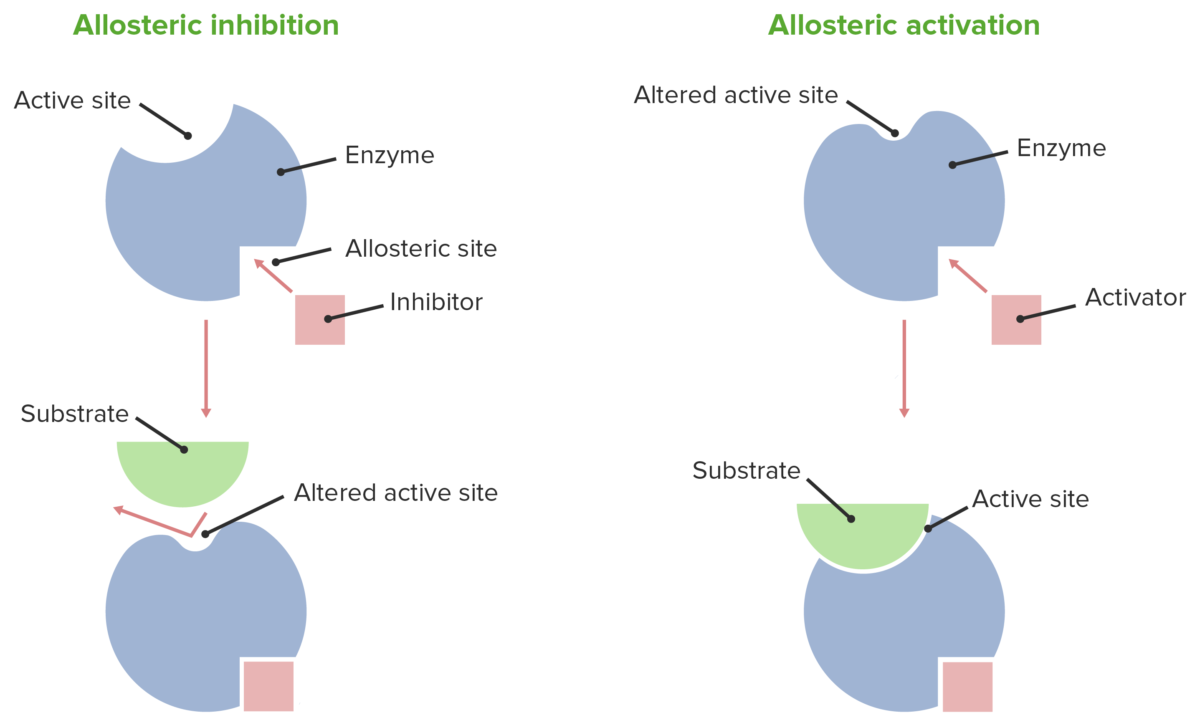
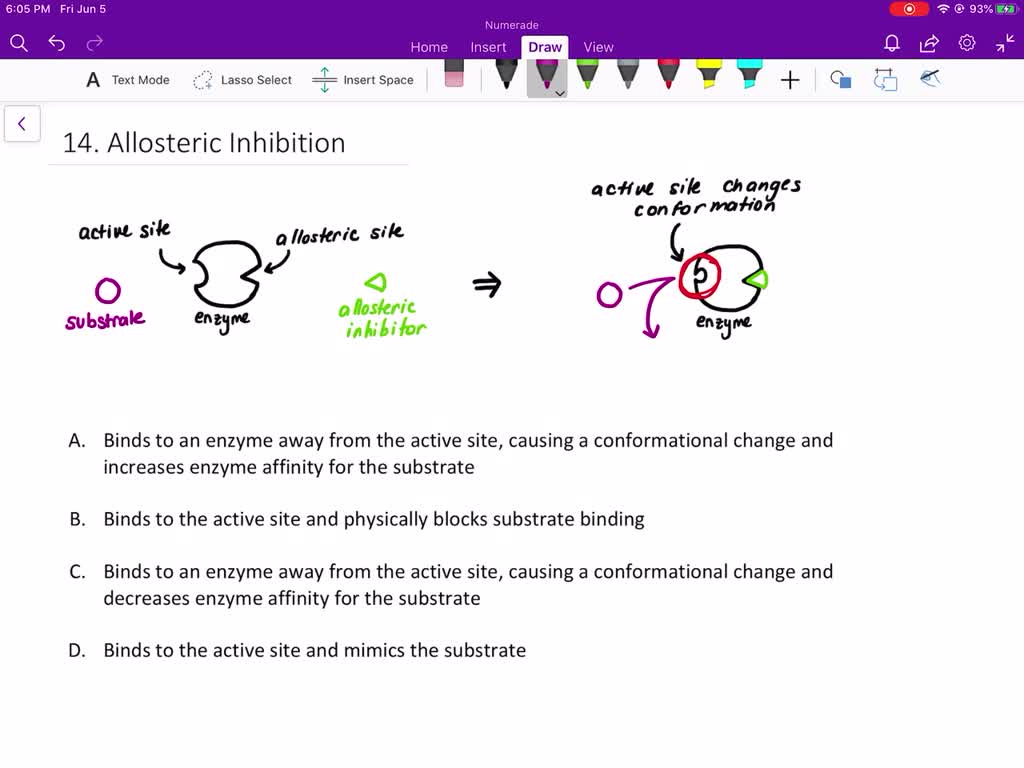
The enzyme substrate complex is maximal. Binds to an enzyme away from the active site and changes the conformation of the active site, increasing its affinity for substrate binding.
An Allosteric Inhibitor Does Which Of The Following. The increase in an enzymes activity that occurs when an allosteric activator binds to its specific regulatory site on the enzyme. Which of the following events does not occur in noncompetitive inhibition involving enzymes? O binding to allosteric inhibitor to the active site on enzyme o binding of substrate to active site on enzyme in the absence of allosteric inhibitor after dissociation of allosteric inhibitor from enzyme, substrate can bind to enzyme at active site change in the. Allosteric inhibition is the type of enzymatic regulation where the inhibitor binds to a site other than the active site.
 What Is An Allosteric Site Of The Enzyme? - Definition & Biology - Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com From study.com
What Is An Allosteric Site Of The Enzyme? - Definition & Biology - Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com From study.com
Related Post What Is An Allosteric Site Of The Enzyme? - Definition & Biology - Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com :
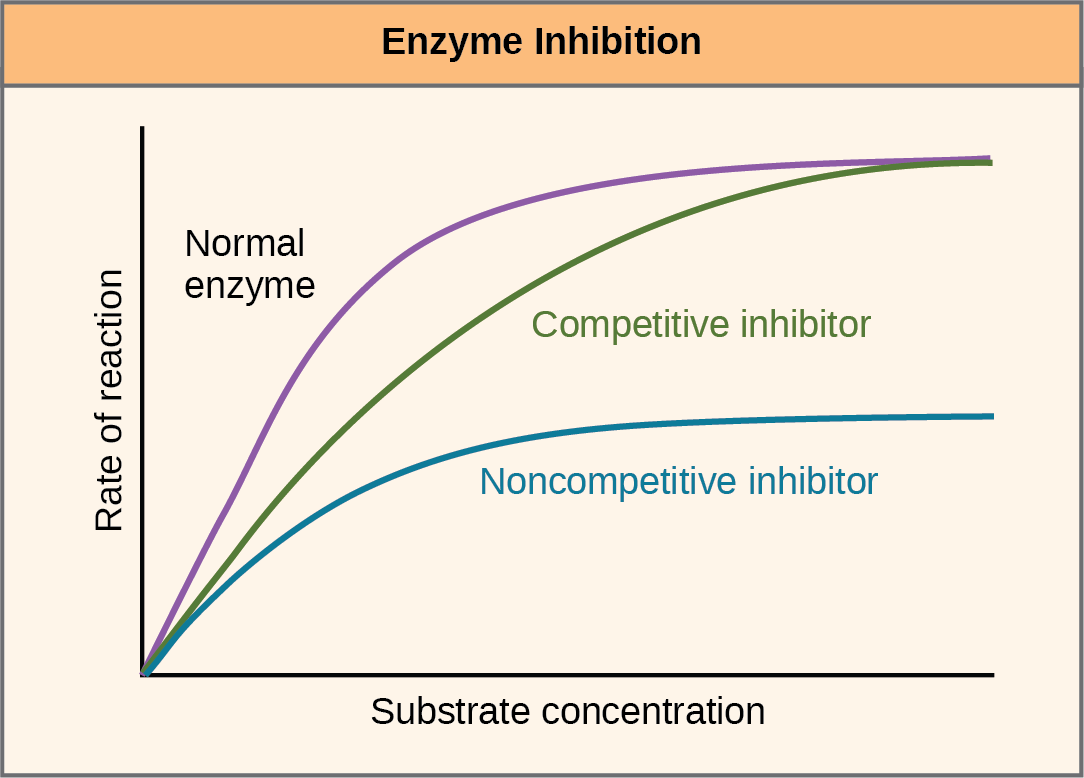
The increase in an enzymes activity that occurs when an allosteric activator binds to its specific regulatory site on the enzyme. The substrate concentration is equal to that of a competitive inhibitor b. The enzyme may react with the inhibitor and release the products as it would usually do to its substrate, thus the inhibitor and substrate compete for the active site. Allosteric enzymes are enzymes that have an additional binding site for effector molecules other than the active site.
Allosteric enzymes have active and inactive shapes differing in 3d structure.
Allosteric inhibition is the type of enzymatic regulation where the inhibitor binds to a site other than the active site. Binds to an enzym… 0:00. The substrate concentration is equal to that of a competitive inhibitor b. The existence of allosteric sites on receptor molecules has expanded potential drug mechanisms. The allosteric activator binds to an enzyme at a site other than the active site. Binds to the active site and blocks it from binding substrate.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
An allosteric inhibitor does which of the following? Allosteric enzymes have active and inactive shapes differing in 3d structure. Which statement about enzyme inhibitors is.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Which is not an allosteric inhibitor of glutamine synthetase? The existence of allosteric sites on receptor molecules has expanded potential drug mechanisms. The substrate concentration exceeds that of a noncompetitive inhibitor.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
This causes a conformational change in the active site for the second molecule, preventing binding. Which is an example of irreversible inhibitor? Which of the following graphs shows the results of reaction rate vs substrate concentration for an allosteric enzyme in the absence and presence of an allosteric inhibitor?
![Solved] Question 12 In Which Of The Following Ways Does An Allosteric Inhibitor Affect The Rate Of A Reaction? | Course Hero](https://www.coursehero.com/qa/attachment/13143840/ “Solved] Question 12 In Which Of The Following Ways Does An Allosteric Inhibitor Affect The Rate Of A Reaction? | Course Hero”) Source: coursehero.com
An allosteric inhibitor bound to one subunit alters substrate binding to other subunits; Allosteric enzymes often have multiple inhibitor or activator binding sites involved in switching between active and inactive shapes. How does enzyme feedback inhibition benefit a cell?
 Source: biologydictionary.net
Source: biologydictionary.net
Allosteric enzymes often have multiple inhibitor or activator binding sites involved in switching between active and inactive shapes. This process is also known as noncompetitive inhibition. Some examples of irreversible inhibitors include nerve gas,.
 Source: lecturio.com
Source: lecturio.com
Allosteric enzymes are enzymes that have an additional binding site for effector molecules other than the active site. How does enzyme feedback inhibition benefit a cell? The inhibition of deoxythymidilate formation and subsequent blockage of cell division is due to a.
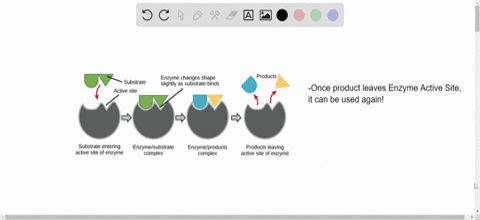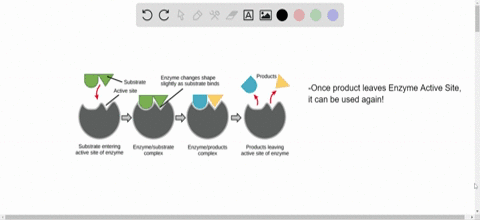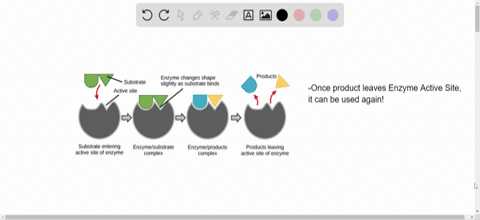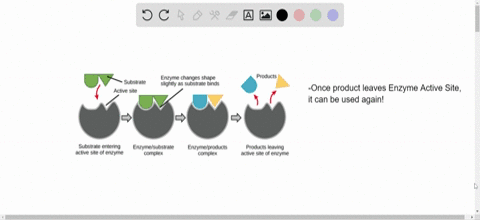 Source: numerade.com
Source: numerade.com
This process is also known as noncompetitive inhibition. This causes a conformational change in the active site for the second molecule, preventing binding. Allosteric regulation (allos = other) •allosteric enzyme has a site other than catalytic site known as allosteric site.
 Source: studocu.com
Source: studocu.com
Allosteric enzymes enzymes with multiple subunits have quaternary structure. Allosteric enzymes enzymes with multiple subunits have quaternary structure. This causes a conformational change in the active site for the second molecule, preventing binding.

Allosteric enzymes typically have multiple active sites located on different protein subunits. This causes the substrate to be unable to bind to the active site. The enzyme may react with the inhibitor and release the products as it would usually do to its substrate, thus the inhibitor and substrate compete for the active site.
 Source: numerade.com
Source: numerade.com
The substrate concentration exceeds that of a noncompetitive inhibitor. The active site changes shape when an inhibitor binds to an allosteric site. The inhibition of deoxythymidilate formation and subsequent blockage of cell division is due to a.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
This means that the affinity between enzyme and substrate is not altered in noncompetitive inhibition. How does enzyme feedback inhibition benefit a cell? An allosteric inhibitor does which of the following?
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
How does enzyme feedback inhibition benefit a cell? Which is not an allosteric inhibitor of glutamine synthetase? The active site changes shape when an inhibitor binds to an allosteric site.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
O binding to allosteric inhibitor to the active site on enzyme o binding of substrate to active site on enzyme in the absence of allosteric inhibitor after dissociation of allosteric inhibitor from enzyme, substrate can bind to enzyme at active site change in the. An allosteric inhibitor does which of the following? Which is an example of irreversible inhibitor?

Allosteric regulation (allos = other) •allosteric enzyme has a site other than catalytic site known as allosteric site. Which is an example of irreversible inhibitor? • first enzyme of the sequence is regulatory allosteric enzyme.
 Source: numerade.com
Source: numerade.com
Question 23 2.5 pts which of the following events does not occur in noncompetitive inhibition involving enzymes? O after dissociation of allosteric inhibitor from enzyme, substrate can bind to enzyme at active site o binding of allosteric inhibitor to the active site on enzyme o binding of substrate to active site. The inhibition of deoxythymidilate formation and subsequent blockage of cell division is due to a.

Allosteric modulation or feedback inhibition is an enzyme regulatory mechanism where a product of a simple or chain reaction can function as a temporary allosteric inhibitor, i.e., an inhibitor that combines with a regulatory or allosteric site (other than the active site) if its concentration. This means that the affinity between enzyme and substrate is not altered in noncompetitive inhibition. The allosteric activator binds to an enzyme at a site other than the active site.
 Source: numerade.com
Source: numerade.com
An allosteric inhibitor does which of the following? The enzyme substrate complex is maximal. Which is not an allosteric inhibitor of glutamine synthetase?
 Source: numerade.com
Source: numerade.com
The substrate concentration is equal to that of a competitive inhibitor b. An allosteric inhibitor does which of the following? Binds to an enzym… 0:00.
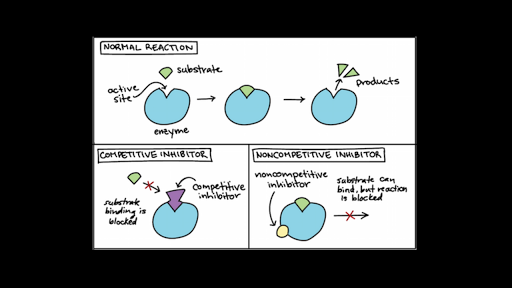
The active site changes shape when an inhibitor binds to an allosteric site. The substrate concentration is equal to that of a competitive inhibitor b. Which is an example of irreversible inhibitor?
 Source: differencebetween.com
Source: differencebetween.com
Binds to an enzyme away from the active site and changes the conformation of the active site, increasing its affinity for substrate binding. In allosteric regulation, effector (inhibitor or activator) binds to a site other than the active site to bring about conformational changes and thereby affecting the activity of the enzyme. Which is an example of irreversible inhibitor?
Also Read :





