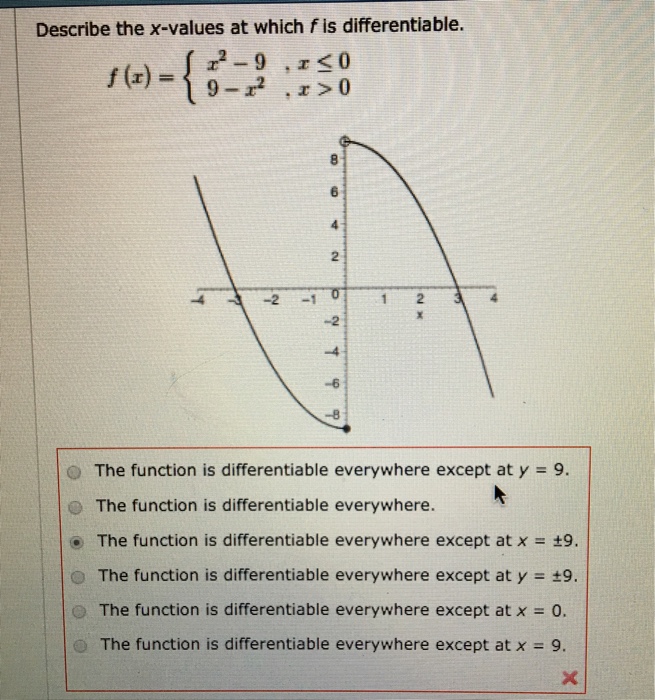
Related Post Solved Describe The X-Values At Which F Is Differentiable. 6 | Chegg.com :
(enter your answer using interval notation. A function f f f is differentiable at a point x 0 x_0 x 0 if. The verb, differentiate means find the derivative. Piecewise functions may or may not be differentiable on their domains.
Definition function f is differentiable at x=a if and only if f�(a) exists.
(enter your answer using interval notation. The function is differentiable from the left and right. (enter your answer using interval notation. Briefly, differentiable means can be differentiated and that mean has a derivative. The function is differentiable for all x + +8. At x=0 the function is not defined so it makes no sense to ask if they are differentiable there.
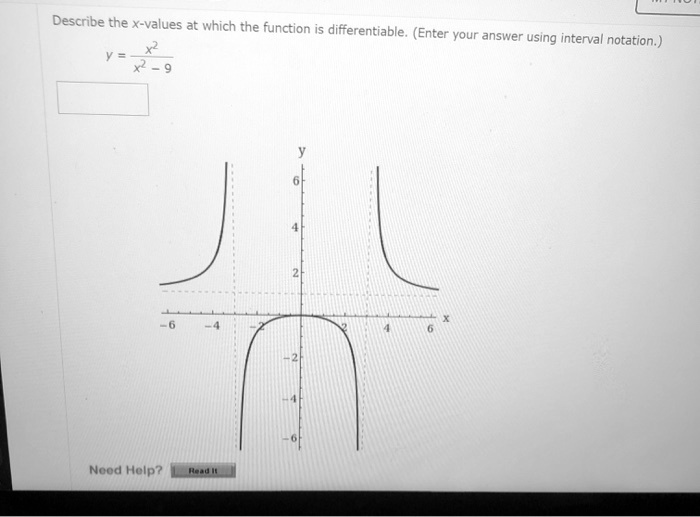 Source: itprospt.com
Source: itprospt.com
- f f f is continuous at x 0 x_0 x 0 and 2) the slope of tangent at point x 0 x_0 x 0 is well defined. Otherwise, it�s not differentiable at x=a. The function is differentiable for all x # +64.
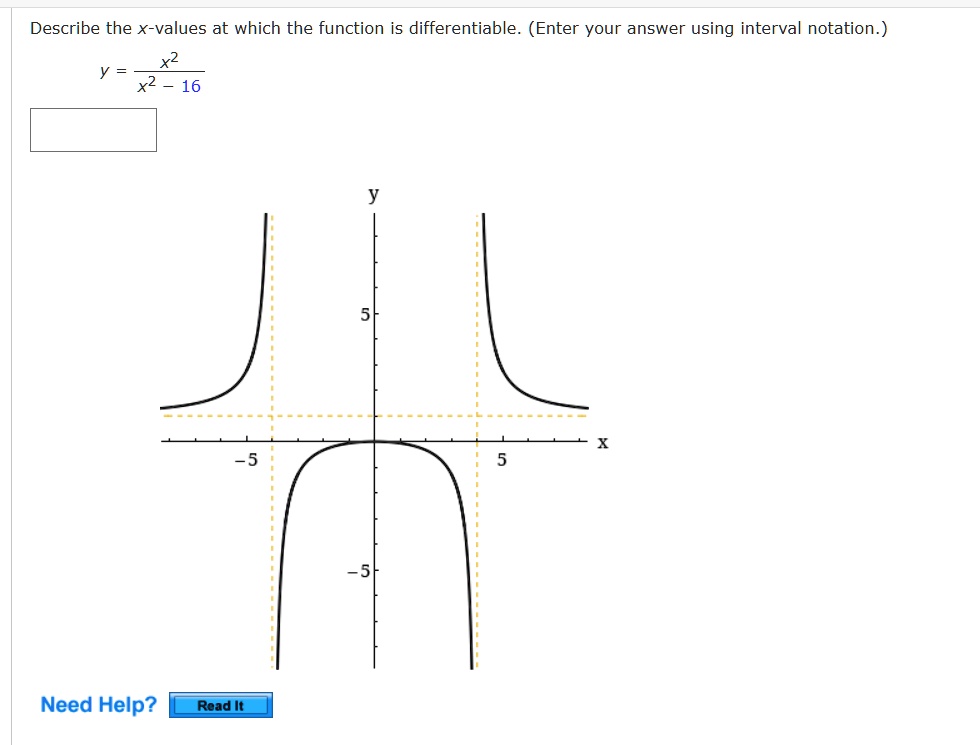 Source: numerade.com
Source: numerade.com
F(x) is differentiable everywhere except at x = 0. (enter your answer using interval notation. More generally, a function is said to be differentiable on if it is differentiable at every point in an open set , and a differentiable function is one in.
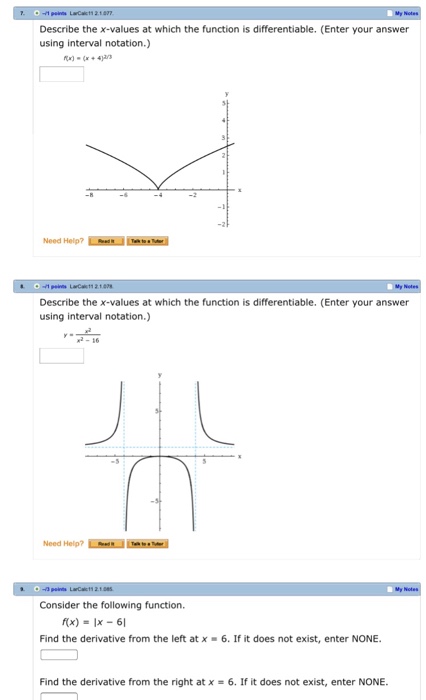
Hence the function f (x) = ∣∣x2 − 9∣∣ is differentiable everywhere with the exception of x = ± 3. We�ve got the study and writing resources you need for your assignments. Function g below is not differentiable at x = 0 because there is no tangent to the graph at x = 0.(try to draw a tangent at x=0!) function h below is not differentiable at x = 0 because there is a jump in the value of the function and also the function is not defined therefore not continuous at x = 0.
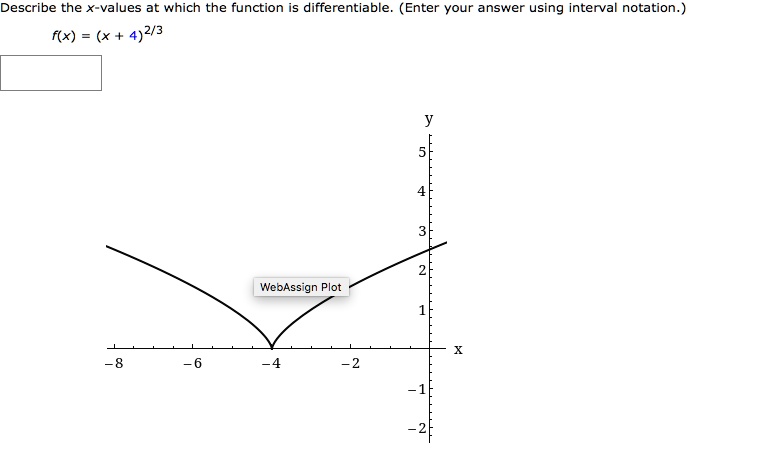 Source: numerade.com
Source: numerade.com
Function g below is not differentiable at x = 0 because there is no tangent to the graph at x = 0.(try to draw a tangent at x=0!) function h below is not differentiable at x = 0 because there is a jump in the value of the function and also the function is not defined therefore not continuous at x = 0. As in the case of the existence of limits of a function at x 0, it follows that. F ′ ( x) = lim δ x → 0 ( x + δ x) 2 − 4 − ( x 2 − 4) δ x = lim .
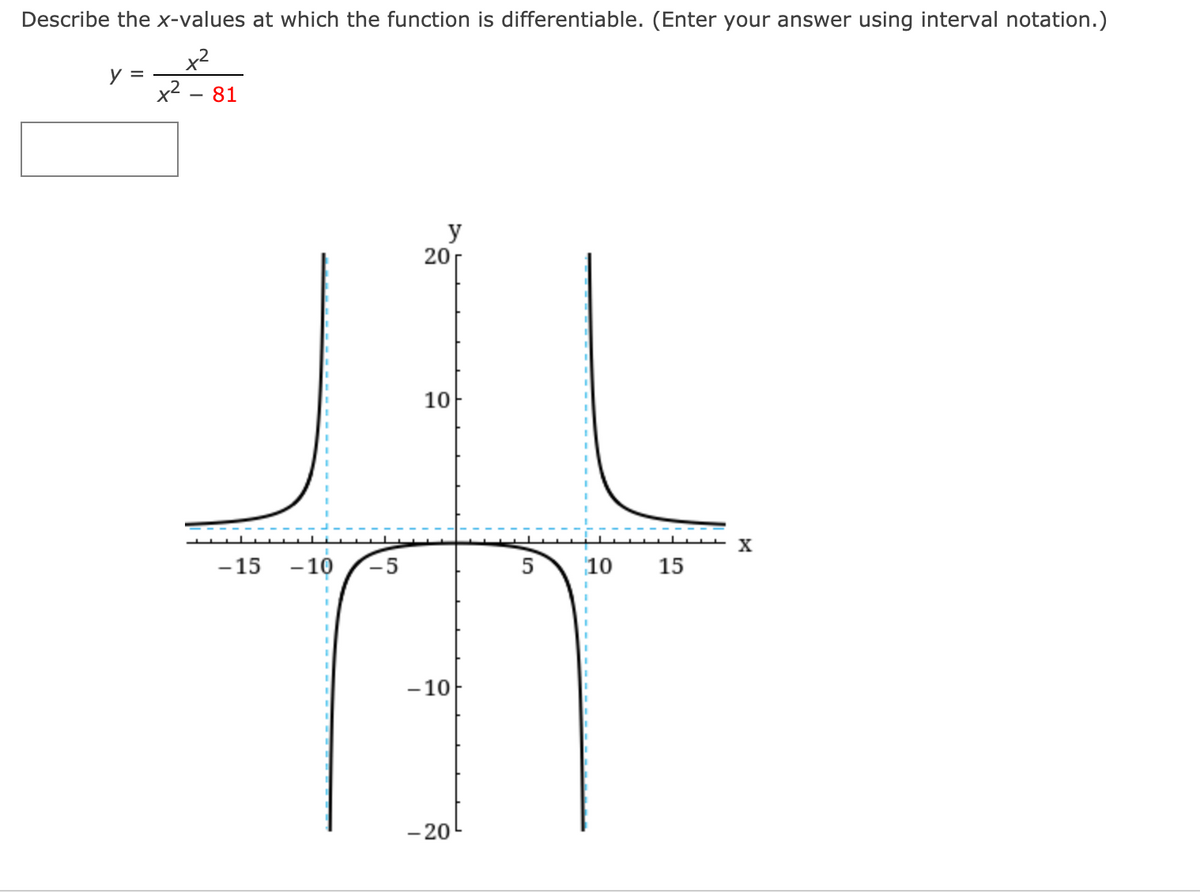 Source: bartleby.com
Source: bartleby.com
If any one of the condition fails then f� (x) is not differentiable at x 0. As in the case of the existence of limits of a function at x 0, it follows that. Briefly, differentiable means can be differentiated and that mean has a derivative.
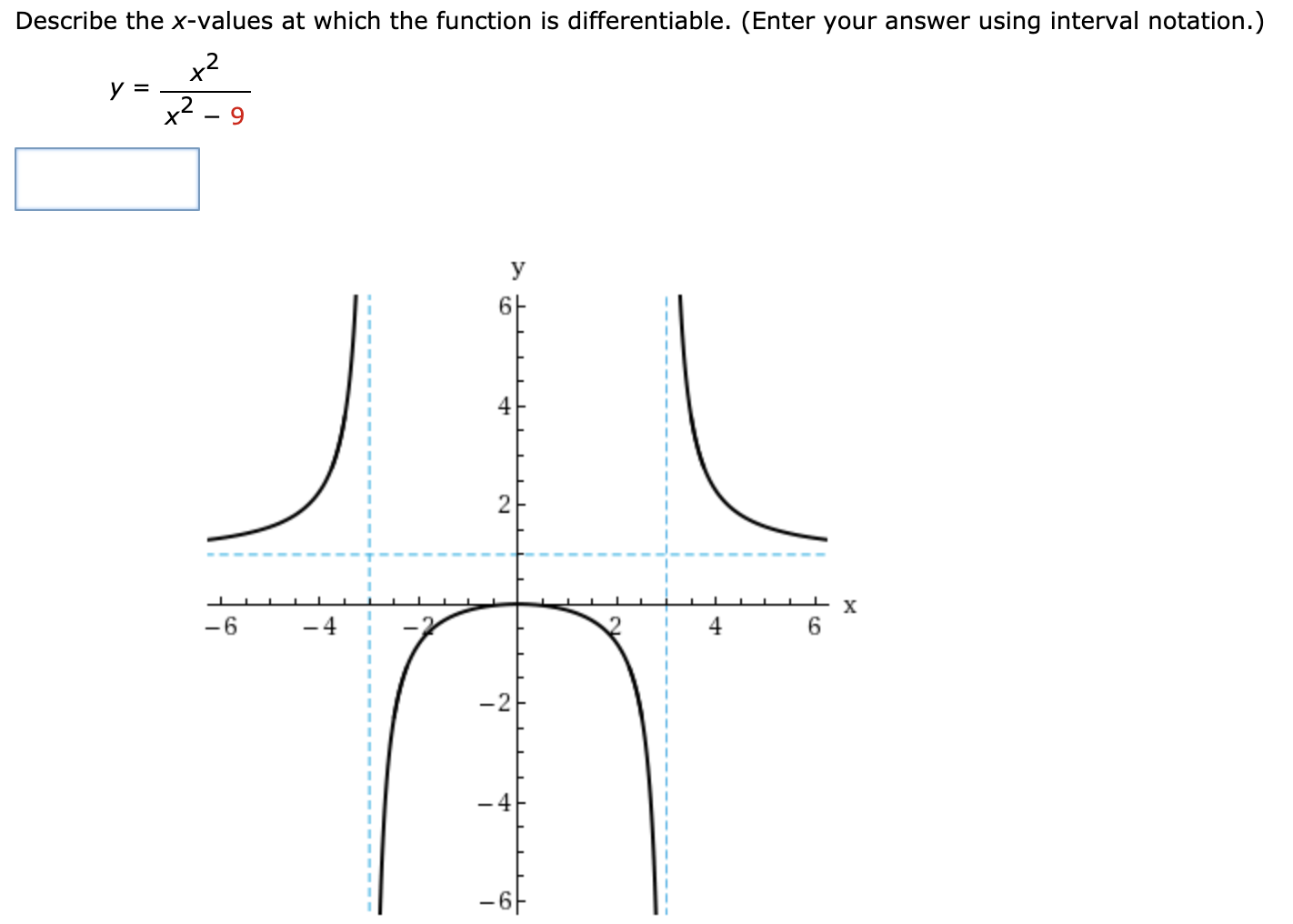 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
The function is differentiable for all x + +8. In other words, it�s the set of all real numbers that are not equal to zero. The noun differentiation is the act or process of differentiating, hence, the act or process of finding a derivative.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
F(x) is differentiable on the interval (2, infinity). So this looks like we are both continuous and differentiable. We�ve got the study and writing resources you need for your assignments.
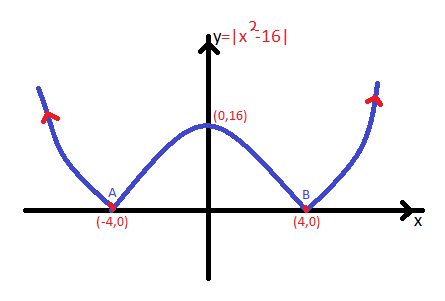 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
A function is said to be differentiable at if. The noun differentiation is the act or process of differentiating, hence, the act or process of finding a derivative. Function j below is not differentiable at x.
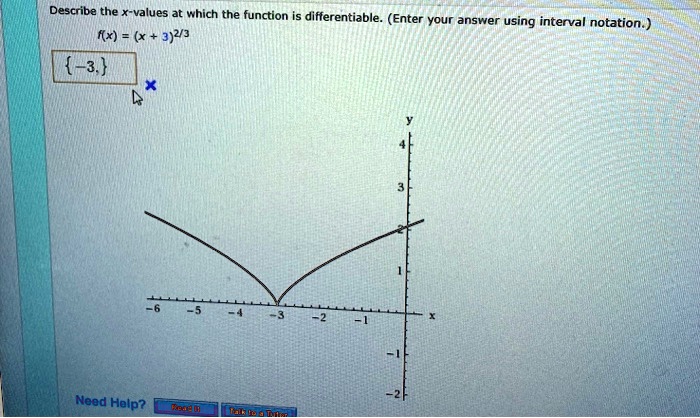 Source: numerade.com
Source: numerade.com
Otherwise, it�s not differentiable at x=a. F ′ ( x) = lim δ x → 0 ( x + δ x) 2 − 4 − ( x 2 − 4) δ x = lim . Function j below is not differentiable at x.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
F ′ ( x) = lim δ x → 0 ( x + δ x) 2 − 4 − ( x 2 − 4) δ x = lim . Piecewise functions may or may not be differentiable on their domains. The function is differentiable for all x + +8.
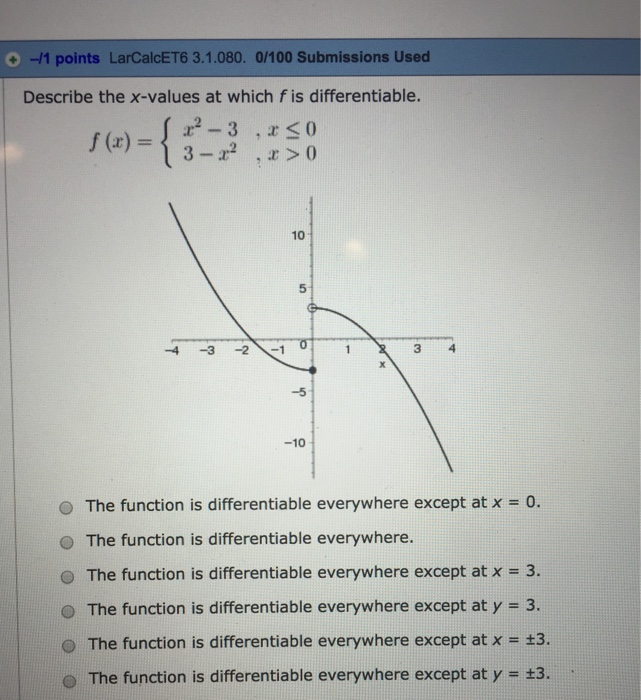
Definition function f is differentiable at x=a if and only if f�(a) exists. Briefly, differentiable means can be differentiated and that mean has a derivative. Hence the function f (x) = ∣∣x2 − 9∣∣ is differentiable everywhere with the exception of x = ± 3.
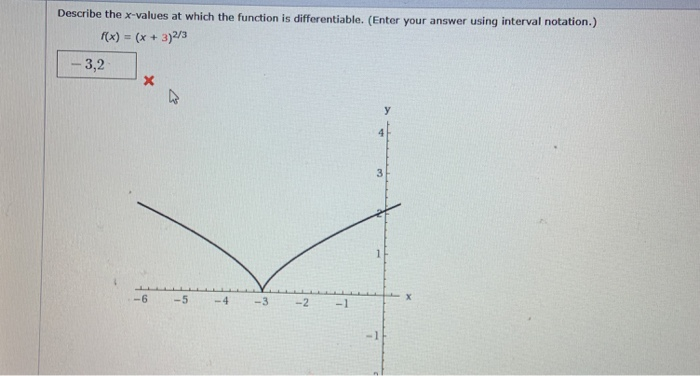 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
At point c c c on the interval [a, b] [a, b] [a, b] of the function f (x) f(x) f (x), where the function is. Let ( ), 0, 0 > − ≤ = x x x x f x first we will check to prove continuity at x = 0 The derivative function, denoted by , is the function whose domain consists of those values of such that the following limit exists:

Hence, |x| is not differentiable at x=0. Although x2 −9 is both continuous and differentiable everywhere the same is not true for ∣∣x2 −9∣∣, which is continuous everywhere but not differentiable at the transition between positive and negative. As we head towards x = 0 the function moves up and down faster and faster, so we cannot find a value it is heading towards.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
The verb, differentiate means find the derivative. Exists if and only if both. (enter your answer using interval notation.
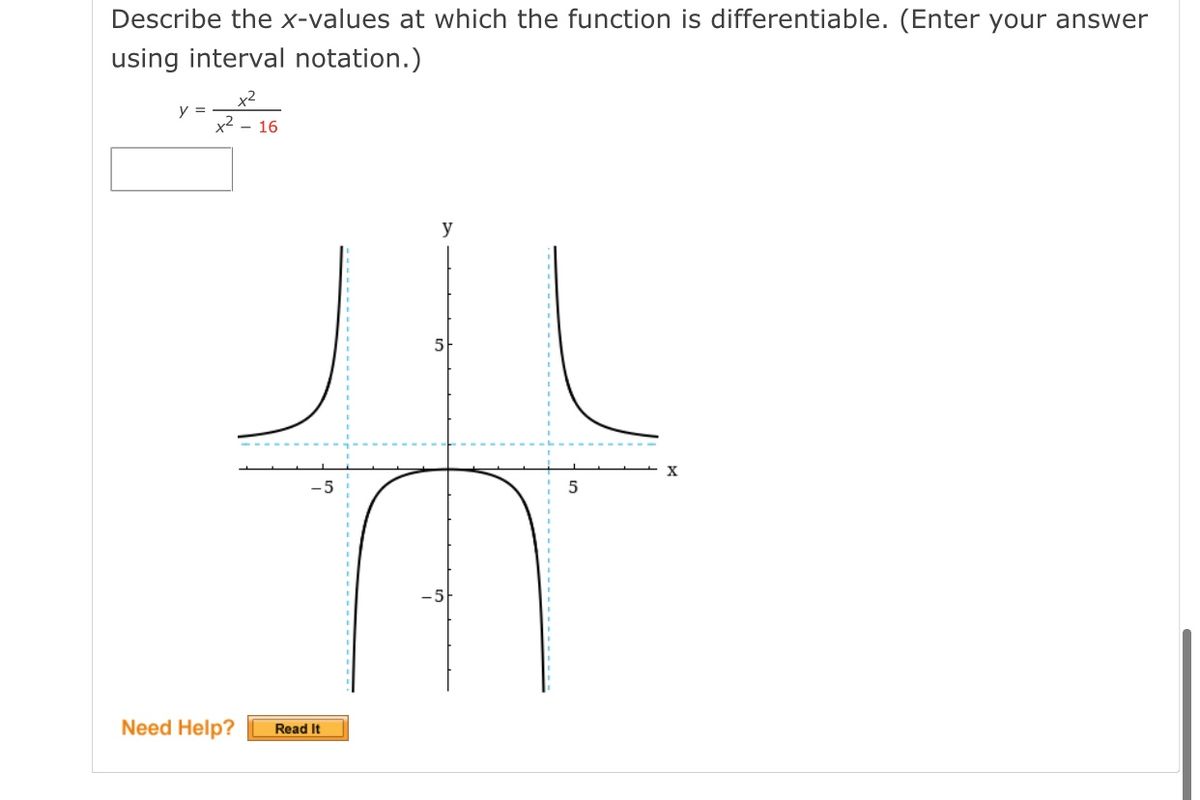 Source: bartleby.com
Source: bartleby.com
(enter your answer using interval notation. The noun differentiation is the act or process of differentiating, hence, the act or process of finding a derivative. For example, the function f ( x) = 1 x only makes sense for values of x that are not equal to zero.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Briefly, differentiable means can be differentiated and that mean has a derivative. At x=0 the function is not defined so it makes no sense to ask if they are differentiable there. But for modulus function at x=0, no unique tangent can be drawn.
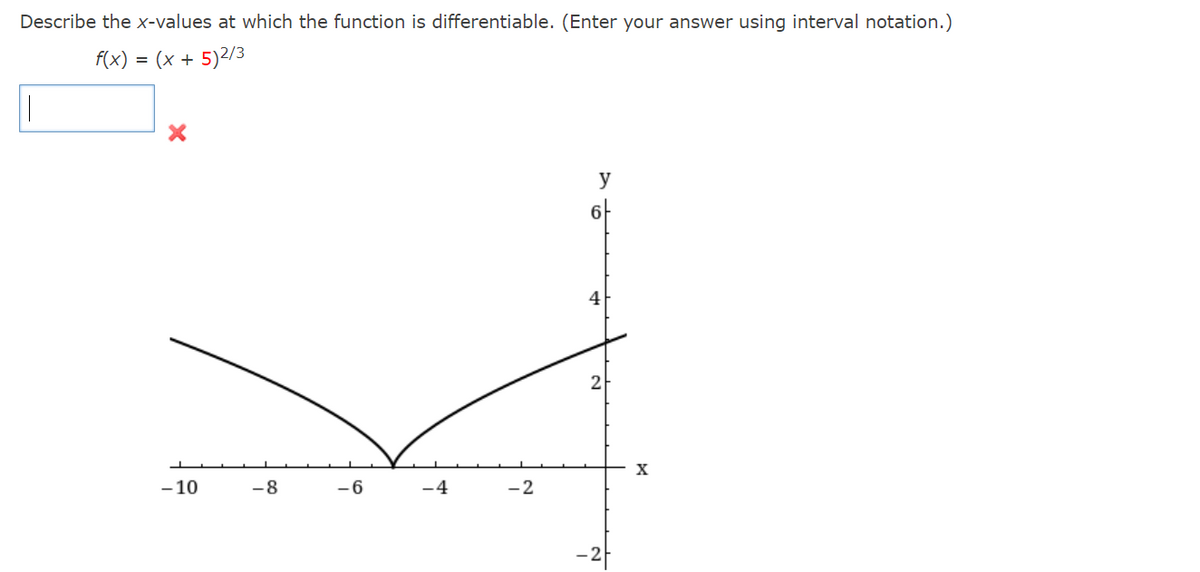 Source: bartleby.com
Source: bartleby.com
Definition function f is differentiable at x=a if and only if f�(a) exists. So this looks like we are both continuous and differentiable. F ′ ( x) = lim δ x → 0 f ( x + δ x) − f ( x) δ x for x ≤ 0:
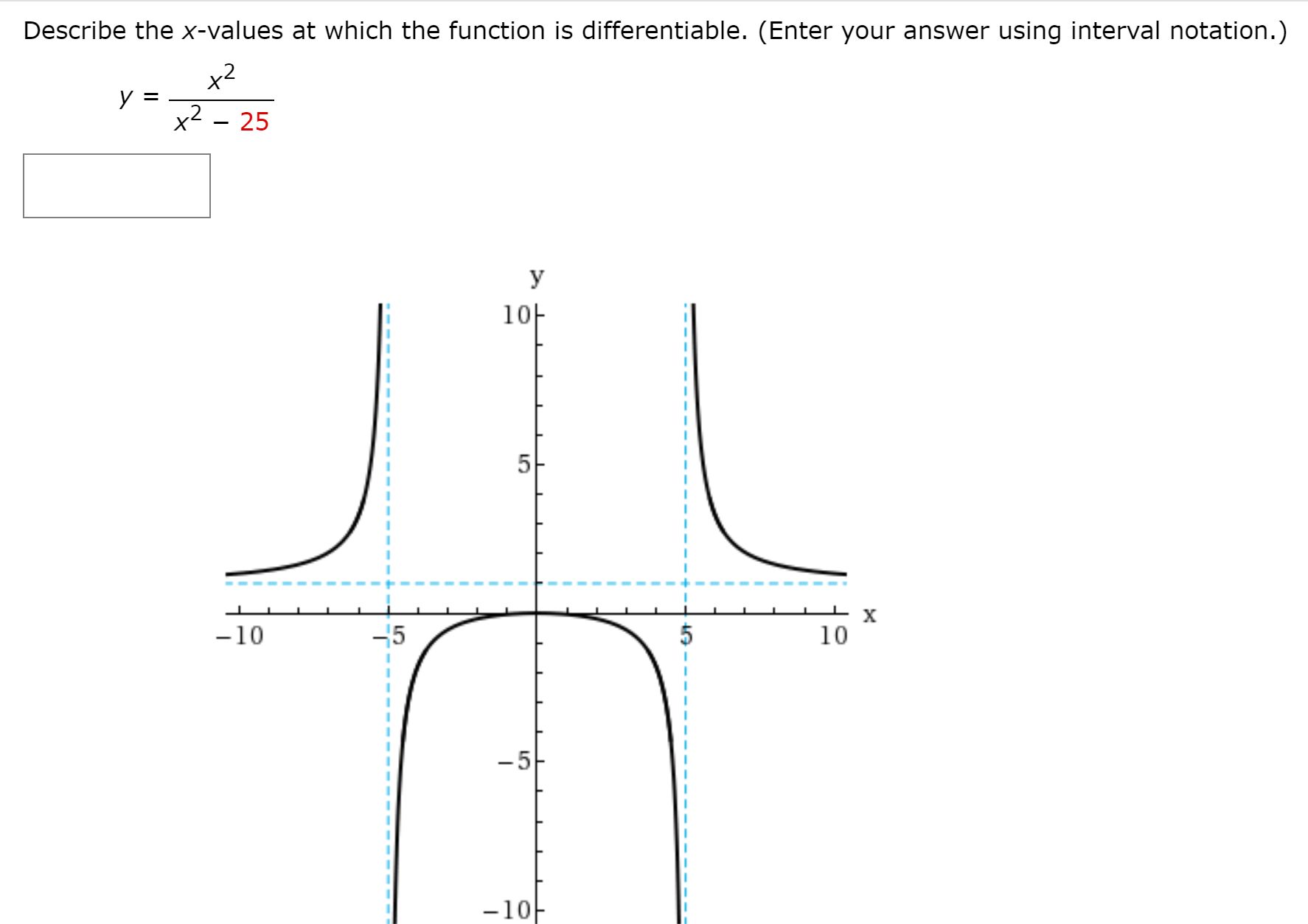 Source: bartleby.com
Source: bartleby.com
So this looks like we are both continuous and differentiable. Function j below is not differentiable at x. The verb, differentiate means find the derivative.
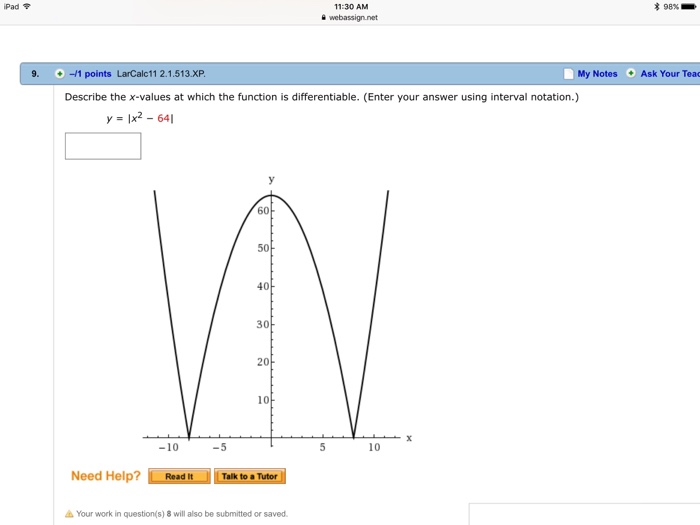
So this looks like we are both continuous and differentiable. F ′ ( x) = lim δ x → 0 f ( x + δ x) − f ( x) δ x for x ≤ 0: Although x2 −9 is both continuous and differentiable everywhere the same is not true for ∣∣x2 −9∣∣, which is continuous everywhere but not differentiable at the transition between positive and negative.
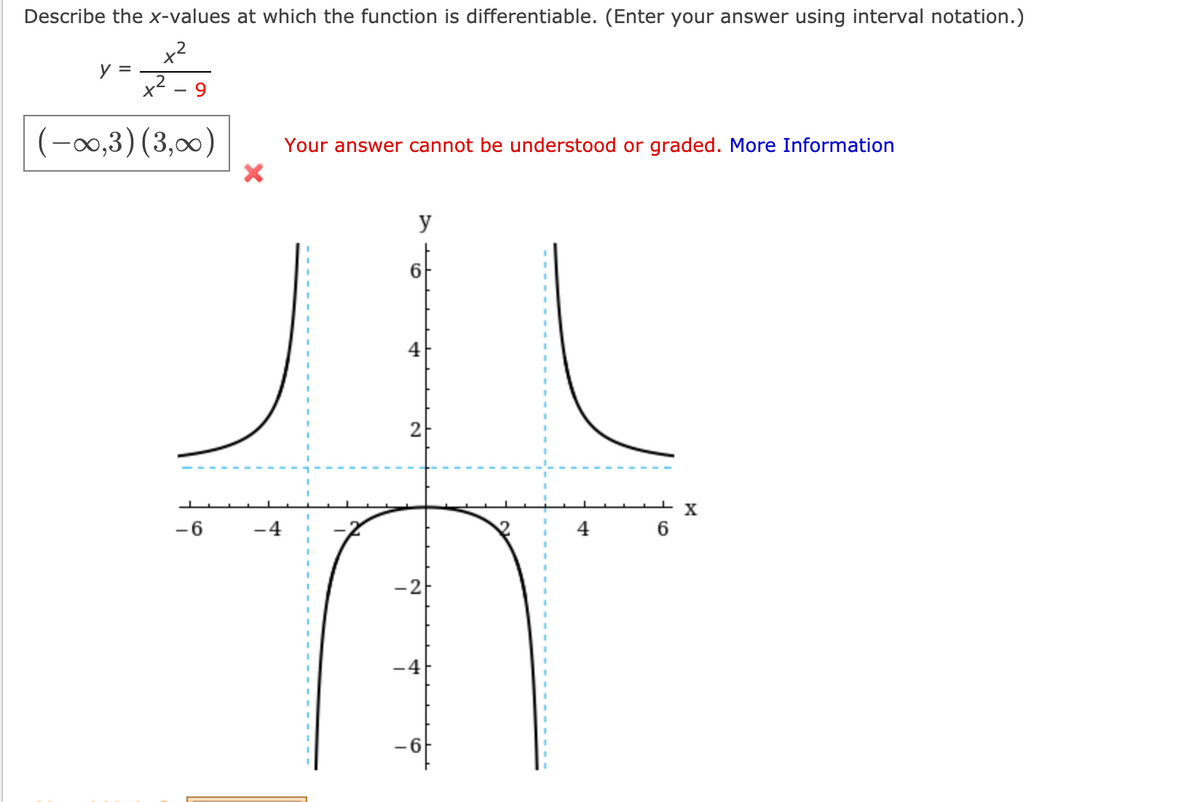 Source: bartleby.com
Source: bartleby.com
Hence, |x| is not differentiable at x=0. A function is said to be differentiable at if. Piecewise functions may or may not be differentiable on their domains.
Also Read :





